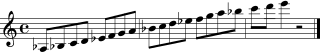Saxophone facts for kids

An alto saxophone
|
|
| Woodwind instrument | |
|---|---|
| Classification | |
| Hornbostel–Sachs classification | 422.212-71 (Single-reeded aerophone with keys) |
| Inventor(s) | Adolphe Sax |
| Developed | 28 June 1846 |
| Playing range | |
|
|
|
| Related instruments | |
|
Military band family:
Orchestral family:
Other saxophones:
|
|
| Musicians | |
|
|
A saxophone is a cool musical instrument that looks like it's made of brass. People often just call it a "sax." Even though it's made of brass, it's actually part of the woodwind family, not the brass family. This is because it uses a reed to make sound, just like a clarinet. The saxophone was even developed from the clarinet! To play it, you blow air into a reed that's attached to the mouthpiece.
There are many different kinds of saxophones, from very low sounds to very high sounds. Some of them are the tubax, contrabass, bass, baritone, tenor, alto, soprano, sopranino, and soprillo. But usually, you'll only see the baritone, tenor, alto, and soprano saxophones being played.
The saxophone was invented in 1842 by a clever person named Adolphe Sax. You can hear saxophones in many types of music, like classical, jazz, and sometimes even rock and pop. Big bands from the 1940s and 1950s always had saxophones too! Some famous saxophone players include Marcel Mule (for classical music) and Charlie Parker (for jazz music).
One cool thing about saxophones is that they are a "transposing" family of instruments. This means that if you learn how to play one saxophone, you can play other types of saxophones without changing how you move your fingers!
Contents
What is a Saxophone?
How Saxophones Make Sound
The saxophone makes different pitches (high or low sounds) using keys. These keys have small cups with soft pads that cover holes on the instrument. When you press a key, it opens or closes a hole, which changes how long the air column inside the saxophone is. This changes the sound.
There's also a special key called an "octave key." When you press it, it opens a small vent hole. This makes the sound jump up an octave, which means it sounds much higher.
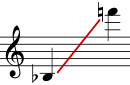
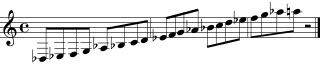
Most modern saxophones can play a low B♭ note when all the keys are closed. Some baritone saxophones can even play a low A. The highest note you can play with the keys is usually an F#. Some soprano saxophones can even play a high G. Notes higher than F# are called the "altissimo" register. These notes are harder to play and need special techniques. Modern saxophonists can play over four octaves on tenor and alto saxophones! Music for most saxophones is usually written using the treble clef.
Because all saxophones use the same finger positions for the same written notes, it's easy for a good player to switch between different sizes of saxophones. Many musicians do this!
Where Saxophones are Used
In Military Bands and Classical Music
The saxophone first became popular in military bands. Countries like France and Belgium quickly added saxophones to their bands. Most French and Belgian military bands use at least four saxophones: an E♭ baritone, B♭ tenor, E♭ alto, and B♭ soprano. These four are the most popular types. British military bands usually have at least two saxophonists, playing the alto and tenor.
Saxophones are also used in concert bands. A concert band usually has an E♭ alto saxophone, a B♭ tenor saxophone, and an E♭ baritone saxophone. Sometimes, they might have two altos, one tenor, and one baritone. A B♭ soprano saxophone is also used, often played by the first alto saxophonist.

Saxophones are also used in chamber music, which is music played by a small group of instruments. A common group is a saxophone quartet. This group usually has a B♭ soprano, E♭ alto, B♭ tenor, and E♭ baritone saxophone (often called SATB). Sometimes, a second alto sax replaces the soprano.
There are many classical pieces written for the saxophone quartet, especially by French composers who knew Adolphe Sax. The modern classical saxophone world really started with Marcel Mule in 1928. Sigurd Raschèr also helped make the saxophone popular as a solo instrument in orchestral music.
In the 20th and 21st centuries, the saxophone became more popular in symphony orchestras. It's also used in operas and choral music. Many musical theater shows also have saxophone parts, sometimes with the player switching to another woodwind or brass instrument.
In Jazz and Popular Music
Around the early 1900s, as saxophones became more common in the US, ragtime music became popular. Ragtime bands, with their exciting rhythms, helped create new dance styles. Dance bands became very popular in the 1920s. Two famous ragtime bands with saxophones were led by W. C. Handy and James R. Europe. The saxophone was also used in Vaudeville shows. These styles of music helped introduce many Americans to the saxophone.
The saxophone became a key instrument in jazz music in the early 1920s. The Fletcher Henderson Orchestra, started in 1923, used saxophones in their arrangements. Later, the Duke Ellington Orchestra and Jean Goldkette's Victor Recording Orchestra also featured jazz solos with saxophones. The saxophone's role in dance bands reached its peak with swing music in the 1930s.
Coleman Hawkins made the tenor saxophone famous as a jazz solo instrument. His powerful, rich sound influenced many swing era tenor players. Other important players like Benny Carter and Johnny Hodges influenced alto sax styles. Harry Carney made the baritone saxophone well-known with the Duke Ellington Orchestra.
As jazz changed, especially with bebop in the 1940s, the saxophone became even more important. Alto saxophonist Charlie Parker became a huge star and changed jazz forever. Bebop groups were smaller, allowing musicians more freedom to improvise long solos.
In the 1950s, many great alto players emerged, like Sonny Stitt and Cannonball Adderley. Famous tenor players included John Coltrane and Sonny Rollins. Gerry Mulligan and Pepper Adams made the baritone saxophone popular for solos. Steve Lacy and John Coltrane also helped make the soprano saxophone more popular in modern jazz. The smooth jazz musician Kenny G often plays the soprano sax.
In the 1960s, saxophonists like John Coltrane and Ornette Coleman pushed the boundaries of jazz with avant-garde styles like modal and free jazz. They explored new sounds, using techniques like "sheets of sound" and playing multiple notes at once. This led to exploring non-Western sounds, like African and Indian influences.
"Jump swing" bands in the 1940s led to rhythm and blues (R&B) music. R&B often featured strong saxophone sections with powerful, bluesy sounds. Illinois Jacquet and Louis Jordan were big influences on R&B saxophone styles. R&B saxophonists then influenced later music like rock and roll, ska, soul, and funk.
Many bands, like Chicago and Blood, Sweat, and Tears, added horn sections with saxophones to their rock and soul music. Famous rock and roll saxophonists include Bobby Keys and Clarence Clemons.
Images for kids
-
Adolphe Sax, the inventor of the saxophone
-
The saxophone was used in Gioacchino Rossini's Robert Bruce (1846)
-
Vintage silver-plated 'Pennsylvania Special' alto saxophone, made in Czechoslovakia, around 1930
-
Yamaha YAS-25 alto saxophone. Around the 1990s
-
Yanagisawa A9932J alto saxophone: has a solid silver bell and neck with solid phosphor bronze body. Manufactured in 2008
-
The lower part of a P. Mauriat alto saxophone, showing the mother of pearl key touches
-
A Yamaha baritone saxophone
See also
 In Spanish: Saxofón para niños
In Spanish: Saxofón para niños