Statesboro, Georgia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Statesboro, Georgia
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

From top to bottom left to right: The Bulloch County Courthouse and Averitt Center for the Arts, Splash in the Boro Water Park, Campus Georgia Southern University, the Emma Kelly Theater
|
|||
|
|||
Location in Bulloch County and the state of Georgia
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| State | Georgia | ||
| County | Bulloch | ||
| Area | |||
| • City | 15.31 sq mi (39.64 km2) | ||
| • Land | 14.99 sq mi (38.84 km2) | ||
| • Water | 0.31 sq mi (0.81 km2) | ||
| Elevation | 253 ft (77 m) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • City | 33,438 | ||
| • Density | 2,229.94/sq mi (860.97/km2) | ||
| • Metro | 71,214 (US: 95th) | ||
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) | ||
| ZIP codes |
30458-30461
|
||
| Area code(s) | 912 | ||
| FIPS code | 13-73256 | ||
| GNIS feature ID | 0323541 | ||
Statesboro is a city in Bulloch County, Georgia, United States. It is the biggest city in the county and also its county seat, which means it's where the county government is located. Statesboro is in the southeastern part of Georgia.
In 2020, about 33,438 people lived there. Statesboro is the main city in the Statesboro micropolitan area, which has about 81,099 residents. It's also part of the larger Savannah–Hinesville–Statesboro combined statistical area.
The city was officially started in 1803. It began as a small place where people could trade goods. It provided important supplies for the many surrounding cotton plantations. Growing cotton was the main way people made money throughout the 1800s, even after the American Civil War.
In 1906, Statesboro was chosen to be the home of the First District A&M School. This was a special kind of college called a land grant college. Over time, this school grew into what is now Georgia Southern University.
Statesboro also inspired a famous blues song called "Statesboro Blues". Blind Willie McTell wrote it in the 1920s. A well-known band called the Allman Brothers Band later made a popular version of the song. In 2017, Statesboro was recognized as one of the top three "America's Best Communities" in a national competition. It was also named one of Georgia's "live, work, play" cities.
Contents
History of Statesboro
In 1801, a man named George Sibbald gave over 9,300 acres (about 3,760 hectares) of land. This land was meant for a central county seat in Bulloch County. White planters developed the area, mostly for cotton farms. These farms relied on the labor of enslaved people. In December 1803, the Georgia government officially created the town of Statesborough. In 1866, the state changed the spelling of the city's name to "Statesboro," which is how it's spelled today.
During the American Civil War, General William T. Sherman led his famous Sherman's March to the Sea through Georgia. A Union officer once asked for directions to Statesboro. A local person replied, "You are standing in the middle of town." This shows how small Statesboro was back then. The soldiers destroyed the courthouse, which was a simple log building also used as a barn.
After the Civil War, the small town began to grow. Statesboro became an important town in southeastern Georgia. Many freed people stayed in the area. They worked on farms as sharecroppers and tenant farmers.
After the Reconstruction era, many African Americans faced difficult times. To find better opportunities, many left Statesboro and Bulloch County. This movement was part of the Great Migration. It was when many African Americans moved from the rural South to cities in the North. This is why Statesboro's population growth slowed down between 1910 and 1930.
Around 1900, new businesses opened in Statesboro. Stores and banks were built along the town's four main streets, all named Main. In 1908, Statesboro was a world leader in selling a special type of cotton called Sea Island Cotton. Statesboro sold ten times more cotton bales than Savannah did.
New farming machines meant fewer workers were needed. Also, a tiny insect called the boll weevil destroyed cotton crops in the 1930s. This made farmers switch to growing tobacco. By 1953, over 20 million pounds of tobacco were sold in Statesboro. It became the largest market in the "Bright Tobacco Belt" of Georgia and Florida.
The First District Agricultural & Mechanical School opened in Statesboro in 1906. It was a land grant college, meaning it received federal support for education. In the 1920s, it started focusing on training teachers. It was renamed the Georgia Normal School in 1924. As it grew to offer four-year programs, it became South Georgia Teachers College in 1929. Later, it was called Georgia Teachers College (1939) and Georgia Southern College (1959). Since 1990, it has been known as Georgia Southern University. It now welcomes students of all backgrounds and offers many advanced programs.
During the Cold War, there was a radar station in Statesboro. It was part of the Strategic Air Command.
Statesboro's Location and Landscape
Statesboro is located at 32°26′43″N 81°46′45″W. The city covers about 13.8 square miles (35.9 square kilometers). Most of this area is land, with a small amount of water.
Statesboro is in the coastal plain region of Georgia, also known as the Low Country. This means the land is mostly flat, with only a few small hills. The downtown area is about 250 feet (77 meters) above sea level. This makes it one of the highest points in Bulloch County. You can find many types of trees here, like pine, oak, magnolia, dogwood, palm, and sweetgum.
People of Statesboro
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 33 | — | |
| 1880 | 29 | −12.1% | |
| 1890 | 425 | 1,365.5% | |
| 1900 | 1,197 | 181.6% | |
| 1910 | 2,529 | 111.3% | |
| 1920 | 3,807 | 50.5% | |
| 1930 | 3,996 | 5.0% | |
| 1940 | 5,028 | 25.8% | |
| 1950 | 6,097 | 21.3% | |
| 1960 | 8,356 | 37.1% | |
| 1970 | 14,616 | 74.9% | |
| 1980 | 14,866 | 1.7% | |
| 1990 | 15,854 | 6.6% | |
| 2000 | 22,698 | 43.2% | |
| 2010 | 28,422 | 25.2% | |
| 2020 | 33,438 | 17.6% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
| Race | Num. | Perc. |
|---|---|---|
| White (non-Hispanic) | 16,323 | 48.82% |
| Black or African American (non-Hispanic) | 13,282 | 39.72% |
| Native American | 66 | 0.2% |
| Asian | 634 | 1.9% |
| Pacific Islander | 34 | 0.1% |
| Other/Mixed | 1,169 | 3.5% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 1,930 | 5.77% |
In 2020, there were 33,438 people living in Statesboro. There were 10,214 households and 4,569 families in the city.
Statesboro's Economy
Statesboro's economy relies on education, making things (manufacturing), and agribusiness (farming-related businesses). Statesboro is a major economic center for the region. It has over a billion dollars in retail sales each year.
Georgia Southern University is the biggest employer in the city. It creates about 6,700 jobs, both directly and indirectly. Farming also brings in $100 million in income each year.
Statesboro has several factories. The Briggs & Stratton Plant is the third-largest employer, with 950 workers. The Development Authority of Bulloch County has over 100 acres (40 hectares) of land ready for new businesses. This land is in the Gateway Industrial Park. Southern Gateway Park is a new 200-acre (81-hectare) area. It is located near U.S. 301 and Interstate 16. This park has water, sewer, and natural gas lines.
GAF, a large roofing manufacturer, moved to Statesboro in the early 2000s.
Arts and Culture in Statesboro
Statesboro's culture mixes its Southern roots with its identity as a college town. The city has a special culture that works with the university students. This creates a lively art and music scene. Statesboro has many restaurants, bars, places for live music, bookstores, and coffee shops. These places fit the creative college town vibe.
Georgia Trend magazine named downtown Statesboro one of eight "Renaissance Cities." The downtown area is being improved. The old Bank of Statesboro and Georgia Theater have been updated. They are now part of the David H. Averitt Center for the Arts. This center has the Emma Kelly Theater, named after a local singer. She was known as the "Lady of 6,000 Songs." The center also has art studios, meeting rooms, and an exhibition area. Downtown Statesboro has been shown in movies like Now and Then (1995) and 1969.
Georgia Southern University offers many cultural activities. These are for both students and the community. You can enjoy the Georgia Southern Symphony and the Georgia Southern Planetarium. There's also the Georgia Southern Museum and the Botanical Gardens at Bland Cottage. Traveling groups perform at the Performing Arts Center. Students and teachers from Georgia Southern also put on shows.
Mill Creek Regional Park is a big outdoor park. It has sports fields and a water park called Splash in the Boro.
Sports in Statesboro
Georgia Southern Eagles
The Georgia Southern University Eagles have 17 sports teams. They play in Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS). They are part of the NCAA Division I Sun Belt Conference.
Before joining the Sun Belt Conference in 2014, the Eagles were in other conferences. Their football team won six national championships. This was when they were in the Football Championship Subdivision (FCS/I-AA).
Tormenta FC
South Georgia Tormenta FC has a professional soccer team. They play in USL League One, which is the third level of soccer in the U.S. The club started in 2016. Their games are played at Optim Sports Medicine Field at Tormenta Stadium. The club won the USL League One championship in 2022.
Education in Statesboro
Colleges and Universities
Georgia Southern University is the main college in Statesboro. It is part of the University System of Georgia (USG). It started in 1906 as the First District Agricultural and Mechanical School. At first, only white students could attend. On July 1, 1990, it became the fifth university in the University System. By 2015, it had almost 20,000 students. The university offers many advanced degrees. You can take classes on campus, at other locations, or online. For the last ten years, the university has built new buildings and made its campus more beautiful. The campus is nearly 700 acres (283 hectares). The university has a museum, a botanical garden, and a wildlife education center. The university's Division I sports teams, the Georgia Southern Eagles, play in the Sun Belt Conference.
Statesboro also has two community colleges. East Georgia State College (EGSC) is a USG school based in nearby Swainsboro. It has a satellite center on the Georgia Southern campus. Ogeechee Technical College (OTC) is part of the Technical College System of Georgia. It teaches technical skills and adult education. OTC is located on U.S. Highway 301 South, outside the city.
Public Schools
The Bulloch County Board of Education manages the public schools in Statesboro. The biggest school in the city is Statesboro High School. Other public schools include Southeast Bulloch High School, William James Middle School, Langston Chapel Middle School, and Southeast Bulloch Middle School. Elementary schools are Julia P. Bryant, Sallie Zetterower, Mattie Lively, Langston Chapel, and Mill Creek.
Private schools in Statesboro include Bulloch Academy, Trinity Christian School, and Bible Baptist Christian School. The Charter Conservatory for Liberal Arts and Technology (CCAT) is a charter school in the city. In 2016, CCAT was renamed Statesboro STEAM – College, Careers, Arts, & Technology Academy.
Media in Statesboro
Statesboro has many ways to get news and entertainment. These include print, radio, television, and the Internet. Statesboro Magazine is a local magazine about life in the community. The local newspaper is the Statesboro Herald. It comes out daily and has about 6,000 copies.
Other newspapers include the George-Anne, made by Georgia Southern University students. Connect Statesboro is a weekly entertainment paper. The E11eventh Hour is an entertainment paper that comes out twice a month. Radio stations include WHKN, WMCD, WPMX, WPTB, WWNS, and WVGS. Statesboro Business Magazine shares business news, articles, and job listings for Statesboro.
StatesboroHerald.com has won many awards for its online news.
Transportation in Statesboro
Hospitals
- East Georgia Regional Medical Center
- Willingway Hospital
Airports
The Statesboro-Bulloch County Airport is about 3 miles (5 km) outside Statesboro. It can be used by private planes. It does not have a control tower or commercial flights. Most travelers use the Savannah/Hilton Head International Airport. This airport is about 45 miles (72 km) east and has flights from eight airlines. Statesboro is about a three-hour drive from the large Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport.
Highways
Interstate 16 is about 10 miles (16 km) south of Statesboro. Statesboro is also served by three U.S. highways:
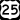 U.S. Highway 25 runs northwest-south through the city.
U.S. Highway 25 runs northwest-south through the city.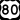 U.S. Highway 80 is the main east-west road.
U.S. Highway 80 is the main east-west road.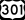 U.S. Highway 301 runs north-south.
U.S. Highway 301 runs north-south.
The Veterans Memorial Parkway (Highway 301 Bypass and Highway 25 Bypass) goes almost all the way around the city.
State Routes:
Walking and Biking
- S&S Greenway Trail
Rail Service
Trains carry freight (goods) through Statesboro. This service is provided by Norfolk Southern Railway.
Famous People from Statesboro
- Jason Childers (born 1975), a baseball player for Major League Baseball.
- Dale Eggeling (born 1954), a golfer who won three LPGA Tour events.
- Sutton Foster (born 1975), a Broadway star and two-time Tony Award winner.
- Joey Hamilton (born 1970), a retired Major League Baseball player.
- Margie Hendrix (1935–1973), a singer with Ray Charles and The Cookies.
- Justin Houston (born 1989), a football player for the Kansas City Chiefs.
- Emma Kelly (1918–2001), a famous pianist.
- Dylan Marlowe (born 1999), an American country music singer.
- Danny McBride (born 1976), an actor known for Pineapple Express and Eastbound & Down.
- Jeremy Mincey (born 1983), a football player for the Dallas Cowboys.
- Blind Willie McTell (1901–1959), a blues musician who wrote "Statesboro Blues".
- Adrian Peterson (born 1979), a former football player for the Chicago Bears. He won the Walter Payton Award.
- Marty Pevey (born 1961), a current manager for the Iowa Cubs baseball team.
- John Rocker, a Major League baseball pitcher.
- Erk Russell (1926–2006), a college football coach.
- DeAngelo Tyson (born 1989), a football player for the Baltimore Ravens.
- Rashad Wright (born 1982), a basketball point guard.
Places to Visit in Statesboro
- Georgia Southern Botanical Garden
- Georgia Southern University
- J. I. Clements Stadium
- Mill Creek Recreational Park
- Paulson Stadium
- Splash in the Boro
- Statesboro Mall
See also
 In Spanish: Statesboro (Georgia) para niños
In Spanish: Statesboro (Georgia) para niños










