- This page was last modified on 1 January 2026, at 00:05. Suggest an edit.
2024 YR4 facts for kids
2024 YR4 (centered) tracked by the Very Large Telescope in January 2025
|
|
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | ATLAS–CHL (W68) |
| Discovery site | Río Hurtado, Chile |
| Discovery date | 27 December 2024 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | 2024 YR4 |
| Orbital characteristics(JPL #78) | |
| Epoch 5 May 2025 (JD 2460800.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 3 | |
| Observation arc | 137 days |
| Earliest precovery date | 25 December 2024 |
| Aphelion | 4.180 AU |
| Perihelion |
|
| 2.5159 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.6616 |
| 3.991 yr (1457.57 days) |
|
| 40.40° | |
|
Mean motion
|
0.2470° per day |
| Inclination | 3.4082° |
| 271.366° | |
|
|
| 134.361° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.00283 AU (423,000 km; 1.10 LD) |
| Jupiter MOID | 1.2716 AU |
| Physical characteristics | |
|
Mean diameter
|
60±7 m |
| 0.32440 ± 0.00002 h (19.4640 ± 0.0012 min) | |
|
Pole ecliptic latitude
|
~ −25° |
|
Pole ecliptic longitude
|
~ 42° |
|
|
|
|
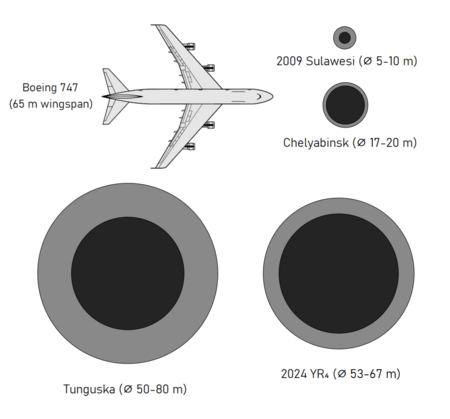
2024 YR4 is an asteroid that is about 60 meters (200 feet) wide. It is known as an Apollo asteroid, which means its path around the Sun crosses Earth's orbit.
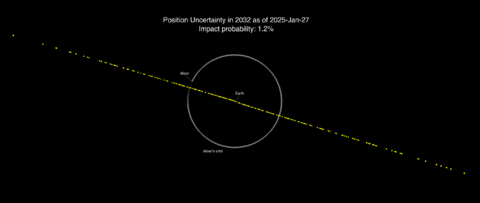
This asteroid was discovered by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) in Chile on December 27, 2024. For a short time, from January 27 to February 20, 2025, scientists thought there was a chance it might hit Earth in 2032. It was given a rating of 3 on the Torino scale, which is a way to measure how risky an asteroid might be. This was because its estimated chance of hitting Earth was more than 1%.
However, by February 23, 2025, new observations showed that 2024 YR4 would not hit Earth in 2032. Its Torino rating was then lowered to 0, meaning there was no longer any risk. More recently, observations from the James Webb Space Telescope on May 11, 2025, showed a small chance (about 4%) that the asteroid could hit the Moon on December 22, 2032. If it misses the Moon, it is expected to pass about 9,000 to 74,000 kilometers (5,600 to 46,000 miles) from the Moon's surface.
When the asteroid's impact chance was higher, it triggered the first steps in planetary defense. This meant that major telescopes gathered more information, and space agencies supported by the United Nations started planning how to deal with such a threat.
The asteroid passed very close to Earth on December 25, 2024, just two days before it was discovered. It was about 828,800 kilometers (515,000 miles) away. Its next close approach to Earth will be on December 17, 2028. Scientists believe 2024 YR4 is a stony asteroid and spins quite fast, completing a full rotation in about 19.5 minutes.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The asteroid's name, "2024 YR4", is a temporary name given by the Minor Planet Center when it was found on December 27, 2024. The "Y" means it was discovered in the second half of December (from the 16th to the 31st). The "R4" shows it was the 117th asteroid found in that half-month.
Asteroid's Features
Size and What It's Made Of
On March 26, 2025, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) measured 2024 YR4's size. It is about 60 meters (200 feet) wide, with a small amount of uncertainty. This makes it similar in size to the asteroid that caused the Tunguska event in 1908. It is much smaller than Dimorphos, the asteroid that NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft hit in 2022.
Before the JWST measurements, scientists guessed its size based on how bright it looked. They thought it was between 40 and 90 meters (130 and 300 feet) wide.
Scientists have not measured the asteroid's exact weight or how dense it is. But by guessing its density (how much stuff is packed into it), they estimate its mass to be around 280 million kilograms (620 million pounds).
How It Spins and Its Shape
Studies from different telescopes suggest that 2024 YR4 is a stony asteroid. This means it is mostly made of rock, like many other asteroids.
Observations from the Very Large Telescope (VLT) and the La Silla Observatory show that 2024 YR4 spins very quickly. It completes one full spin in about 19.5 minutes. Even though it spins fast, it is not fast enough to break apart if it were a pile of loose rocks.
The asteroid's brightness changes as it spins, which tells scientists about its shape. It is not perfectly round; it is elongated, meaning it is longer in one direction than the other. Its longest side is about 1.4 times longer than its shortest side. Other measurements suggest it is quite flattened, with its width about three times its thickness.
