San Juan Island National Historical Park facts for kids
Quick facts for kids San Juan IslandNational Historical Park |
|
|---|---|
|
IUCN Category V (Protected Landscape/Seascape)
|
|

British Camp
|
|
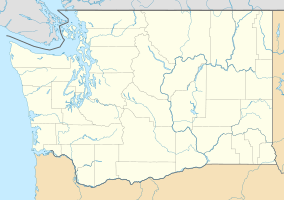
| Location | San Juan County, Washington, US |
| Nearest city | Friday Harbor, Washington |
| Area | 2,141 acres (8.66 km2) |
| Authorized | September 9, 1966 |
| Visitors | 266,717 (in 2011) |
| Governing body | National Park Service |
| Website | San Juan Island National Historical Park |
| Designated: | November 5, 1961 |
| Designated: | October 15, 1966 |
| Reference #: | 66000369 |
San Juan Island National Historical Park is a special place in Washington. It's managed by the National Park Service. This park tells the story of the "Pig War." This was a disagreement between the British and the U.S. Army. They argued over who owned San Juan Island. The park includes the sites where both armies set up their camps. These camps are now important historical landmarks. The park was officially created in 1966.
Contents
A Park with a Story: San Juan Island
San Juan Island is one of many islands in Puget Sound. It's the westernmost of the main San Juan Islands. These islands are between Vancouver Island in Canada and the Washington mainland. The Haro Strait separates them from Canada. The Rosario Strait separates them from Washington.
Who Lived Here First?
People first lived on these islands about 11,000 years ago. This was after the big ice sheets melted. These early people were ancestors of six Coast Salish tribes. They hunted and gathered food on the islands. Scientists found old shell piles at both English and American Camp areas. This shows that busy villages existed here long before Europeans arrived.
The English Camp area was likely a good spot for year-round homes. It had a sheltered bay. The American Camp area might have been used mostly in warmer seasons. People would go there for fishing and gathering food. European explorers brought diseases like smallpox in the 1770s. This sadly reduced the local population. Today, the Lummi Nation is working to bring back traditional uses. This includes special reef net fishing at English Camp.
The Pig War: A Funny Name for a Serious Dispute
After the Oregon Treaty of 1846, the border between the U.S. and Great Britain was mostly set. But the Haro Strait and Rosario Strait caused a problem. Both countries claimed the San Juan Islands. American settlers moved onto San Juan Island. The British Hudson's Bay Company also started a farm there.
Why Did the Pig War Start?
In 1859, a simple event sparked a big international argument. An American settler shot a pig that belonged to the British. This started the "Pig War." American settlers asked for military help. So, the U.S. Army set up a camp. The British sent their Royal Navy ships.
Two Camps, One Island
Luckily, people on both sides stayed calm. They agreed that both armies would keep camps on the island. This would last until the problem could be solved peacefully. From 1860 to 1872, British Royal Marines stayed at their camp. The American soldiers also had their own camp. A famous person, Henry Martyn Robert, was part of the American group. He later wrote "Robert's Rules of Order."
How the Pig War Ended Peacefully
The time when both armies were on the island was peaceful. A road was even built between the two camps. People in the nearby American village traded with both camps. In 1871, the Treaty of Washington was signed. Both countries agreed to let German Kaiser Wilhelm I decide who owned the islands. In 1872, he declared that the Haro Strait was the border. This meant the islands belonged to the United States.
The British left their camp soon after. The American camp became smaller. The buildings were sold or left behind. William Crook, a farmer, settled at the British camp in 1876. His family later gave their land to the state. The state also bought land around the American camp. These lands became the national park in 1966.
Exploring the Camps Today
The park has two main sites: English Camp and American Camp. Both are free to visit and have visitor centers.
English Camp: A Glimpse into British Life
English Camp is on Garrison Bay, on the northwest side of the island. You can still see the British flag, the Union Jack, flying there every day. Park rangers raise and lower it. This is one of the few places where U.S. government workers regularly fly another country's flag. Some original buildings from the British time are still there. These include a commissary, barracks, a blockhouse, and a hospital. The hospital building was moved away but later brought back to the park.
American Camp: Where History Meets Nature
American Camp is on the southernmost part of the island. It partly covers the old Hudson's Bay Company farm. The park also includes the site of the old San Juan village. This village was abandoned after the dispute ended. Three buildings from the American military time are still standing. These are two officers' quarters and the house of the camp laundress.
Fun Things to Do at the Park
San Juan Island National Historical Park covers 2,146 acres. It's split between American Camp and English Camp.
Hiking and Beaches
American Camp has three hiking trails. One trail goes to the top of Mount Finlayson. English Camp has the Bell Point Trail, Young Hill Trail, and Mitchell Hill Trail Network. American Camp also has South Beach, with views of the Olympic Mountains. You can also visit 4 July Beach on Griffin Bay.
Kayaking Adventures
Both English and American Camps have places where you can launch kayaks. This lets you explore the beautiful waters around the island.
Amazing Animals and Nature
The park is home to many interesting animals.
The Rare Island Marble Butterfly
The American Camp prairie is very special. It's the only place in the world with a healthy population of the island marble butterfly. This butterfly was thought to be gone for 90 years. But it was found again in 1998! It was listed as an endangered species in 2020.
Other Wildlife You Might See
Many birds live at American Camp. You might spot a bald eagle, harrier, Harlequin duck, American goldfinch, Great horned owl, or Osprey. Foxes are also common, especially on the American Camp prairie. They hunt rabbits there. Sometimes, you can even see orca, humpback, and gray whale from the park's shores.
 | Ernest Everett Just |
 | Mary Jackson |
 | Emmett Chappelle |
 | Marie Maynard Daly |