Tamu Massif facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tamu Massif |
|
|---|---|
A map showing the volcano's shape underwater
|
|
| Summit depth | 1,980 metres (6,500 ft) |
| Height | 4,460 metres (14,620 ft) |
| Location | |
| Location | Northwest Pacific Ocean |
| Range | Shatsky Rise |
| Coordinates | 33°N 158°E / 33°N 158°E |
| Geology | |
| Type | Seamount (underwater volcano), shield volcano |
| Age of rock | 144.6 ± 0.8 Ma |
Tamu Massif is a huge seamount, which means it's a mountain under the sea. It's actually an underwater volcano! You can find it in the northwest Pacific Ocean, about 1,600 km (990 mi) east of Japan. This giant volcano sits on top of a special place where three underwater mountain ranges meet.
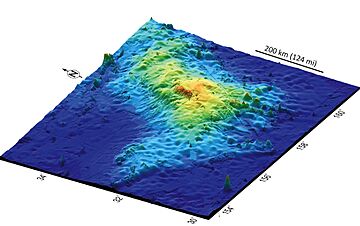
Tamu Massif is incredibly big, covering an area of about 553,000 square kilometres (214,000 sq mi). Imagine a volcano half the size of Texas or almost as big as France! Its highest point, or summit, is about 1,980 m (6,500 ft) below the ocean's surface. From there, it stretches down to the ocean floor, reaching depths of about 6.4 km (4.0 mi). The entire volcano stands about 4,460 metres (14,620 ft) tall from its base.
This massive underwater mountain is part of a larger area called the Shatsky Rise. For a long time, scientists thought it was a group of volcanoes. But in 2013, they announced that Tamu Massif might be the single largest volcano ever found on Earth!
A scientist named William Sager, who studies the Earth's oceans and rocks, started looking into Tamu Massif around 1993. He worked at the University of Houston and the Texas A&M College of Geosciences. In September 2013, after many years of research, Sager and his team made an exciting announcement. They believed Tamu Massif was the "biggest single shield volcano ever found on Earth!"
There are other huge rock formations on our planet, like the Ontong Java Plateau. But scientists are still trying to figure out if these are one giant volcano or many volcanoes grouped together. This makes Tamu Massif's discovery even more special.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name Tamu comes from the first letters of Texas A&M University. This is where Professor William Sager, one of the main scientists who studied the volcano, used to teach. The word Massif means "massive" in French. It describes a very large mountain or a big part of the Earth's crust. So, "Tamu Massif" basically means "Texas A&M's Massive Mountain"!
How Tamu Massif Formed
Tamu Massif was born a very long time ago, about 145 million years ago! This was during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous periods, when dinosaurs roamed the Earth. It formed quite quickly, over just a few million years, and then stopped erupting, becoming an extinct volcano.
Scientists were amazed because they thought it was impossible for such a huge volcano to form from a single, short period of eruptions. If it truly is one single volcano, Tamu Massif would be the largest known volcano on Earth. It would be much bigger than Pūhāhonu in the Hawaiian Islands, which was previously thought to be the largest.
A Giant Among Volcanoes
The main part of Tamu Massif is shaped like a rounded dome. It spreads out over an area of more than 292,500 km2 (112,900 sq mi). To give you an idea, that's many times larger than Mauna Loa, a famous volcano in Hawaii. It's even about half the size of Olympus Mons, the giant volcano on Mars!
The entire volcano is made of a type of rock called basalt, which is common in volcanic eruptions. Its sides, or slopes, are very gentle, barely rising more than one degree near the top. This makes it a shield volcano, which looks like a warrior's shield lying on the ground.
The whole area where Tamu Massif sits, called the Shatsky Rise, is as big as California or Japan. But Tamu Massif itself is comparable in size to New Mexico, or even Britain and Ireland put together! A study in 2016 suggested that Tamu Massif might actually cover the entire Shatsky Rise. If so, its area would be about 533,000 square kilometres (206,000 sq mi), making it even larger in surface area than Olympus Mons.
A Unique Underwater Giant
For a while, scientists debated if Tamu Massif was one huge volcano or several smaller ones. They used special tools to map the ocean floor and study rock samples. Some early maps showed features that looked like three separate volcanoes. However, other studies, including one in 2016, strongly suggested it was indeed a single, massive volcano.
In 2015, researchers discovered something very interesting. The volcano's structure showed patterns of magnetic stripes. These stripes are usually found where new ocean floor is created at mid-ocean ridges. This suggests that Tamu Massif is a unique blend, a "hybrid" volcano. It has features of both a mid-ocean ridge and a shield volcano. It also formed at a very unusual spot: where three mid-ocean ridges met!
Why It Won't Erupt Again
Scientists have also studied the deep structure of Tamu Massif. They found that the boundary between the Earth's crust and its mantle, called the "Moho line," is very deep beneath the volcano. It goes down more than 30 kilometres (19 mi)! This thick layer makes it very unlikely for magma (molten rock) to push through and cause another eruption. So, Tamu Massif is considered an extinct volcano, a sleeping giant of the deep.
See also
- Mauna Loa – the third-largest volcano on Earth; also the largest active volcano and the largest volcano extending above sea level
- Gardner Pinnacles – peaks of Pūhāhonu, the second-largest volcano on Earth, the largest shield volcano on Earth, nearly twice as large as Mauna Loa
- Ring of Fire – belt of volcanoes on the rim of the Pacific Ocean
- Tharsis – a massive volcanic plateau on the western hemisphere of Mars that includes Olympus Mons