Asteroid's Path in Space
2024 YR4 travels around the Sun in an oval-shaped path that crosses Earth's path. Since its close visit in December 2024, it takes about 1458 days (almost 4 years) to go around the Sun once. Its path is tilted slightly (about 3.41 degrees) compared to Earth's path.
The asteroid's path can change over time. When it passes close to Earth or the Moon, their gravity can pull on it and slightly change its orbit. For example, its orbit will be strongly affected by its close pass in 2032.
Because 2024 YR4 spins backward (opposite to its orbit), its path around the Sun slowly shrinks. This suggests it originally came from farther out in the Solar System, likely from the main main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
The asteroid was closest to the Sun on November 22, 2024. It then made a close pass by Earth on December 25, 2024, at a distance of 828,800 kilometers (515,000 miles). It also passed about 488,300 kilometers (303,400 miles) from the Moon.
Its next close approach to Earth will be on December 17, 2028. It will pass about 8 million kilometers (5 million miles) from Earth. This will be a great chance for astronomers to observe it again and get even more precise information about its orbit. This improved data will help them better predict its path for the 2032 close approach.
After 2032, the asteroid's path becomes harder to predict because of the strong gravitational pull from Earth and the Moon. The uncertainty in its position grows larger over time.
The 2032 Close Approach
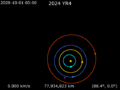
On December 22, 2032, 2024 YR4 will come closest to Earth. It is expected to pass about 270,000 kilometers (168,000 miles) from Earth. Its closest approach to the Moon is expected to be around 11,000 kilometers (6,800 miles) away.
Because of its size and the earlier chance of impact, 2024 YR4 reached a Torino scale rating of 3 on January 27, 2025. This was the second-highest rating ever for an asteroid. However, as more observations were made, the risk of an Earth impact in 2032 was removed by April 2, 2025.
What if it Hit Earth?
If 2024 YR4 had hit Earth in 2032, it would have released a huge amount of energy. Scientists estimated it would be like 7.7 megatons of TNT. This is about 500 times more powerful than the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima.
Because it is a stony asteroid, it would likely have exploded in the air, creating a powerful air burst, rather than making a crater on land or a tsunami in the ocean. The damage from such an event could have spread up to 50 kilometers (30 miles) from the impact point.
Even with this potential, 2024 YR4 is not considered a "potentially hazardous object" (PHO). This is because PHOs are usually larger than 140 meters (460 feet) and could cause widespread damage. 2024 YR4 is smaller, so any damage would be more local.
What if it Hit the Moon?
Based on observations up to May 11, 2025, there is still about a 4% chance that 2024 YR4 could hit the Moon on December 22, 2032. The impact would happen around 15:17 to 15:21 UTC.
If it hits the Moon, it could create a crater between 500 and 2,000 meters (0.3 to 1.2 miles) wide. The impact would release energy equal to about 5.2 megatons of TNT, which is about 340 times more powerful than the Hiroshima bomb.
Such an impact could send about 100,000 tons of Moon rocks and dust into space. This debris could cause an amazing meteor shower visible from Earth. It could also be a danger to satellites orbiting Earth.
Some astronomers believe the impact flash would be bright enough to be seen from Earth, even during the daytime. One expert suggested it "could be brighter than the full moon," making it clearly visible without a telescope.
Watching the Asteroid
2025 Observations
More observations of 2024 YR4 helped scientists better understand its path. Since the asteroid was moving away from Earth after its discovery, it became fainter and harder to see. This meant that very large telescopes, like the Keck Observatory and the Very Large Telescope, were needed to observe it.
By March 14, 2025, the asteroid was 63 million times too faint to be seen with the naked eye. The last ground-based observation was on March 23, 2025. After that, only space telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) could see it from farther away.
The JWST observed 2024 YR4 on March 8, March 26, and for a final time on May 11, 2025. These observations were important for measuring its position, how much heat it gives off, and its size. These were the last observations before its next close approach in 2028.
Finding Old Pictures
Scientists also looked for "precovery" observations. These are old telescope images taken before the asteroid was officially discovered. The earliest known image of 2024 YR4 was from ATLAS on December 25, 2024, just two days before its discovery. However, this image was not very clear because the asteroid was moving so fast.
Astronomers checked old images from other surveys like Catalina Sky Survey, Pan-STARRS, and data from spacecraft like Gaia and NEOWISE. But they did not find any other clear pictures of 2024 YR4 from earlier dates.
2028 Observations
When the asteroid passes near Earth again in 2028, astronomers will have another chance to observe it. These new observations will greatly improve how accurately they can predict its orbit. This is very important for understanding the likelihood of a Moon impact in 2032.
The asteroid will be too faint to see until June 2028. It will be brightest around July 19, 2028, when it is opposite the Sun from Earth. It will continue to get closer until December 17, 2028, when it will pass about 20.8 times the Earth-Moon distance from Earth.
What if it Was a Threat?
If the observations had not shown that 2024 YR4 would miss Earth in 2032, a mission like NASA's DART might have been considered to push it off course. However, building and launching such a mission in less than eight years would have been very difficult.
Scientists could have prepared a mission before the 2028 close encounter. That way, it would be ready to launch if new data showed an impact was likely. If deflecting the asteroid was not possible and it was predicted to hit a populated area, people might have needed to be evacuated.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: 2024 YR4 para niños
In Spanish: 2024 YR4 para niños