Cricket facts for kids


Cricket is an exciting sport played between two teams. Each team has eleven players. One team tries to score points, called runs, by hitting a ball. The other team tries to stop them from scoring.
Players score runs by hitting the ball and running between two sets of wooden sticks called wickets. They can also score by hitting the ball to or over the edge of the playing area, called the boundary. The team that is fielding tries to get the batting players out by hitting the wickets with the ball.
The wickets are three small wooden posts with two tiny sticks, called bails, balanced on top. They are placed at each end of a 22-yard long strip of short grass called the pitch. The pitch is in the middle of a much larger oval-shaped grassy area, known as the area of play.
When a player gets out, a teammate replaces them. A team keeps batting until ten of its players are out. Then, the other team gets a turn to bat and score runs. In some shorter games, a team might stop batting after a certain number of balls have been thrown. The team with the most runs at the end of the game wins!
Cricket started in England in the 1500s. The first clear mention of the game was in a court case in 1598. A man named John Derrick said he played cricket as a student 50 years earlier. Over time, the game spread to countries that were part of the British Empire in the 1800s and 1900s.
Today, cricket is very popular in many countries. These include England, Australia, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, South Africa, New Zealand, and the West Indies. It's also played in countries like Afghanistan, Ireland, Kenya, Scotland, the Netherlands, and Zimbabwe.
Contents
How Do You Play Cricket?
Cricket involves two teams. The team that is bowling has eleven players on the field. The team that is batting has two players on the field at a time, one at each end of the pitch. The rest of the batting team waits off the field.
Runs are scored after a player hits the ball. Most runs are made by hitting the ball and running, or by hitting the ball to or over the boundary.
Understanding the Bowler and Fielders
The captain of the bowling team chooses a player to be the bowler. The other players are called fielders.
- The bowler tries to aim the ball at the wicket. The wicket is made of three wooden sticks, called stumps, with two small sticks, called bails, on top.
- One fielder, called the wicket-keeper, stands behind the wicket to catch the ball if the bowler misses.
- Other fielders chase the ball after the batsman hits it.
The bowler runs towards their wicket and bowls the ball towards the batsman at the other wicket.
- A bowler does not throw the ball. They bowl it overarm with a straight arm. If their arm bends too much, the other team gets one run, and the bowler has to bowl again.
- Six balls bowled by one bowler is called an over. After six balls, a different player becomes the bowler for the next over. The same bowler cannot bowl two overs in a row.
How Does a Batsman Score Runs?
The batsman tries to protect their wicket from being hit by the ball using a bat. When they hit the ball, they can run towards the other wicket.
- To score a run:
- Both batsmen must run from their wicket to the other wicket before they can be run out.
- Batsmen can run between the wickets as many times as they want. Each completed run scores one point.
- If the ball leaves the field after being hit without bouncing, six runs are scored.
- If the ball rolls or bounces out of the field, whether the batter hit it or not, it counts as four runs.
How Do Batsmen Get Out?
There are several ways a batsman can get out. Here are the most common ones:
- The batsman misses the ball, and it hits their wicket: This is called bowled out.
- The ball hits the batsman's body when it would have hit the wicket otherwise: This is called LBW (leg before wicket). This rule can be a bit tricky!
- A fielder catches the ball after the batsman hits it, but before it bounces or leaves the field: This is called caught.
- While the batsmen are running, a fielder can throw the ball at a wicket. If the batsmen don't finish their run in time and the ball hits the wicket, the batsman closer to that wicket is out. This is called run out.
When a batsman gets out, another player from their team comes onto the field to bat. A team's turn to bat, called an innings, ends when ten batsmen are out. After this, the team that was fielding gets their turn to bat. They need to score more runs than the first team to win. If they do, they win! If they don't, the other team wins.
In shorter games, each team bats once, and there's a limit to how many overs they can bat. In longer games, each team bats twice, and there's no specific limit to the number of overs.
Where Is Cricket Played Around the World?
Cricket is popular in many countries, especially those that are part of the Commonwealth.
The top countries where cricket is most popular play international matches that can last up to five days. These are called Test matches. The countries that play Test matches are England, Australia, West Indies, South Africa, New Zealand, India, Bangladesh, Zimbabwe, Ireland, Afghanistan, and Sri Lanka. The West Indies team is made up of players from several Caribbean countries playing together. Ireland and Afghanistan are the newest teams to play Test cricket.
Cricket is also played in Kenya, Canada, Bermuda, Scotland, Holland, and Namibia. Their national teams can play one-day international matches, but not Test matches.
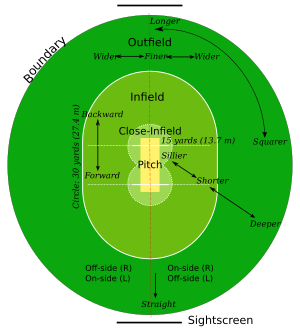
The Cricket Field
A cricket field is a large, grassy area where the game is played. It's usually circular or oval-shaped. There are no exact fixed sizes for a cricket field, but its width usually ranges from about 450 feet (137 meters) to 500 feet (100 meters).
Different Types of Cricket Games
Cricket is played in different formats, each with its own rules and length.
Test Matches: The Longest Game
Test matches are the highest level of international cricket played between countries. They are designed to test players' skills over a long period. The International Cricket Council (ICC) decides which countries can play Test matches.
Test matches can last for up to five days! This is why some people call it "5-day cricket." Even after five days, a match can still end in a draw. It's the longest form of cricket.
Here are the Test Playing Nations, listed by when they first started playing:
- England
- Australia
- South Africa
- West Indies
- New Zealand
- India
- Pakistan
- Sri Lanka
- Zimbabwe
- Bangladesh
- Afghanistan
- Ireland
Limited Overs Cricket: Faster Games
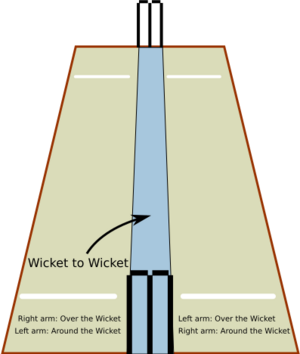
In these games, the length is set by the number of overs (sets of six balls). Each team bats only once. If rain stops play, a special calculation called the 'Duckworth–Lewis method' is used to figure out the target score for the team batting second.
One Day Internationals (ODI50)
ODIs are usually limited to 50 overs for each team's batting turn. Each bowler can bowl a maximum of 10 overs.
- The highest team score ever in an ODI is England's 481 runs against Australia in 2018.
- The highest individual score is 264 runs by Rohit Sharma for India against Sri Lanka.
Twenty20 Cricket (T20 Cricket)
Twenty20 cricket is a much faster game. Each team bats for only 20 overs. Each bowler can bowl a maximum of 4 overs, unlike the 10 overs in an ODI.
- The highest team score in a T20 match is 263 runs by Royal Challengers Bangalore (RCB) in 2013.
- The highest individual score is 175 runs by Chris Gayle for RCB in the same match.
Understanding Cricket Averages
In cricket, two special types of averages help measure how good a player is:
- A batsman's batting average shows how many runs they score on average each time they get out. You calculate it by dividing their total runs by the number of times they were out. A good batsman has a high batting average.
- The highest T20 batting average for a player with at least 20 innings is 70.66 by Chris Harris.
- A bowler's bowling average shows how many runs are scored against them for each wicket they take. You calculate it by dividing the runs scored while they were bowling by the number of batsmen they got out. A good bowler has a low bowling average.
- The lowest T20 bowling average for a bowler who has bowled at least 500 balls is 13.80 by Mushtaq Ahmed.
There are different averages for each type of cricket game (Test, ODI, T20).
Related Pages
Images for kids
-
A painting by Francis Cotes called The Young Cricketer, from 1768.
-
The first known photo of a cricket match, taken on July 25, 1857, by Roger Fenton.
-
English cricketer W. G. Grace in 1883. His gear was similar to what players use today.
-
Glenn McGrath of Australia holds the world record for most wickets in the Cricket World Cup.
-
Sachin Tendulkar is the only player to score one hundred international centuries.
-
Mithali Raj of India is the highest run scorer in women's international cricket.
-
A Test match between South Africa and England in January 2005. The umpires wear black trousers.
-
Yorkshire County Cricket Club in 1895. They first won the County Championship in 1893.
-
Tom Wills, a cricketer and co-founder of Australian football.
See also
 In Spanish: Críquet para niños
In Spanish: Críquet para niños



















