Saurashtra (region) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Saurashtra
Kathiyawad
|
|
|---|---|
|
Region
|
|
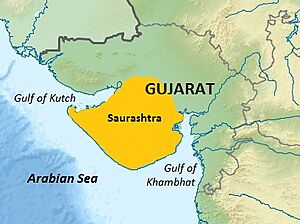
Saurashtra region within Gujarat, India
|
|
Location of Saurashtra in India
|
|
| Country | India |
| State | Gujarat |
| Area | |
| • Total | 66,000 km2 (25,000 sq mi) |
| Population
(2011)
|
|
| • Total | 15,300,000 |
| • Density | 231.8/km2 (600/sq mi) |
| Languages | |
| • Gujarati | Gujarati |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| Vehicle registration | GJ |
| Large cities | Botad, Rajkot, Jamnagar, Bhavnagar, Morbi, Gir Junagadh, Porbandar, Veraval, Surendranagar, |
Saurashtra, also known as Kathiawar, is a region in Gujarat, India. It is a peninsula, meaning it is mostly surrounded by water. Saurashtra is located on the coast of the Arabian Sea.
This region covers about one-third of the Gujarat state. It includes 11 districts of Gujarat, like Rajkot District. Saurashtra was once a separate state of India. Later, it joined the Bombay state. In 1961, it became part of Gujarat.
Contents
Where is Saurashtra?
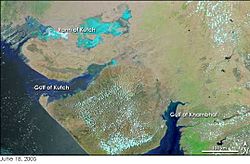
The Saurashtra peninsula has the Arabian Sea to its south and southwest. To the northwest, it has the Gulf of Kutch. The Gulf of Khambhat is to its east.
From these two gulfs, there are large areas of land. These areas are partly salty marshland and partly sandy desert. They stretch inland and make Kathiawar almost like an island. Only a narrow strip of land connects it to the main part of Gujarat in the northeast.
The peninsula is sometimes called Kathiawar. This name comes from the Kathi Darbar people. They used to rule most of this area. However, Saurashtra and Kathiawar are not exactly the same. A small part of the historical Saurashtra region is outside the Kathiawar peninsula. The southern part of the peninsula is called Sorath.
What Does the Name Saurashtra Mean?
Some experts believe the name Saurashtra comes from "Saura Rashtra." In the ancient language Sanskrit, "Saura" means Sun. "Rashtra" means country. So, it means "country of the Sun."
In ancient times, there were 12 sun temples in this region. Due to many invasions, the idols from these temples were moved. One of them is now at Kanakaditya Temple in Maharashtra. The locations of the other 11 idols are not known today.
The name "Saurashtra" itself comes from the Sanskrit word saurāṣṭra. This word means "from Saurashtra." It comes from surāṣṭra, which means "good nation." So, the name literally means "good nation."
Districts of Saurashtra
The Saurashtra region is the southwestern part of the modern Gujarat state. The districts in this region are:
- Devbhoomi Dwarka
- Jamnagar
- Morbi
- Rajkot
- Porbandar
- Junagadh
- Gir Somnath
- Amreli
- Bhavnagar
- Botad
- Surendranagar
- Part of Ahmedabad (Dhandhuka taluka)
Historically, the Diu district was also part of this region. Diu is now a union territory of India.
History of Saurashtra
Saurashtra has been known by different names for a very long time. It is mentioned in ancient texts like the Mahabharata and during the Vedic period.
In the first century CE, a Greek book called the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea mentioned this region. It called the coast "Syrastrene." The book described it as a fertile country. It grew wheat, rice, sesame oil, and cotton. Many cattle were raised there.
The Egyptian geographer Ptolemy and the Greek manuscript Periplus both called this region "Surastrene."
The region is also mentioned in the Junagadh Rock inscription from 150 CE. This inscription is linked to Rudradaman I. Before this, during the rule of Ashoka (268–232 BCE), the region was governed by Pushyagupta. This was during Chandragupta Maurya's time (322BC – 298BC).
Saurashtrian People and Trade
From the 8th to 11th centuries, Brahmin merchants from Saurashtra started moving to Southern India. They moved because of frequent invasions. Kings like the Chola and Pandya invited these merchants.
