Geography of Equatorial Guinea facts for kids
  |
|
| Continent | Africa |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 2°00′N 10°00′E / 2.000°N 10.000°E |
| Area | Ranked 141st |
| • Total | 28,051 km2 (10,831 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 296 km (184 mi) |
| Borders | 539 km |
| Highest point | Pico Basile, 3,008 m |
| Lowest point | Atlantic Ocean, 0 m |
| Longest river | Benito River |
| Climate | Tropical |
| Natural resources | petroleum, timber, small unexploited deposits of gold, manganese, uranium |
| Environmental issues | drinking water, desertification |
| Exclusive economic zone | 303,509 km2 (117,185 sq mi) |
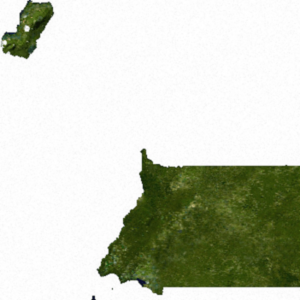
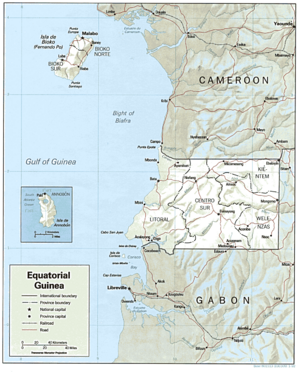
The Republic of Equatorial Guinea is a country located in west central Africa. It's made up of a part on the mainland and several islands. The country's total land area is about 28,051 square kilometers (10,831 square miles). It also has a large area of ocean that it controls, called an Exclusive Economic Zone, which is about 303,509 square kilometers (117,185 square miles).
The largest island, Bioko Island, is about 40 kilometers (25 miles) away from Cameroon. Another island, Annobón Island, is much farther, about 595 kilometers (370 miles) southwest of Bioko. The main part of the country, called Río Muni, is on the mainland between Cameroon and Gabon. Río Muni also includes smaller islands like Corisco, Elobey Grande, and Elobey Chico.
Bioko Island, once called Fernando Po, is the biggest island in the Gulf of Guinea. It covers about 2,017 square kilometers (779 square miles). The island looks a bit like a boot, with two large mountains that are actually old volcanoes. A valley cuts across the middle of the island. The coastline is steep in the south but flatter in the north. There are good harbors at Malabo and Luba, and some nice beaches too.
On the mainland, Río Muni covers about 26,003 square kilometers (10,040 square miles). Near the coast, the land is flat, but as you go inland, you find valleys and low hills. These hills are part of the Crystal Mountains. The Rio Benito (also called Mbini) divides Río Muni in half. You can only travel by boat on a small part of this river near the ocean. Temperatures and humidity in Río Muni are usually lower than on Bioko Island.
Annobon Island is a small volcanic island, only about 18 square kilometers (7 square miles). It was discovered on New Year's Day in 1472, which is how it got its name ("Annobon" means "New Year"). Most of its coastline is steep, but there's a small lake inside its main volcanic cone. About 1,900 people live there, mostly fishermen who catch tuna and whales using traditional methods. The island has a tropical climate with lots of rain, high humidity, and strong winds during certain seasons.
Equatorial Guinea is located in central Africa. It borders the Bight of Biafra, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is positioned between the countries of Cameroon and Gabon.
Borders and Ocean Claims
Equatorial Guinea shares a land border of 539 kilometers (335 miles) with its neighbors.
- It borders Cameroon for 189 kilometers (117 miles) to the north.
- It borders Gabon for 350 kilometers (217 miles) to the east and south.
The country also has claims over the ocean:
- Its territorial sea extends 12 nautical miles (22 kilometers or 14 miles) from its coast.
- Its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) covers 303,509 square kilometers (117,185 square miles). This zone extends 200 nautical miles (370 kilometers or 230 miles) from the coast, giving the country special rights to explore and use marine resources.
Climate
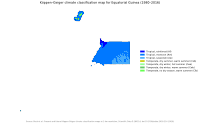
The climate in both the mainland and the islands is tropical. This means it has high temperatures, lots of rain, and many cloudy days for most of the year. How close a place is to the sea and its altitude can cause small differences in the weather.
