Temperature facts for kids
Temperature tells us how hot or cold something is. Our bodies can feel if something is hot or cold. To measure temperature more accurately, we use a thermometer. Thermometers use a special scale to show how hot or cold something is. Most of the world uses degrees Celsius, sometimes called "centigrade." In the USA and a few other places, degrees Fahrenheit are used more often. Scientists mostly use kelvins to measure temperature because this scale never goes below zero.
In science, temperature describes how fast tiny particles called molecules are moving inside a material. In solids and liquids, molecules vibrate around a fixed spot. But in gases, they fly freely and bounce off each other. For a gas, its temperature, pressure, and volume are all connected by a rule of physics.
Contents
Changing Temperature Scales
It's easy to change temperatures from one scale to another!
- To change Celsius to Fahrenheit: Multiply the Celsius temperature by 9/5, then add 32.
* Example: F = (9/5)C + 32
- To change Fahrenheit to Celsius: Subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature, then multiply the result by 5/9.
* Example: C = (F - 32) * 5/9
Important Temperatures to Know
Scientists found some temperatures are always the same for certain things:
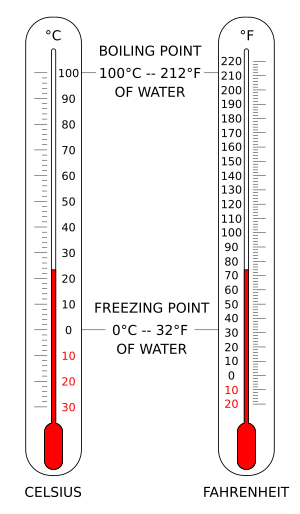
- Water freezes at 0°C, 32°F, or 273.15 K.
- The temperature inside the human body is usually around 37°C or 98°F.
- Water boils at 100°C, 212°F, or 373.15 K.
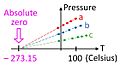
- The coldest possible temperature is called absolute zero. This is 0 K, -459°F, or -273.15°C. At absolute zero, molecules and atoms stop moving and have no heat energy.
Temperature and Heat: What's the Difference?
Temperature is not the same as heat. Heat is energy that moves from one thing to another. When heat moves, one thing cools down, and the other heats up. Temperature measures how much the molecules inside something are moving or vibrating. If something has a high temperature, its molecules are moving very fast on average. Something can have a high temperature but very little heat if it has only a few or very light atoms.
Heat Capacity: How Much Heat Can It Hold?
The amount of heat needed to make a substance one degree hotter is called its heat capacity. Different substances need different amounts of heat to warm up. For example, a kilogram of water has a higher heat capacity than a kilogram of steel. This means it takes more energy to make water 1°C hotter than it does to make steel 1°C hotter.
Temperature and Weather
Temperature is very important in weather and climate. It's linked to the amount of heat energy in the air. Isotherm maps show how temperature changes across an area. Temperature changes during different times of day, in different seasons, and in different places. It's affected by how much heat a place gets from the sun's rays (insolation), how high the place is above sea level, and how much heat is carried by winds and ocean currents.
Temperature Scales
Temperature scales need two main things to be defined. First, they need a starting point, which is called zero degrees. Second, they need to define the size of each step, or "degree."
The Celsius scale (°C) is used for everyday temperature measurements in most of the world. It was created based on the freezing and boiling points of water. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C, both at normal atmospheric pressure at sea level. It was called "centigrade" because there are 100 degrees between these two points. Now, the Celsius scale is connected to the kelvin scale. This means that one degree Celsius is the same size as one kelvin, but the numbers are different by exactly 273.15.
The Fahrenheit scale is commonly used in the United States. On this scale, water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F at sea-level pressure.
Absolute Zero: The Coldest Possible Temperature
At absolute zero temperature, no energy can be taken away from matter as heat. This is a key idea in physics. At this temperature, matter has no regular heat energy. However, it still has a tiny bit of energy called quantum-mechanical zero-point energy. Scientists can get very, very close to absolute zero, but they can never actually reach it. In theory, at absolute zero, all the particles in a substance would stop moving in the classical sense. Absolute zero is defined as 0 K, which is exactly -273.15°C, or -459.67°F.
Kelvin Scale: For Scientists
Many scientific measurements use the Kelvin scale (unit symbol: K). It's named after Lord Kelvin, the physicist who first defined it. This is an absolute scale, meaning its zero point (0 K) is at absolute zero. Since May 2019, the kelvin has been defined based on how particles move. In the International System of Units (SI), the size of the kelvin is set by a fixed value called the Boltzmann constant. The temperature of anything in a balanced state is always positive on the Kelvin scale.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
This shows how a part of a protein moves more as the temperature goes up.
See also
 In Spanish: Temperatura para niños
In Spanish: Temperatura para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |