Extraversion and introversion facts for kids
Have you ever wondered why some people love being the center of attention, while others prefer quiet time alone? It often comes down to two main personality traits: extraversion (also spelled extroversion) and introversion. These ideas are a big part of how we understand human personality.
The terms introversion and extraversion were first used in psychology by a man named Carl Jung. Extraversion usually means being outgoing, talkative, and full of energy. Introversion, on the other hand, means being more thoughtful and reserved. Jung said that introverts focus their energy inward, on their own thoughts and feelings. Extraverts focus their energy outward, on the world around them and other people.
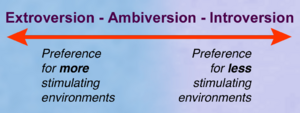
Most people see extraversion and introversion as two ends of a single line. If you are high in one, you are usually lower in the other. However, Jung thought that everyone has both an extraverted and an introverted side, but one side is usually stronger. Many important personality models include these ideas, like the Big Five personality traits and the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator.
Contents
History of the Ideas
In 1909, a Swiss psychiatrist named Carl Jung first used the word introverted in a speech. He later wrote about it in detail in his 1921 book, Psychologische Typen, which was translated into English as Personality Types.
Jung described introverts as people who often keep to themselves. They might not enjoy big crowds and can feel lost in large groups. He said they prefer to do things their own way and don't like being told what to do by others. Introverts might seem a bit awkward or quiet to some people.
For an introvert, their own thoughts and feelings are a safe and special place. They enjoy their own company the most. They do their best work when they can use their own ideas and work at their own pace. Big crowds or popular opinions don't usually change their minds. They only truly open up to others when they feel safe and trust them. This is why introverts often have a small number of close friends.
Different Types of Personalities
William McDougall, another thinker, said that introverts tend to think a lot before they act or speak. Extraverts, he believed, let their energy flow out freely into actions and words.
Extraversion
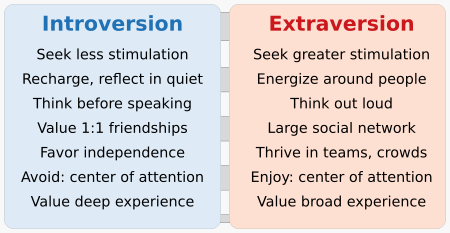
Extraverts get their energy and excitement from the outside world. They love being around people and tend to be enthusiastic, talkative, confident, and very social. Extraverts feel energized when they are with others. They enjoy activities that involve many people, like parties, community events, or group projects. They also tend to work well in teams. An extraverted person usually loves spending time with friends and finds less joy in being alone. They can get bored easily when by themselves.
Introversion
Introverts get their energy and satisfaction from their own thoughts and inner world. They are often seen as more reserved or thoughtful. Some people think introverts use up their energy when they are around others and recharge when they are alone. This is similar to Jung's idea. Introverts often enjoy quiet activities like reading, writing, or thinking. They usually prefer spending time alone and find large groups of people less rewarding.
Introverts can easily feel overwhelmed by too much noise or social activity. They often prefer a calm, less stimulating environment. They like to focus on one thing at a time and often observe a situation carefully before joining in. This is especially true for children and teenagers. They also tend to think carefully before they speak.
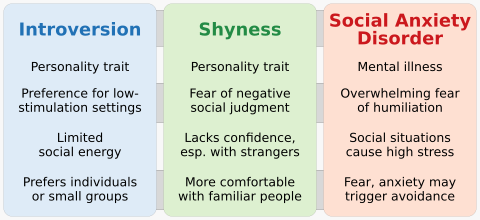
It's a common mistake to confuse introversion with shyness. Introversion is a choice or preference for certain activities. Shyness, however, comes from feeling worried or afraid of what others might think. Introverts prefer quiet activities, but they don't necessarily fear social situations like shy people do.
Susan Cain, who wrote the book Quiet: The Power of Introverts in a World That Can't Stop Talking, says that modern Western society often misunderstands introverts. She believes this leads to a waste of their talents and happiness. Cain points out that society often favors extraverted behavior, making introversion seem like a "problem." But Cain says introversion is a valuable trait. Both introverts and extraverts make important contributions to society. Famous introverts include J. K. Rowling, Isaac Newton, Albert Einstein, and Steven Spielberg.
Ambiversion
Most modern ideas about personality see extraversion-introversion as a continuous scale. Some people are strongly extraverted, some are strongly introverted, and many fall somewhere in the middle. People who are more or less in the middle are called ambiverts. They can show qualities of both introverts and extraverts, depending on the situation.
How Common Are They?
Susan Cain's research suggests that about 33% to 50% of people in America are introverts. Some jobs seem to attract more introverts. For example, a survey based on the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator found that 60% of lawyers and 90% of intellectual property lawyers are introverts.
How We Measure These Traits
We usually figure out if someone is more extraverted or introverted by asking them questions about themselves. Sometimes, friends or family can also give their opinions. These questions can be single words, like "outgoing" or "quiet," or longer statements.
For example, a person might be asked how much they agree with statements like, "I talk to a lot of different people at parties" or "I often feel uncomfortable around others." These tests help psychologists understand where someone falls on the extraversion-introversion scale.
Eysenck's Theory
Hans Eysenck was a psychologist who also described extraversion-introversion. He believed that these differences in behavior come from how our brains work. Eysenck thought that extraverts naturally have lower levels of brain activity, so they look for excitement and social interaction to raise their energy. Introverts, on the other hand, have higher natural brain activity, so they avoid too much social stimulation to keep their energy from getting too high.
Eysenck saw extraversion as one of three main personality traits, along with psychoticism and neuroticism. He thought extraversion was a mix of being impulsive and sociable. He later added other traits like being lively and excitable.

Biological Factors
Scientists often debate how much of our personality comes from our genes (nature) and how much comes from our experiences (nurture). Studies on twins suggest that about 39% to 58% of extraversion-introversion can be linked to our genes. This means that our family environment might not be as important as our unique life experiences in shaping these traits.
Some research suggests that extraverts are more sensitive to things that might give them a reward or make them feel good. This could explain why extraverts often feel more positive emotions.
Other studies have looked at blood flow in the brain. Introverts tend to have more blood flow in areas of the brain that handle internal thinking, like planning and solving problems. Extraverts have more blood flow in areas involved in sensory experiences and emotions. This research shows that introversion-extraversion is connected to how different brains work.
How People Behave
Extraverts and introverts often show different behaviors. For example, extraverts might wear more decorative clothes, while introverts might prefer practical and comfortable clothes. Extraverts often like upbeat and energetic music more than introverts.
Personality can also affect how people set up their workspaces. Extraverts tend to decorate their offices more, keep their doors open, and have extra chairs to encourage people to visit. Introverts, however, might decorate less and arrange their space to discourage too much social interaction.
Despite these differences, studies show that extraverts and introverts often act in similar ways. For example, both extraverts and introverts behave in extraverted ways sometimes, and in introverted ways at other times. The main difference is that extraverts simply act more extraverted more often. This suggests that being an "extravert" is more about what you "do" than what you "are."
People can also change their behavior depending on the situation. For example, an introvert might act more extraverted if it's important for a school project or a job. This idea is called "free traits," where people can choose to act in ways that are not their usual "first nature" to achieve important goals or even to feel happier.
Why This Matters
Understanding introversion and extraversion can help us accept ourselves and understand others better. For instance, an extravert can understand why their introverted friend needs quiet time alone. An introvert can also understand why their extraverted friend needs to socialize a lot.
Researchers have found that extraverted people often report being happier than introverts. Studies have also shown that even if you're an introvert, acting more extraverted can make you feel more positive emotions.
This doesn't mean introverts are unhappy. Extraverts just tend to feel more strong positive emotions, while introverts might feel more calm or neutral. This could be because Western culture often prefers extraverted behavior, making introversion seem less desirable. Extraverts also tend to report higher self-esteem. However, some people think these results might be biased because of how the "happiness" questions are asked.
While extraversion is often seen as good in Western culture, it's not always an advantage. For example, extraverted young people might be more likely to engage in risky or delinquent behavior. On the other hand, introversion is linked to positive traits like intelligence and being "gifted." Introverts often do very well in school, while extraverts might find academic settings boring.
Understanding these traits can also help teachers. They can encourage introverted children to speak up more in class and understand that extraverted children might get restless during long periods of quiet study.
Where People Live Matters
Some people say that America is an "extraverted society" that rewards outgoing behavior. This is because American culture often values external personality. In other cultures, like Japan, China, or places with Orthodox Christianity or Buddhism, introversion is often valued more. These cultural differences can affect how happy people are, as people tend to be happier if their personality matches their culture's values.
Researchers have also found that people living on islands tend to be more introverted than those on the mainland. Also, people whose families have lived on an island for many generations are often more introverted than newer arrivals.
In the United States, people in states like North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Illinois tend to be more extraverted than the national average. Utah, Florida, and Georgia also score high in extraversion. The most introverted states include Maryland, New Hampshire, Alaska, Washington, Oregon, and Vermont. People in Idaho, Montana, and Wyoming are also relatively introverted.
Happiness and Personality
Extraverts are often found to have more positive feelings than introverts. However, this is mostly true for active, excited types of positive feelings. There isn't a strong link between extraversion and calm positive feelings like contentment or peacefulness.
Many studies show that personality, especially extraversion and emotional stability (not being too neurotic), is the best way to predict how happy someone will be. For example, studies have found that extraversion is strongly linked to positive feelings.
Other Factors Affecting Happiness
While extraversion and neuroticism seem to have the biggest impact on happiness, other personality traits also play a role. For example, being conscientious (organized and careful) and agreeable (kind and cooperative) can also be linked to happiness.
Also, how you define "happiness" can change the results. Some studies show extraversion is a key factor, while others find that conscientiousness or neuroticism are more important.
Other things that are not personality traits can also affect happiness. For example, making progress toward your goals or having conflicts between your goals can affect how you feel. In some cultures, having a clear sense of who you are and acting in a way that matches your self-image is also linked to well-being. So, focusing only on extraversion might not give us the full picture of happiness.
Culture and Happiness
Your culture can also affect your happiness. The overall level of happiness and how people express it can be different from one culture to another. For example, studies have shown differences in average life satisfaction between countries and even between different ethnic groups within a country.
Scientists think that things like a country's income levels, how people see themselves, and how they approach or avoid situations can explain these differences. All these findings suggest that while extraversion-introversion is strongly linked to happiness, it's not the only thing that predicts how happy someone will be. Many other factors need to be considered.
See also
 In Spanish: Introversión y extraversión para niños
In Spanish: Introversión y extraversión para niños
- Analytical psychology
- Alternative five model of personality
- Big Five personality traits
- Personality
- Reinforcement sensitivity theory
- Seattle Freeze
- Trait theory