Arenysuchus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Arenysuchus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
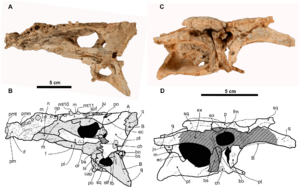
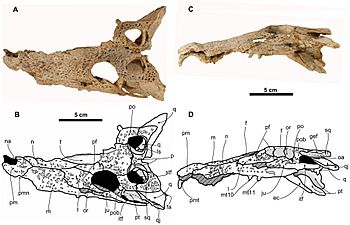
| Skull (ELI-1) and diagram | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Eusuchia |
| Clade: | †Allodaposuchidae |
| Genus: | †Arenysuchus Puértolas, Canudo & Cruzado-Caballero, 2011 |
| Type species | |
| †Arenysuchus gascabadiolorum Puértolas, Canudo & Cruzado-Caballero, 2011
|
|
Arenysuchus (meaning "Arén crocodile") is an extinct type of crocodylomorph. This is a group of reptiles that includes modern crocodiles and their ancient relatives. Arenysuchus lived in northern Spain during the Late Cretaceous period, about 66 to 67.6 million years ago.
Scientists found its holotype (the main specimen used to describe a species) which is a partial skull. They also found four teeth. These fossils were discovered by researchers José Manuel Gasca and Ainara Badiola in a place called Arén, in the Tremp Formation of Spain. Arenysuchus was first named in 2011 by Eduardo Puértolas, José I. Canudo, and Penélope Cruzado-Caballero. The only known species is Arenysuchus gascabadiolorum.
Contents
What does the name Arenysuchus mean?
The name Arenysuchus was given in 2011. It combines two parts. "Areny" comes from Arén, the place in Spain where the skull was found. "Suchus" is an Ancient Greek word for crocodile.
The second part of its name, "gascabadiolorum," honors the two researchers who discovered the main fossil. They are José Manuel Gasca and Ainara Badiola.
What did Arenysuchus look like?
Scientists know Arenysuchus from a partial skull and four teeth. Its skull had some features that link it to early crocodilians. For example, its frontal bones (bones at the front of the skull) touched the edges of two holes on top of its skull. These holes are called supratemporal fenestrae.
The frontal bone of Arenysuchus was also very long at the front. It divided the nasal bones (nose bones). This is unusual because in most other crocodile relatives, the nasal bones are in the middle. The bones near the eyes, called lacrimal bones, were wider than they were long.
Behind the eyes, there were long openings on the side of the skull called Infratemporal fenestra. A thin bone structure below these openings was very tall and flat. In most other crocodilians, this part is thicker and wider, not taller. The edges of its eye sockets, called orbits, were raised. Modern crocodiles also have raised eye socket edges.
Another special feature of Arenysuchus was its small palatine process. This is a bony plate on the maxilla (upper jaw bone) that forms the front part of the palate (roof of the mouth). In Arenysuchus, this plate was much shorter than in its close relatives. It also had a small pit between its seventh and eighth upper jaw teeth. This pit would have held a tooth from the lower jaw when its mouth was closed.
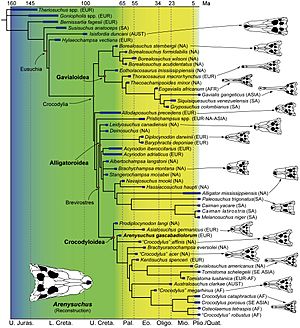
Scientists use phylogenetic analysis to understand how different animals are related. This is like building a family tree. When Arenysuchus was first described in 2011, studies suggested it was one of the earliest members of Crocodyloidea. This group includes modern crocodiles and their extinct relatives.
However, later studies suggested a different idea. They found that Arenysuchus might be a "sister taxon" to Allodaposuchus. This means they are very closely related, like siblings. These studies place Arenysuchus within a group called Allodaposuchidae.
Here are two ways scientists have shown its family tree:
| Crocodylia |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Alternatively, some studies show:
| Allodaposuchidae |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
What was life like for Arenysuchus?
Paleobiology is the study of ancient life. Arenysuchus was part of a new wave of crocodilians that spread across the Northern Hemisphere during the Late Cretaceous period.
At that time, Europe was not a single landmass. It was a group of islands surrounded by shallow seas. On these islands, crocodilians were the most common type of crocodylomorph. In contrast, in the Southern Hemisphere, other types of crocodylomorphs were more common. Before this period, crocodilians were not found in Europe at all.
There were many Dinosaurs around, including different kinds of sauropods (long-necked dinosaurs), theropods (meat-eating dinosaurs), and ornithopods (plant-eating dinosaurs). But as Europe became an island chain, things changed. Dinosaurs became much rarer, mostly represented by hadrosaurs (duck-billed dinosaurs). Crocodilians, like Arenysuchus, became a much bigger part of the island ecosystems.
Where did Arenysuchus live?
Paleoecology is the study of ancient environments and how living things interacted with them. The fossils of Arenysuchus were found at the Elias site, near Arén in Spain. This site is part of a large rock formation called the Tremp Formation.
The Tremp Formation is made up of about 900 meters (about 2,950 feet) of reddish rock. This formation dates back to the late Cretaceous period. Scientists have used tiny fossils and magnetic patterns in the rocks to figure out its age. The Elias site itself is about 67 million years old.
Other dinosaurs, like Arenysaurus and Blasisaurus, were also found in different parts of the Tremp Formation. This tells us that Arenysuchus shared its ancient home with various dinosaurs.
See also
 In Spanish: Arenysuchus para niños
In Spanish: Arenysuchus para niños