Quaoar facts for kids

A low-resolution image of Quaoar and its moon Weywot, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2006.
|
|
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by |
|
| Discovery site | Palomar Observatory |
| Discovery date | 4 June 2002 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | (50000) Quaoar |
| Pronunciation | KWA-wahr |
|
Named after
|
Qua-o-ar / Kwawar (deity of the Tongva people) |
| 2002 LM60 | |
|
|
| Adjectives | Quaoarian |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch 31 May 2020 (JD 2459000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 3 | |
| Observation arc | 65.27 yr (23,839 d) |
| Earliest precovery date | 25 May 1954 |
| Aphelion | 45.488 AU (6.805 Tm) |
| Perihelion | 41.900 AU (6.268 Tm) |
| 43.694 AU (6.537 Tm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.04106 |
| 288.83 yr (105,495 d) | |
| 301.104° | |
|
Mean motion
|
0° 0m 12.285s / day |
| Inclination | 7.9895° |
| 188.927° | |
| 11 February 2075 ±17 days |
|
| 147.480° | |
| Known satellites | 1 (Weywot) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 1,286 × 1,080 × 932 km |
|
Mean diameter
|
1,090±40 km (2024; volume equivalent) |
|
Mean radius
|
545±20 km (2024; volume equivalent) |
| 3.78×106 km2 | |
| Volume | 6.78×108 km3 |
| Mass | (1.208±0.063)×1021 kg (system) |
|
Mean density
|
1.66–1.77 g/cm3 |
|
Equatorial surface gravity
|
0.31 m/s2 at poles to 0.16 m/s2 at longest axis |
|
Equatorial escape velocity
|
0.59 km/s at poles to 0.5 km/s at longest axis |
| 17.6788±0.0004 h | |
| 12.6° to ecliptic (if coplanar with rings) | |
|
North pole right ascension
|
259.5°±0.2° (rings) |
|
North pole declination
|
+55.0°±0.2° (rings) |
| 0.124±0.006 | |
| Temperature | ≈ 44 K |
| IR (moderately red) B–V=0.94±0.01 V−R=0.64±0.01 V−I=1.28±0.02 |
|
| 19.0 | |
| 2.737±0.008 2.4 (assumed) |
|
| 40.4±1.8 milliarcseconds | |
Quaoar (pronounced KWA-wahr), also known as 50000 Quaoar, is a dwarf planet located far away in the Kuiper Belt. The Kuiper Belt is a huge ring of icy objects that orbit the Sun beyond Neptune. Quaoar is about half the size of Pluto and has a slightly stretched, egg-like shape.
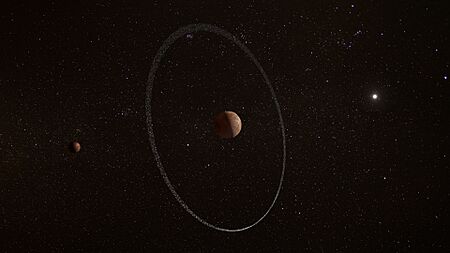
This distant world is full of surprises. It has one small moon named Weywot. In 2023, scientists discovered that Quaoar also has two rings. This was a big surprise because the rings are in a place where scientists thought rings couldn't exist.
Quaoar was discovered on June 4, 2002, by astronomers Chad Trujillo and Michael Brown. Its surface is covered in frozen water, ammonia, and a little bit of methane. This suggests that Quaoar might have "ice volcanoes," also known as cryovolcanism.
Contents
Discovery and Name
How Was Quaoar Found?

Quaoar was discovered on June 4, 2002, by American astronomers Chad Trujillo and Michael Brown. They were using the Samuel Oschin telescope at the Palomar Observatory in California. They were searching for large, bright objects in the Kuiper Belt.
Trujillo first spotted Quaoar in images as a dim object moving slowly through the constellation Ophiuchus. Even though it was far away, it was quite bright. This made the astronomers think it could be very large, maybe even as big as Pluto.
After the discovery, the team searched for older pictures of Quaoar. They found images dating all the way back to 1954. These "precovery" images helped them calculate Quaoar's orbit accurately. The discovery was officially announced on October 7, 2002. At the time, it was the largest object found in the Solar System since Pluto.
What Does "Quaoar" Mean?
When it was first found, the discovery team nicknamed it "Object X," like the mysterious "Planet X" that some astronomers had searched for. Once they knew its size, they wanted a real name. They chose to honor the local Native American people of the Los Angeles area, the Tongva people.
Following the rules for naming objects in the Kuiper Belt, they needed a name from a creation myth. They chose Quaoar (originally spelled Kwawar). In Tongva mythology, Quaoar is the powerful creator god who sang and danced the universe into existence. Quaoar first created Weywot (the Sky Father), and together they created the Earth Mother and Grandfather Sun.
The astronomers contacted members of the Tongva tribe, who approved of using the name for this new world. Quaoar was officially given the number 50000 to celebrate its large size.
Orbit and Location
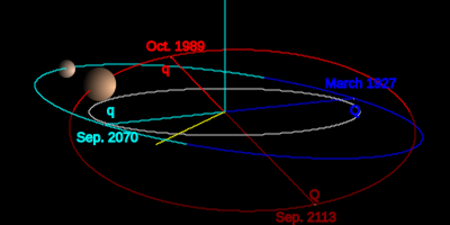
Quaoar orbits the Sun in the Kuiper Belt, a region filled with thousands of icy bodies beyond Neptune. It is very far away, at an average distance of about 43.7 AU from the Sun. One AU is the distance from the Earth to the Sun. It takes light from the Sun more than five hours to reach Quaoar.
It takes Quaoar about 289 Earth years to complete one orbit around the Sun. Its orbit is almost a perfect circle, which is unusual for objects in the Kuiper Belt. This means its distance from the Sun doesn't change very much.
Because its orbit is so stable and it is not in a special orbital rhythm with Neptune, Quaoar is called a classical Kuiper belt object or cubewano. Its orbit is tilted by about 8 degrees compared to Earth's orbit around the Sun.
What is Quaoar Like?
Size and Shape
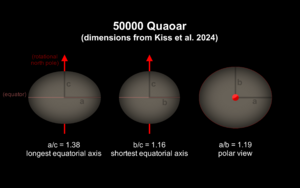
Quaoar is not a perfect sphere. Instead, it is a triaxial ellipsoid, which means it's shaped like a slightly squashed and stretched ball. Its average diameter is about 1,090 kilometers (677 miles), which is about half the diameter of Pluto.
This shape is a puzzle for scientists. For an object of its size and slow rotation (it takes about 17.7 hours to spin once), it should be in hydrostatic equilibrium, meaning it should have pulled itself into a nearly perfect sphere. One idea is that Quaoar used to spin much faster. This fast spin would have stretched it out, and its shape "froze" in place as it slowed down over billions of years.
Mass and Density
By studying the orbit of its moon, Weywot, scientists calculated Quaoar's mass to be about 1.2×1021 kg. This is very light compared to Earth, but it's a lot for a Kuiper Belt object.
Its density is about 1.7 times that of water. This tells scientists that Quaoar is likely made of a mixture of rock and ice. It probably has a rocky core surrounded by a thick mantle of ice.
Surface and Atmosphere
Quaoar has a dark, reddish surface. This color is common for objects in the outer Solar System that have been exposed to space radiation for a long time.
Spectroscopes, which analyze light to figure out what things are made of, have shown that Quaoar's surface has crystalline water ice. This type of ice usually forms in warmer temperatures, so its presence suggests that Quaoar may have been heated in the past, possibly by impacts or by cryovolcanism (ice volcanoes).
The surface also has frozen ammonia, ethane, and a small amount of methane. Methane is a gas that easily escapes into space, so only the largest Kuiper Belt objects like Pluto and Eris can hold onto it. The fact that Quaoar has some methane makes it very interesting. However, searches for an atmosphere have shown that if one exists, it must be extremely thin.
Quaoar's Moon and Mysterious Rings
Quaoar is not alone. It has a small moon and a surprising system of rings, making it a mini-solar system of its own.
Weywot: A Tiny Moon
Quaoar has one known moon, named Weywot. It was discovered in 2006. In Tongva mythology, Weywot is the son of Quaoar. Weywot is quite small, with a diameter of about 170 km (105 miles). It orbits Quaoar at a distance of about 13,300 km and takes about 12.5 days to complete one orbit.
The Puzzling Rings of Quaoar
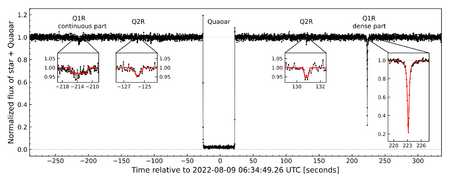
In 2023, astronomers announced a shocking discovery: Quaoar has two rings. They were found by watching Quaoar pass in front of distant stars, an event called a stellar occultation. As Quaoar moved, the star's light blinked out where the rings blocked it.
The discovery is puzzling because the rings are very far from Quaoar. They orbit outside the Roche limit. The Roche limit is the distance from a planet or dwarf planet where its gravity is strong enough to pull apart a moon or prevent loose material from clumping together to form one. Rings are usually found inside this limit.
Quaoar's rings are the first to be found so far outside the Roche limit. This challenges what scientists thought they knew about how rings form and survive. One theory is that the rings are located in a special orbital resonance with Quaoar's spin. This means the ring particles orbit in a perfect rhythm with Quaoar's rotation, which might keep them stable.
The outer ring, called Q1R, is uneven and lumpy, while the inner ring, Q2R, is thinner and more uniform.
Future Exploration
Quaoar is a high-priority target for future space missions. Its strange rings, possible ice volcanoes, and methane on its surface make it one of the most interesting objects in the Kuiper Belt.
No mission has visited Quaoar yet, but the New Horizons spacecraft, which flew past Pluto, took some long-distance images of it in 2016. Scientists are designing new missions that could one day fly by Quaoar to study it up close. Such a mission would help us understand not just Quaoar, but also how our Solar System formed.
See also
 In Spanish: (50000) Quaoar para niños
In Spanish: (50000) Quaoar para niños
 | Madam C. J. Walker |
 | Janet Emerson Bashen |
 | Annie Turnbo Malone |
 | Maggie L. Walker |