These merchants set up silk-weaving guilds across Southern India. They traded silk clothes and diamonds with royal families. Silk became popular for royal families after the Gupta dynasty period. These Brahmins are now known as the Saurashtra people.
Some historians think that Saurashtrian textile merchants brought Idli (a popular South Indian dish) to South India. This might have happened between the 10th and 12th centuries. Some even say that the mix of rice and urad dal, steamed to form cakes, started in Gujarat. This dish was called Iddada.
Sorath and Junagadh
For a long time, this region was known as Sorath. From the 9th to 14th century, the Chudasama Rajputs ruled Sorath. Their capitals were Vanthali and Junagadh. The Chudasama Rajputs ruled Sorath for a very long time. Eventually, the Sorath area came under Muslim rule.
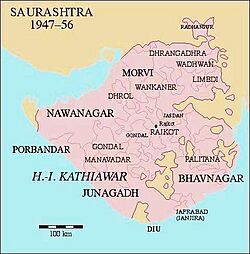
Sorath was one of ten main areas, but by the time of British rule, only four remained. The others had been absorbed. The salute state of Junagadh was founded during British rule. Its Muslim ruler wanted to join Pakistan in 1947. However, most people in Junagadh were Hindu and they rebelled.
Saurashtra State Formation
After India became independent in 1947, many small princely states in Kathiawar joined together. There were 217 such states, including the former Junagadh State. They formed the state of Saurashtra on February 15, 1948.
At first, it was called the United State of Kathiawar. It was renamed Saurashtra State in November 1948. Vallabhbhai Patel worked hard to convince the local princes to join India. Maharaja Krishnakumar Sinhji of Bhavnagar State was the first to offer his large kingdom to India.
The capital of Saurashtra was Rajkot. Uchharangray Navalshankar Dhebar became Saurashtra's first Chief Minister. He later became the President of the Indian National Congress. Rasiklal Umedchand Parikh took over as Chief Minister in 1954.
On November 1, 1956, Saurashtra joined the Bombay state. In 1960, Bombay state was divided into two new states based on language: Gujarat and Maharashtra. The territory of Saurashtra, including Junagadh, became part of the state of Gujarat.
Postage Stamps of Saurashtra
The first postage stamps for the Princely State of Junagadh were issued in 1864. They had three lines of Hindi writing in colorless letters on black. They were made by hand-stamping with watercolor ink. In 1868, a second set of stamps used colored letters. These were printed in black or red on different colors of paper.
The 1877 stamps were the first to include Latin letters. They had a round design with "SORUTH POSTAGE" at the top. At the bottom, it said "ONE ANNA OF A RUPEE" or "FOUR ANNAS...". Some of these stamps had extra charges added in 1913–14. New stamp designs followed in 1914.
In 1929, a set of eight stamps was released. These stamps showed pictures of Junagadh, the Gir lion, and the Kathi horse. They also showed the nawab (ruler). In 1937, the one anna stamp was reissued. It now read "POSTAGE AND REVENUE."
The Indian province of Saurashtra did not design its own stamps. Before using India's stamps, Saurashtra used a court fee stamp. This stamp was overprinted for postal use. Then, more one anna stamps were made by adding extra charges to three stamps from the 1929 issue.
Natural Resources and Water
Saurashtra has always been a rich region with many natural resources. However, it has also faced several droughts, especially in the 20th century. Water resources have greatly affected the region and its farming economy.
A survey in 1998 showed that water was easily available 10 to 15 years before that. The region had 700,000 dugwells. This means there was one well for fewer than 20 people. It also means there was one well every 300 meters. This shows there was a lot of groundwater.
Saurashtra went through severe droughts. People could not grow crops, and they did not have drinking water. In recent times, there has been a campaign to collect rainwater.
The "Check dam" campaign started in the late 1990s. This campaign helped raise water levels in Saurashtra. However, in 2019, the region had a severe drought. It affected 20 districts in Gujarat. Water had to be brought in by tanker from the Sardar Sarovar Dam on the Narmada River.
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |