Mullein nightshade facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mullein nightshade |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Solanum
|
| Subgenus: |
Brevantherum
|
| Section: |
Brevantherum
|
| Species: |
S. erianthum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Solanum erianthum D.DonL.
|
|
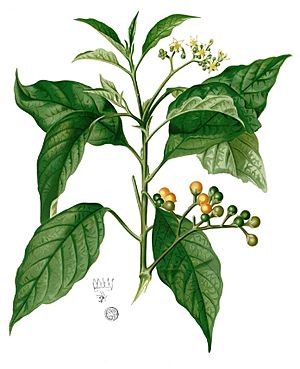
Solanum erianthum is a type of nightshade plant. It is originally from southern North America and northern South America. This plant has spread to many other parts of the world, so you can find it in tropical areas almost everywhere.
People call it by several common names, like potatotree, mullein nightshade, velvet nightshade, and salvadora. Even though it's called "potatotree," it doesn't actually grow the potatoes we eat. The name comes from how some parts of the plant look or smell.
Contents
What is Solanum erianthum?
The potatotree is a plant that grows quickly. It can be a evergreen shrub (a bushy plant) or a small tree. It can grow to be about 2 to 8 meters (6.5 to 26 feet) tall. Its bark is usually grey or brown and feels smooth. The main trunk is about 2 to 5 centimeters (0.8 to 2 inches) thick.
The top part of the tree, called the crown, is often flat and spreads out. Even though the wood is soft and can break easily, the branches are strong enough to hold birds like chachalacas.
Leaves and Flowers
The leaves of the potatotree are simple and grow in an alternate pattern (meaning they don't grow directly opposite each other). They are shaped like an oval or an ellipse and can be quite long, from 12 to 37 centimeters (4.7 to 14.5 inches).
The Flowers grow in clusters called cymes on the sides of the branches. Each flower is about 1.1 to 1.8 centimeters (0.4 to 0.7 inches) across. They have five white petals and five yellow stamens (the parts that make pollen).
Fruits and Smell
The fruit of the potatotree is a yellow berry. It's about 1 to 1.2 centimeters (0.4 to 0.5 inches) wide and contains many seeds.
The name erianthum comes from ancient Greek words. "Erion" means "wooly," and "anthos" means "flower." This name describes how the flowers are covered in tiny hairs, called trichomes, which make them look woolly. Many other parts of the plant, like the berries, leaves, and stems, also have these hairs.
If you break the roots of the plant, they might smell like cooked potatoes. Also, if you rub the hairs on the leaves or stems, they can release a smell similar to tar.
Where it Grows
Solanum erianthum is naturally found in the very southern parts of the contiguous United States (like southern Florida and the Lower Rio Grande Valley in Texas). It also grows in the Bahamas, Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean, and northern South America, including the Galápagos Islands.
It is thought that explorers from Spain brought the potatotree to the Philippines in the 1500s. From there, it spread to other places like Malesia, Australia, and parts of Asia. It probably arrived in West Africa from the Caribbean during the time of the Atlantic slave trade. Interestingly, it's not found in most of South America.
Habitats
You can find the potatotree growing in many different places, from sea level up to about 1500 meters (4900 feet) high. It likes areas near rivers (riparian zones), dry forests, and moist forests.
This plant often grows in places where the land has been disturbed, such as along roadsides, in fields, or in empty lots. Because it grows so easily in these areas, some people might consider it a weed. It's also a "pioneer species," meaning it can be one of the first plants to grow in damaged areas, like old mining sites, helping to prepare the soil for other plants.
Uses of the Potatotree
Like other plants in the Solanum group, S. erianthum has been used by people for different purposes, especially in traditional medicine. This is because it contains special natural chemicals called steroidal saponins and steroidal alkaloids. These chemicals are interesting to scientists.
- In the Philippines, the leaves of the potatotree are used to help clean grease from dishes.
- The berries of the plant are not safe for humans to eat raw and can cause problems like headaches or cramps. However, in some parts of Southeast Asia and southern India, people cook them carefully before eating them, sometimes in curry dishes.
- Historically, in Tropical Asia, parts of the plant were used as a component in arrow poison.
- The potatotree is also grown as an ornamental plant in the Caribbean because it looks nice. It can also provide good shade for shade-grown coffee plants.
See also
 In Spanish: Solanum erianthum para niños
In Spanish: Solanum erianthum para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |


