Chernyakhov culture facts for kids
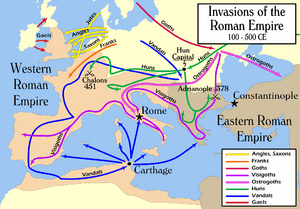
Quick facts for kids Invasions of the Roman Empire |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Time | c. 300–800 or later |
| Place | Europe and the Mediterranean region |
| Event | Tribes invading the Roman Empire |
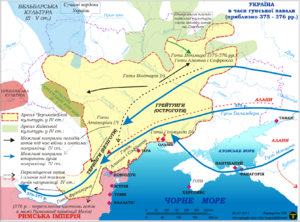
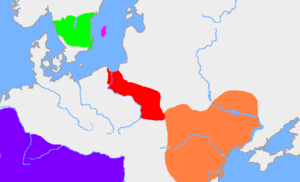
The Chernyakhov culture was an ancient group of people who lived in Eastern Europe. They existed between the 2nd and 5th centuries CE. This culture covered a large area, including parts of modern-day Ukraine, Romania, Moldova, and Belarus.
Many experts believe the Chernyakhov culture was a mix of different groups. These included the Geto-Dacian, Sarmatian, and Gothic peoples. This mix created a unique way of life.
The Chernyakhov culture took the place of an older culture called the Zarubintsy culture. Both were discovered by an archaeologist named Vikentiy Khvoyka. He found many ancient sites near Kyiv. The Chernyakhov culture eventually faded away when the Huns arrived. It was then replaced by other cultures.
Scientists have also noticed similarities between the Chernyakhov culture and the Wielbark culture. The Wielbark culture was found closer to the Baltic Sea.
Contents
Where was the Chernyakhov Culture Located?
The Chernyakhov culture was found in areas that are now Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania. The name Chernyakhov comes from a site near Kyiv in Ukraine. You might see it spelled in different ways, like Cherniakhiv (Ukrainian) or Czerniachów (Polish).
The culture is also sometimes called the Sântana de Mureș—Chernyakhov culture. This second name comes from a cemetery site in Transylvania, Romania. Different historians used different names for the culture in the past.
Who were the Chernyakhov People?
For a long time, historians debated where the Chernyakhov people came from. Some thought they were early Slavic people. Others, especially German and Polish historians, believed they were Goths.
Today, most experts agree that the Chernyakhov culture was a mix of many different groups. These were mainly people who already lived in the region. This included the Sarmatians and the Getae-Dacians. Some even think the Getae-Dacians played a big role in starting this culture.
What Did We Find from the Chernyakhov Culture?
Archaeologists have found many interesting things from the Chernyakhov culture. These finds help us understand how they lived.
How Did They Bury Their Dead?
The Chernyakhov people used two main ways to bury their dead:
- Inhumation: This means burying the body whole.
- Cremation: This means burning the body.
They often buried items with the dead, like pottery, iron tools, and bone combs. They also included personal ornaments. Over time, fewer items were buried with the dead. Bodies buried whole were usually placed with their heads facing north.
Grave gifts often included brooches, belt buckles, and glass drinking cups. Women's burials were very similar to those in the Wielbark culture. Women were often buried with two brooches, one on each shoulder. Unlike some other cultures, Chernyakhov burials usually did not include weapons. This was similar to the Wielbark culture.
What Kind of Pottery Did They Make?
Most of their pottery was made locally. They used both a potter's wheel and their hands. Wheel-made pottery was more common and made from finer clay. It looked similar to older Sarmatian styles, but also had influences from Roman and La Tene designs.
Hand-made pottery had more different shapes. It was sometimes decorated with carved lines. Archaeologists also found Roman amphorae (large jars). This shows that the Chernyakhov people traded with the Roman Empire. Some unique hand-made pottery, typical of western Germanic groups, also suggests that Germanic people were present.
How Did They Live and Work?
The Chernyakhov people mostly stayed in one place. They were farmers who grew grains like wheat, barley, and millet. Archaeologists have found many farming tools, such as ploughshares, sickles, and scythes.
Raising cattle was their main way of keeping animals. Horses were mostly kept in the open steppe areas. Metalworking was also very common. Local craftspeople made most of their tools and objects. There is also some proof that certain people specialized in making specific items.
Why Did the Chernyakhov Culture Decline?
The Chernyakhov culture ended around the 5th century. Many historians believe this happened because the Huns arrived. It's now thought that the culture didn't just disappear because people moved away. Instead, the political system that held the culture together broke down.
Some of the local ways of life continued even after the Goths, who were a powerful group, left the area. This change is linked to the rise and spread of the early Slavs.
Ideas About How the Culture Spread
Historians have different ideas about how the Chernyakhov culture developed and spread.
Migration Theory
Some historians, like Peter Heather, believe the Goths played a big role in the Chernyakhov culture. They think the Goths moved from an area called Gothiscandza to Oium, as described in old writings. They also point to the Wielbark culture as a key influence. The Wielbark culture started near the Baltic Sea and spread south.
Similar items, like pottery and brooches, found in both the Wielbark and Chernyakhov areas suggest a connection. Heather believes that a large number of Goths and other Germanic groups moved into the Chernyakhov region. This movement helped create the Chernyakhov culture. He thinks it wasn't one big move, but many smaller groups moving over time.
Diffusion Theory
Other historians, like Guy Halsall, disagree with some of these ideas. They say there isn't a clear timeline showing the Wielbark culture directly leading to the Chernyakhov culture. They also note that the two regions didn't overlap much.
Michael Kulikowski also questions the strong link to the Wielbark culture. He argues that the Chernyakhov culture could have developed from local groups already living there. Or it could have been a mix of cultures from the Przeworsk and steppe regions. He even suggests that the Goths as a distinct group didn't exist before the 3rd century. He believes the "Goths" formed in the region itself, much like other groups like the Alemanni.
Some influences from the Przeworsk and Zarubinec cultures are also seen. The Zarubinec culture has been linked to early Slavic people.
What Do Genetics Tell Us?
In 2019, a study looked at the DNA of ancient people, including some from the Chernyakhov culture. Three individuals from the Chernyakhov culture were studied. Their DNA showed they were similar to modern Europeans. They had a lot of ancestry from "Western Steppe Herders" and also from "Central European Middle Neolithic" farmers.
The study suggests that the Chernyakhov culture was a mix of different ethnic groups. The DNA samples from the study seemed to represent the Gothic part of this mix.
See also
- Oium
- Carpathian Tumuli culture
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |