Tule Valley facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tule Valley |
|
|---|---|
| 1859: White Valley | |

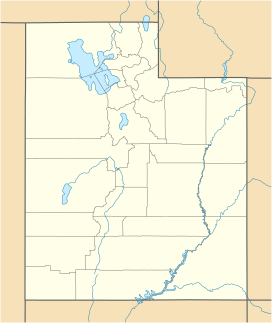
Shadow on the eponymous white rocks of the
Tule Valley, November 2009 |
|
| Floor elevation | 4,780 ft (1,460 m) |
| Area | 248 sq mi (640 km2) |
| Geography | |
Tule Valley, also known as White Valley, is a large valley located in Millard County, Utah, in the United States. It's a special kind of valley because it's a "closed basin," meaning all the water that falls there stays inside and doesn't flow out to a river or ocean. This valley is part of the bigger Great Basin area, which is known for its dry, desert-like conditions.
Contents
What is Tule Valley?
Tule Valley stretches from north to south and is a "closed basin" or endorheic valley. This means that any rain or snow that falls within the valley's boundaries collects inside it and does not flow out to the ocean. It's part of the Great Basin Desert, which is a very dry area in western North America.
The valley is surrounded by mountain ranges. To the west, you'll find the Confusion Range, and to the east, the House Range. The Middle Range and the Great Salt Lake Desert are to the north, while Wah Wah Valley and the Wah Wah Mountains are to the south. In the middle of the valley, there are several small hills called knolls, with the largest one being Coyote Knolls.
The name "White Valley" was given in 1859 by James H. Simpson. He noticed many white rocks on the valley floor. These white rocks are mostly made of Lake Bonneville marls, which are soft, chalky deposits left behind by an ancient lake.
Cool Features of Tule Valley

One of the most important spots in Tule Valley is Coyote Springs. This is a vital water source for local wildlife, including feral horses that roam freely in the valley. It's also a starting point for people who want to visit Notch Peak.
Notch Peak: A Giant Cliff
Notch Peak is a huge cliff made of carbonate rock. It stands about 4,450-foot (1,360 m) tall, and an amazing 2,200 feet [670 m] of that is a pure vertical drop! This makes it the tallest carbonate cliff in North America. The name "Tule" for the valley comes from a type of swamp plant that was likely found near Coyote Springs when explorers first came to the area.
Getting Around the Valley
Tule Valley is very isolated. There's only one paved road, U.S. Route 6/U.S. Route 50, which crosses its southern part. No people live in the valley permanently, though shepherds sometimes bring their sheep to graze there in the spring.
The center of the valley has a large dry lakebed called a playa. This is where all the water from rain and snow collects, as it's the lowest point in the valley. It's also the lowest point in all of Millard County, Utah.
Ibex Crags: A Climber's Paradise
On the eastern edge of the valley, you'll find the Ibex Crags. These rock formations are famous among climbers for "world class" bouldering, which is a type of rock climbing done on large rocks or small cliffs without ropes.
How Tule Valley Was Formed
The ground in Tule Valley is mostly made up of Quaternary alluvial sediments, which are materials like sand, silt, and gravel carried and deposited by water. You can also find chalky white Pleistocene marls, which are soft rocks formed from ancient lake beds.
The valley itself is a true graben. This means it's a section of land that has dropped down between two normal faults, which are cracks in the Earth's crust where the land on one side moves down relative to the other. The small hills (knolls) in the valley are actually horsts, which are blocks of land that have moved up relative to the surrounding area. These horsts are made of older Silurian to Devonian carbonates.
Water in Tule Valley
The Tule Valley area is part of a larger hydrologic unit that includes several valleys and mountain ridges in the Basin and Range Province. Because it's a closed basin, all the surface water stays within its boundaries. On average, the valley holds about 4,000 acre-feet (4,900,000 m3) of surface water.
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |