Apple-ring acacia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Apple-ring acacia |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Faidherbia albida growing with palms and maize crops | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Faidherbia A.Chev. |
| Species: |
F. albida
|
| Binomial name | |
| Faidherbia albida (Delile) A.Chev.
|
|
 |
|
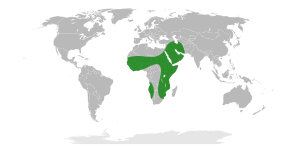
| The range of Faidherbia albida. | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Faidherbia tree (scientific name: Faidherbia albida) is a special type of legume plant. It used to be known as Acacia albida. This tree is originally from Africa and the Middle East. It has also been brought to countries like Pakistan and India.
People call it by different names. Some common names are apple-ring acacia because its round seed pods look like apple rings. Another name is winter thorn. In South Africa, it is called the ana tree.
Contents
About the Faidherbia Tree
The Faidherbia tree is a thorny tree that can grow very tall. It can reach between 6 and 30 meters (about 20 to 100 feet) in height. Its trunk can be up to 2 meters (about 6.5 feet) wide.
This tree has a very deep tap root. This long root helps it find water deep underground. Because of this, the tree can survive very well during dry periods. The bark of the tree is grey and gets cracks as it gets older.
Where Faidherbia Trees Grow
You can find Faidherbia trees in many parts of Africa. They grow in places like the Zambezi and Limpopo floodplains in Southern Africa. They are also found in the Kruger National Park.
In other parts of Africa, they grow across the eastern half of the continent. This includes areas from Maputaland in the south all the way to Egypt. They are also common in the Subsaharan Sahel region and the Horn of Africa.
In Asia, these trees are native to Yemen and Saudi Arabia in the Arabian Peninsula. They also grow in Iran and the Levant region, which includes Israel, Syria, and Lebanon.
Some populations of these trees are found in Israel. Scientists believe these trees have multiplied by themselves for thousands of years. They are also found in Cyprus, Ascension Island, Pakistan, and India.
How Faidherbia Trees Live
Faidherbia trees often grow near rivers or in areas that flood during the rainy season. They can be found in woodlands and savannahs. These trees prefer heavy soils that drain water well.
They can grow in places that get between 250 and 600 millimeters (about 10 to 24 inches) of rain each year. Sometimes they grow alone, but often they are the main type of tree in dry woodlands.
Uses of the Faidherbia Tree
The Faidherbia tree is very important for many reasons, especially in farming and for local communities.
For Animals and Bees
- Bee Food: The flowers of the Faidherbia tree provide food for bees. This is very helpful at the end of the rainy season when other plants are not flowering.
- Animal Feed: The seed pods are excellent food for livestock like camels, cattle, and goats. Wild animals like elephants, antelope, buffalo, and baboons also love to eat them.
- Fish Stupefying: In Zimbabwe, people use the pods to make fish sleepy, which helps with fishing.
Wood and Other Products
- Wood Uses: The wood from the Faidherbia tree is used to make canoes, mortars (for grinding), and pestles. Its wood is quite dense, meaning it's strong and heavy.
- Soap and Tanning: The ashes from burning the wood can be used to make soap. They are also used to remove hair from animal hides when preparing leather.
- Natural Fences: The thorny branches are useful for creating natural, strong fences.
Helping Farms and the Environment
- Agroforestry: This tree is very valuable in agroforestry. This is a farming method where trees are grown among crops. The Faidherbia tree helps crops grow better because it can "fix" nitrogen in the soil. Nitrogen is a nutrient that plants need to grow.
- No Competition with Crops: A special thing about this tree is that it drops its leaves during the rainy season. This means it doesn't block sunlight from crops growing below it.
- Erosion Control: The tree's roots and presence help to stop soil from washing away, which is called erosion control.
- Environmental Transformation: In parts of Niger, farmers have used this tree to improve damaged soils. This practice is seen as a huge positive change for the environment in the Sahel region.
Medicinal Uses
Parts of the Faidherbia tree are used in traditional medicine. An extract from the tree can be used to treat eye infections in farm animals. The bark is also used in traditional medicine in Southern Africa and Niger.
Cultural Importance
The Faidherbia tree has special meaning in some cultures.
- In the Bambara language, it is called balanzan. It is the official tree of the city of Segou in Mali. A legend says that Segou has 4,444 balanzan trees, plus one mysterious "missing tree" that no one can find.
- In the Serer language, it is called Saas. The Saas tree is very important in the creation myth of the Serer people. They believe it is the tree of life and fertility.
Conservation Status
The Faidherbia tree is not currently listed as a threatened species. This means it is not in danger of disappearing.



