Battle of Milliken's Bend facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Battle of Milliken's Bend |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the American Civil War | |||||||
 An illustration of the Milliken's Bend battle from the Harper's Weekly periodical, showing black U.S. soldiers battling Confederates. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Hermann Lieb | Henry E. McCulloch | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| African Brigade 23rd Iowa Infantry Regiment Two gunboats |
McCulloch's brigade | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 1,100 | 1,500 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 492 | 185 | ||||||
The Battle of Milliken's Bend happened on June 7, 1863. It was a part of the Vicksburg Campaign during the American Civil War. General Ulysses S. Grant led the Union Army. He had surrounded the important city of Vicksburg, Mississippi.
Confederate leaders thought Grant's supplies still came through Milliken's Bend in Louisiana. So, General Richard Taylor was told to stop these supplies. He hoped this would help defend Vicksburg. Taylor sent General Henry E. McCulloch with his soldiers from Texas to attack Milliken's Bend.
Milliken's Bend was defended by a group of newly recruited African American soldiers. McCulloch's attack started early on June 7. The fighting was very close. But fire from the Union gunboat USS Choctaw stopped the Confederate attack. McCulloch left after a second gunboat arrived. The plan to help Vicksburg failed. This battle was one of the first times African American soldiers fought. It showed how valuable they were to the Union Army.
Why the Battle Happened
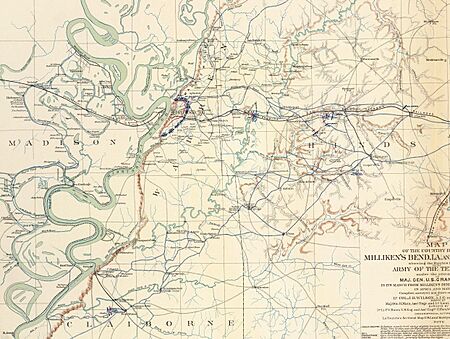
In the spring of 1863, General Ulysses S. Grant began his plan to capture Vicksburg, Mississippi. Vicksburg was a key city held by the Confederates. Grant's soldiers crossed the Mississippi River from Louisiana into Mississippi in late April. By May 18, the Union army had surrounded Vicksburg. This started the Siege of Vicksburg.
During this time, Grant had a supply base at Milliken's Bend, Louisiana. Soldiers stayed there before going to fight. Hospitals were also set up there. But during the siege, Grant opened a new supply line. The Union Navy took control of part of the Yazoo River. This new spot became Grant's main supply point. So, Milliken's Bend was still held, but it was not as important anymore.
Meanwhile, Confederate President Jefferson Davis wanted to help Vicksburg. He told General E. K. Smith to try and break the siege. Smith did not know that Grant had moved his main supply line. He still thought Milliken's Bend was very important.
General Richard Taylor was put in charge of this attack. He had about 5,000 soldiers from Texas. Taylor moved his troops to Richmond, Louisiana. But he did not think his plan would actually stop Grant's siege. On June 5, Taylor learned that Milliken's Bend was no longer a big supply point. But the attack still went ahead. The Confederates hoped to take back control of the west side of the Mississippi River. This would let them send food into Vicksburg.
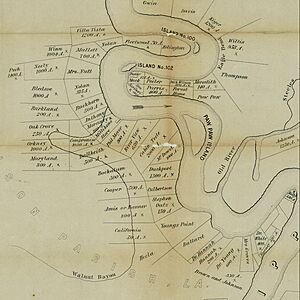
On June 6, Taylor sent some soldiers to attack Lake Providence, Louisiana. Other soldiers went to Oak Grove Plantation. From there, one group went to Young's Point. Another group, led by General Henry E. McCulloch, went to Milliken's Bend. A third group stayed at Oak Grove as a backup.
The Union camps at Milliken's Bend, Young's Point, and Lake Providence were used to train African American soldiers. Most of these soldiers were newly freed slaves. Union leaders first planned to use them for labor and guarding camps. So, they only received basic military training. At this time, white officers led these Colored Troop units.
Some people were against letting these soldiers join the Union Army. They thought the African American soldiers would not fight well. But several officers, like General John A. Logan, supported them. This helped reduce some of the resistance. The soldiers at Milliken's Bend had never used guns before joining the army. Their shooting skills were not very good during training. Colonel Hermann Lieb was in charge of the camp. His camp had African American infantry soldiers and some cavalry from Illinois.
Both Colonel Lieb and General Elias Dennis thought the Confederates might attack Milliken's Bend. Lieb's soldiers had met Confederates near Tallulah on June 6. Lieb asked for more soldiers. So, the 23rd Iowa Infantry Regiment and the ironclad USS Choctaw were sent to Milliken's Bend.
