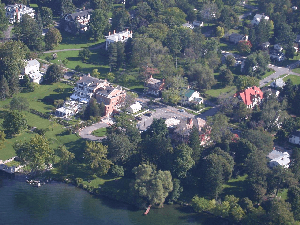Aurora, Cayuga County, New York facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Aurora, New York
|
|
|---|---|

Aerial view of Aurora from south by southwest, 2013. The village is along the straight stretch of the Cayuga Lake shore just above lower right of photo.
|
|
| Country | United States |
| State | New York |
| County | Cayuga County |
| Town | Ledyard |
| Established | 1795 |
| Incorporated (village) | 1837 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 0.92 sq mi (2.38 km2) |
| • Land | 0.92 sq mi (2.38 km2) |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2) |
| Elevation | 411 ft (125 m) |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • Total | 607 |
| • Density | 660.50/sq mi (255.00/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP code |
13026
|
| FIPS code | 36-03188 |
Aurora, also known as Aurora-on-Cayuga, is a small village in Cayuga County, New York. It sits right on the shore of Cayuga Lake. In 2020, about 607 people lived there.
Aurora was once home to Wells College, a special school for women started in 1868 by Henry Wells. It became a school for both men and women in 2005 but closed its doors in 2024.
The village is famous for its history. The Aurora Village-Wells College Historic District was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1980. This means many of its old buildings are protected. From 2001 to 2007, a lot of work was done to fix up these historic places. This project brought both praise and some disagreements.
Contents
History of Aurora Village
Early Native American Life
Long ago, Indigenous peoples lived along the lakes and rivers in what is now New York. Before European settlers arrived, a large Cayuga Indian village called Chonodote was located near where Aurora is today. The Cayuga people had permanent homes and grew important crops like corn, beans, and squash.
During the Revolutionary War in 1779, Chonodote was destroyed by the Sullivan Expedition. This happened because the Cayuga were allies of the British army. Most of the Cayuga people moved to Canada with other Iroquois nations. Some returned after the war, but they lost their land to New York.
Settlement and Growth
After the Revolutionary War, parts of the village land were given to veterans as payment for their service. Many soldiers from New England settled in the Finger Lakes area.
In the 1800s, Aurora grew into a small center for making things. It became a busy stop for canal boats after the Cayuga–Seneca Canal opened. The village officially became a village in 1837. It was a port where farmers could ship their crops up Cayuga Lake and then by the Erie Canal to bigger markets.
Education in Aurora
Education was important in Aurora from early on. Schools like Cayuga Lake Academy were started in 1800. Many famous people went to Cayuga Lake Academy, including President Millard Fillmore. In 1868, Henry Wells founded Wells College to provide education for women.
Modern Aurora
Over time, new ways of transportation and changes in farming made the canals less important. Today, Aurora is known for its well-preserved historic buildings. These buildings make up the Aurora Village–Wells College Historic District. Wells College was a major employer for many years. When the college was open, students made up nearly half of the village's population.
Other historic places listed on the National Register of Historic Places include the Aurora Steam Grist Mill (1976) and Mosher Farmstead (2003).
In 2005, a special farm called S.H.A.R.E. Farm was given to the Cayuga Nation of New York. This was important because it was the first time the Cayuga Nation owned a significant piece of land in their ancestral homeland in over 200 years.
Notable People from Aurora
Many interesting people have connections to Aurora:
- Frances Folsom Cleveland: She was the First Lady of the United States and went to Wells College.
- Robert P. T. Coffin: A well-known writer, poet, and professor.
- Victor Hammer: A talented painter, sculptor, printer, and typographer.
- Edwin B. Morgan: A congressman and one of the people who started The New York Times newspaper.
- Lewis Henry Morgan: A very important early anthropologist who studied human societies.
- Pleasant Rowland: The founder of the popular "American Girl" series of dolls and books. She also went to Wells College.
- Henry Wells: The founder of Wells College, Wells Fargo (a banking company), and the American Express Company.
Changes and Renovations in Aurora
Around the year 2000, Wells College planned some changes, including renovating buildings. They also decided to close the historic Aurora Inn and find someone to fix it up. These plans caused some discussion, especially because many buildings were in the historic district.
In 2001, Pleasant Rowland, who created the "American Girl" dolls, worked with Wells College to renovate the Aurora Inn. She also bought and fixed up other properties, like the E. B. Morgan House. Rowland wanted to make the village more beautiful and help the local economy.
Some people had concerns about these changes. They worried that the renovations were happening too quickly and that proper steps for reviewing projects in historic areas were not always followed. A group called the Aurora Coalition even filed a lawsuit. The National Trust for Historic Preservation and the Preservation League of New York joined the lawsuit. They were concerned that local rules for historic districts were not being followed closely enough.
The court eventually allowed the renovation of the Aurora Inn to continue. The discussions about the village's future continued. In 2007, Pleasant Rowland ended her direct partnership with Wells College. However, she continued to own and operate many of the renovated properties in the village. By 2013, she owned most of the village's business district.
Geography and Climate
Aurora is located on the eastern shore of Cayuga Lake. Long Point State Park is just south of the village. The village covers about 2.38 square kilometers (0.92 square miles) of land.
Aurora's Weather
Aurora has a warm-summer humid continental climate. This means it has warm summers and cold, snowy winters. The hottest temperature ever recorded in Aurora was 101°F (38°C) in July 1988. The coldest was -21°F (-29°C) in January 1982.
| Climate data for Aurora, New York, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1956–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 68 (20) |
75 (24) |
85 (29) |
93 (34) |
94 (34) |
96 (36) |
101 (38) |
97 (36) |
98 (37) |
87 (31) |
81 (27) |
69 (21) |
101 (38) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 56.0 (13.3) |
54.3 (12.4) |
65.0 (18.3) |
78.6 (25.9) |
86.4 (30.2) |
90.0 (32.2) |
90.7 (32.6) |
89.7 (32.1) |
88.1 (31.2) |
78.6 (25.9) |
68.4 (20.2) |
57.3 (14.1) |
92.6 (33.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 31.2 (−0.4) |
33.2 (0.7) |
40.9 (4.9) |
54.4 (12.4) |
67.3 (19.6) |
75.7 (24.3) |
79.8 (26.6) |
78.7 (25.9) |
72.1 (22.3) |
59.3 (15.2) |
47.1 (8.4) |
36.6 (2.6) |
56.4 (13.5) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 23.9 (−4.5) |
25.3 (−3.7) |
32.5 (0.3) |
44.7 (7.1) |
57.1 (13.9) |
66.1 (18.9) |
70.3 (21.3) |
68.8 (20.4) |
62.0 (16.7) |
50.7 (10.4) |
39.9 (4.4) |
30.3 (−0.9) |
47.6 (8.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 16.6 (−8.6) |
17.4 (−8.1) |
24.1 (−4.4) |
35.0 (1.7) |
46.9 (8.3) |
56.5 (13.6) |
60.8 (16.0) |
58.9 (14.9) |
51.9 (11.1) |
42.1 (5.6) |
32.6 (0.3) |
23.9 (−4.5) |
38.9 (3.8) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −2.7 (−19.3) |
0.3 (−17.6) |
6.7 (−14.1) |
22.6 (−5.2) |
33.5 (0.8) |
43.8 (6.6) |
50.6 (10.3) |
48.6 (9.2) |
39.6 (4.2) |
30.3 (−0.9) |
19.2 (−7.1) |
7.6 (−13.6) |
−5.6 (−20.9) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −21 (−29) |
−19 (−28) |
−11 (−24) |
3 (−16) |
24 (−4) |
34 (1) |
43 (6) |
37 (3) |
27 (−3) |
20 (−7) |
0 (−18) |
−15 (−26) |
−21 (−29) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.08 (53) |
1.85 (47) |
2.63 (67) |
3.26 (83) |
3.13 (80) |
3.78 (96) |
3.76 (96) |
3.37 (86) |
3.83 (97) |
3.80 (97) |
2.94 (75) |
2.56 (65) |
36.99 (942) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 15.0 (38) |
12.7 (32) |
11.8 (30) |
2.1 (5.3) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
3.8 (9.7) |
10.5 (27) |
56.2 (142.76) |
| Average extreme snow depth inches (cm) | 9.7 (25) |
9.7 (25) |
10.5 (27) |
3.0 (7.6) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.1 (0.25) |
4.0 (10) |
5.3 (13) |
14.9 (38) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 14.4 | 11.3 | 12.8 | 13.9 | 13.3 | 13.0 | 12.4 | 11.2 | 11.7 | 15.3 | 12.8 | 13.7 | 155.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 8.3 | 7.2 | 5.1 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 2.1 | 5.3 | 29.3 |
| Source 1: NOAA | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: National Weather Service | |||||||||||||
Population Facts
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 500 | — | |
| 1850 | 600 | 20.0% | |
| 1860 | 459 | −23.5% | |
| 1870 | 450 | −2.0% | |
| 1880 | 444 | −1.3% | |
| 1890 | 555 | 25.0% | |
| 1900 | 499 | −10.1% | |
| 1910 | 493 | −1.2% | |
| 1920 | 416 | −15.6% | |
| 1930 | 389 | −6.5% | |
| 1940 | 372 | −4.4% | |
| 1950 | 711 | 91.1% | |
| 1960 | 834 | 17.3% | |
| 1970 | 1,072 | 28.5% | |
| 1980 | 926 | −13.6% | |
| 1990 | 687 | −25.8% | |
| 2000 | 720 | 4.8% | |
| 2010 | 724 | 0.6% | |
| 2020 | 607 | −16.2% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
In 2000, Aurora had 720 people living in 181 households. About 52 of these households had children under 18. Most people were White (659), with smaller numbers of African American, Native American, and Asian residents.
The average age in the village was 22 years old. This was because many college students lived there. The population was 62.3% female and 37.7% male, also due to the college having mostly female students at that time.
The average income for a household in 2000 was $57,222. A small number of families and individuals lived below the poverty line.
See also
 In Spanish: Aurora (condado de Cayuga, Nueva York) para niños
In Spanish: Aurora (condado de Cayuga, Nueva York) para niños
 | Jackie Robinson |
 | Jack Johnson |
 | Althea Gibson |
 | Arthur Ashe |
 | Muhammad Ali |