Coast Salish languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Coast Salish |
|
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution: |
Salish Sea (Strait of Georgia (British Columbia, Canada) and Puget Sound (Washington state) |
| Linguistic classification: | Salishan |
| Subdivisions: | |
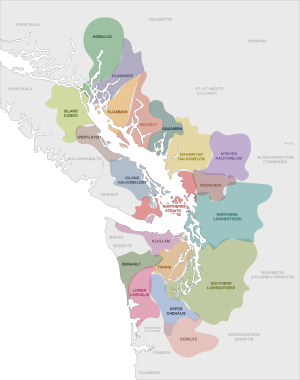 Distribution of Coast Salish languages in the early 19th century
|
|
Coast Salish languages are a group of languages spoken by First Nations and Native American peoples. These languages are part of the larger Salishan language family. People who speak these languages live in the Pacific Northwest. This area includes the southwest coast of British Columbia in Canada, around the Strait of Georgia, and Washington state in the USA, around Puget Sound. The name "Coast Salish" also describes the cultures of these people.
Where Coast Salish Languages Are Spoken
Coast Salish languages are spoken in a large area. This area is known as the Georgia and Puget Sound Basins. It includes places where big cities like Vancouver, British Columbia, and Seattle, Washington, are today.
Scientists who study old cultures believe that Coast Salish peoples have lived in this area for a very long time. They might have been there as far back as 9,000 BCE. For example, the land where Seattle is now has been lived on for about 10,000 years. This was since the last Ice Age ended.
Different Coast Salish Languages
There are many different Coast Salish languages. Some of them are no longer spoken today. The people who speak these languages often lived near certain rivers or bodies of water. They also shared resources and customs with nearby groups. This means their territories were not always strictly separated.
Here is a list of some Coast Salish languages:
| Language Name | Other Names | Community Where Spoken |
|---|---|---|
| Comox/Island Comox (†) | ʔayʔajusəm | Comox, Island Comox (Courtenay area). |
| Sliammon/Mainland Comox | ʔayʔajuθəm | Homalco (Xwemalhkwu), Klahoose, and Sliammon (Tla A'min). |
| Pentlatch (†) | Puntlatch, Puntledge | |
| Halkomelem | Hul'q'umín'um | Snaw-naw-as, Snuneymuxw, Somena, Chemainus, Cowichan, Halalt, Lyackson, Lamalchi, and Penelakut. |
| hǝn̓q̓ǝmin̓ǝm̓ | Musqueam, Tsleil-waututh, Kwikwetlem, Tsawwassen, Kwantlen. | |
| Halq'eméylem, Stó:lō, Teyt | Aitchelitz, Chawathil, Cheam, Chehalis (Sts'Ailes), Katzie, Kwantlen, Kwaw-kwaw-Apilt, Leq'a:mel, Matsqui, Peters, Popkum, Scowlitz (Skaulits), Seabird Island, Shxw'ow'hamel, Skawahlook, Skowkale, Skwah, Skway (Shxwhá:y), Soowahlie, Squiala, Sumas, Tzeachten, Union Bar, New Westminster Indian Band, and Yakweakwioose First Nations. | |
| Sechelt | Shíshalh, Sháshíshálhem | Shishalh |
| Squamish | Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Snichim, Sko-mesh | Squamish |
| Nooksack | Lhéchalosem | Nooksack |
| Saanich | Northern Straits Salish, SENĆOŦEN | Saanich, T'souke |
| Lummi | Northern Straits Salish, xʷləmiʔčósən | Lummi or Lhaq'temish |
| Klallam | Sklallam, Nəxʷsƛ̕áy̓emúcən | S'Klallam or Klallam |
| Lushootseed | dxʷləšúcid or xʷləšúcid | Samish or Sʼabš, Skagit or Sqaĵət, Sauk-Suiattle or Suiʼaẋbixʷ, Snohomish or Sduhubš, Swinomish, Duwamish or Dxʷ'Dəw?Abš and Xacuabš, Smulkamish, Sammamish, Snoqualmie or Sduqʷalbixʷ, Stkehlmish or Sacakałəbš, Suquamish or Suqʷabš, Nisqually or Sqʷaliʼabš, Muckleshoot or Bəpubšł, Puyallup or Spuyaləqəlpubšut, Sahewamish or Sʼəhiwʼabš, Squaxin Island Tribe |
| Twana | Skokomesh | Skokomish |
| Cowlitz | Chehalis | |
| Quinault | Quinault |
See also
 In Spanish: Lenguas salish de la costa para niños
In Spanish: Lenguas salish de la costa para niños
- Interior Salish languages
- Tillamook (an extinct Salishan language)