The Battle Begins
On June 7, McCulloch's 1,500 Confederate soldiers marched to Milliken's Bend at night. By 2:30 AM, they were very close. By 3:00 AM, they were just one mile from the Union position. Lieb's 1,100 Union soldiers had built a defense. They used cotton bales to make a wall on top of a levee (a raised bank).
The Union guards were quickly pushed back by the Confederates. McCulloch lined up his soldiers. The Union soldiers fired their guns. This slowed the Confederates for a moment. But the African American soldiers were not well trained. They could not reload their guns fast enough. The Confederate charge continued, and the fighting became very close. Soldiers used Bayonets (knives attached to rifles). The Union defenders were forced to fall back.
Lieb's men moved to a second levee. The Confederates charged again, shouting that they would show no mercy. During this part of the fight, not many shots were fired. Soldiers used their rifles as clubs and fought with bayonets. By 4:00 AM, it looked like the Confederates would win. But they made a mistake. They showed themselves on top of the levee.
Heavy fire from the big guns of USS Choctaw pushed McCulloch's men back. The Confederate leaders could not get their soldiers to attack the levee again. McCulloch asked for more soldiers to keep fighting. But another Union ship, the timberclad USS Lexington, arrived around 9:00 AM. McCulloch pulled his men back from the battlefield. He went back to Oak Grove Plantation because of the gunboats.
After the Battle
The Battle of Milliken's Bend was costly for the Union. They lost 492 men: 119 killed, 241 wounded, and 132 missing. Many of the missing African American soldiers were captured. They were then forced back into slavery. All but 65 of the Union losses were African American soldiers. The 9th Louisiana Infantry lost 68 percent of its strength. This was the highest percentage loss for any African American regiment during the entire war. They had 66 men killed. This was the most killed in action for any Union regiment (black or white) in one day during the Vicksburg campaign.
The Confederates lost 185 men. There were rumors that captured Union soldiers were killed. General Grant asked Taylor about these reports. Taylor said that no killings happened.
| Unit | Officers Killed | Men Killed | Officers Wounded | Men Wounded | Officers Missing | Men Missing | Totals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16th Texas Infantry Regiment | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 17th Texas Infantry Regiment | 1 | 20 | 4 | 61 | 0 | 3 | 92 |
| 19th Texas Infantry Regiment | 0 | 2 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 6 | 19 |
| 16th Texas Cavalry Regiment | 1 | 8 | 6 | 41 | 1 | 0 | 67 |
The other Confederate attacks at the Battle of Young's Point and the Battle of Lake Providence did not achieve much. The group sent to Young's Point was delayed. They did not reach the Union camp until 10:30 AM. After seeing more Union soldiers and gunboats arrive, the Confederates left without a fight.
After Milliken's Bend, the Confederates went back to Monroe, Louisiana. Taylor went to Alexandria, Louisiana. He focused more on Union forces in New Orleans, Louisiana, than Vicksburg. The Confederates in the Trans-Mississippi Department could no longer affect the Siege of Vicksburg. The city surrendered on July 4. The position at Milliken's Bend became unimportant soon after the battle. The soldiers and supplies there were moved to Young's Point.
Parts of the battle site have been destroyed by changes in the Mississippi River. A study in 2010 found that about 2,000 acres of the battlefield could be listed on the National Register of Historic Places. At that time, there was no public information about the battle at the site. As of March 2021, a plaque for Milliken's Bend is near Richmond. Exhibits about the battle are at Vicksburg National Military Park. There is also an exhibit at Grant's Canal in Louisiana.
Why This Battle Was Important
Leaders on both sides noticed how well the African American troops fought at Milliken's Bend. Charles Dana, a Union official, said the battle convinced many in the Union Army to support African American soldiers. General Dennis said "it is impossible for men to show greater gallantry than the Negro troops in this fight."
Grant said the battle was the first big fight where the Colored Troops saw combat. He called their actions "most gallant." He also said that "with good officers they will make good troops." He later praised them in his book. He wrote, "These men were very raw, having all been enlisted since the beginning of the siege, but they behaved well."
Confederate leader McCulloch later reported that the white Union troops had run away. But the Colored Troops fought with "considerable obstinacy." One historian wrote in 1960 that the fighting at Milliken's Bend led to "the acceptance of the Negro as a soldier." This was important for "his acceptance as a man."
U.S. Secretary of War Edwin M. Stanton also praised the black U.S. soldiers. He said their good performance proved wrong those who were against their service. He wrote in a letter to Abraham Lincoln on December 5, 1863:
{{{1}}}