On the mainland, the wet seasons are from February to June and from September to December. Coastal areas get more rain than inland areas. For example, in Bata, the rainiest months are September, October, and November, with over 94 inches (2,400 mm) of rain each year. In some southern coastal areas, it can even reach 180 inches (4,600 mm). However, inland places like Mikomeseng only get about 58 inches (1,500 mm) of rain. The average yearly temperature is around 26°C (79°F) and stays pretty much the same all year. The air is also very humid.
Bioko Island has a challenging climate. The "dry season" is from November to March, but it's still quite wet. The rest of the year is very rainy. The average temperature is about 25°C (77°F) and doesn't change much. Afternoon temperatures can reach the low 30s °C (high 80s °F) and only drop to about 21°C (70°F) at night. The sky is often cloudy. The southern part of the island gets extreme rainfall, with monsoon winds bringing about 450 inches (11,000 mm) of rain each year around San Antonio de Ureca.
| Climate data for Malabo | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 34.2 (93.6) |
35.3 (95.5) |
34.5 (94.1) |
36.5 (97.7) |
34.0 (93.2) |
32.5 (90.5) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.0 (89.6) |
32.5 (90.5) |
32.5 (90.5) |
32.5 (90.5) |
33.5 (92.3) |
36.5 (97.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 31.1 (88.0) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.3 (88.3) |
31.3 (88.3) |
30.5 (86.9) |
29.5 (85.1) |
28.4 (83.1) |
28.0 (82.4) |
28.1 (82.6) |
28.8 (83.8) |
29.8 (85.6) |
30.8 (87.4) |
30.0 (86.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.9 (80.4) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.6 (81.7) |
27.2 (81.0) |
26.7 (80.1) |
25.9 (78.6) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.0 (77.0) |
25.1 (77.2) |
25.5 (77.9) |
26.1 (79.0) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.3 (79.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23.0 (73.4) |
23.9 (75.0) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.3 (73.9) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.9 (73.2) |
23.0 (73.4) |
22.7 (72.9) |
23.3 (73.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 17.0 (62.6) |
16.5 (61.7) |
15.5 (59.9) |
16.5 (61.7) |
15.0 (59.0) |
18.0 (64.4) |
17.1 (62.8) |
15.0 (59.0) |
18.5 (65.3) |
17.6 (63.7) |
19.0 (66.2) |
17.5 (63.5) |
15.0 (59.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 28.9 (1.14) |
70.6 (2.78) |
102.7 (4.04) |
155.7 (6.13) |
227.1 (8.94) |
260.8 (10.27) |
202.0 (7.95) |
177.1 (6.97) |
250.1 (9.85) |
254.3 (10.01) |
100.3 (3.95) |
39.6 (1.56) |
1,869.1 (73.59) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 3.5 | 4.6 | 9.8 | 12.0 | 17.2 | 19.0 | 17.5 | 14.8 | 20.6 | 19.5 | 10.3 | 4.0 | 152.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 83 | 83 | 84 | 84 | 87 | 89 | 90 | 89 | 91 | 90 | 88 | 84 | 87 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 120.9 | 121.5 | 108.5 | 114.0 | 99.2 | 66.0 | 43.4 | 52.7 | 48.0 | 71.3 | 87.0 | 117.8 | 1,050.3 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 3.9 | 4.3 | 3.5 | 3.8 | 3.2 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 2.9 | 3.8 | 2.9 |
| Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Bata (1956–1965) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 33.5 (92.3) |
35.6 (96.1) |
34.1 (93.4) |
34.1 (93.4) |
33.2 (91.8) |
32.8 (91.0) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.5 (90.5) |
32.0 (89.6) |
32.4 (90.3) |
33.0 (91.4) |
35.6 (96.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30.5 (86.9) |
31.1 (88.0) |
31.3 (88.3) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.7 (87.3) |
29.7 (85.5) |
28.8 (83.8) |
28.9 (84.0) |
29.1 (84.4) |
29.1 (84.4) |
29.6 (85.3) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.0 (86.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 25.6 (78.1) |
25.8 (78.4) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.0 (77.0) |
24.1 (75.4) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.6 (76.3) |
24.8 (76.6) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.0 (77.0) |
25.1 (77.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 20.7 (69.3) |
20.4 (68.7) |
20.1 (68.2) |
20.1 (68.2) |
20.6 (69.1) |
20.2 (68.4) |
19.4 (66.9) |
19.6 (67.3) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
20.8 (69.4) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.2 (68.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 15.3 (59.5) |
13.7 (56.7) |
14.5 (58.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
12.5 (54.5) |
15.5 (59.9) |
12.5 (54.5) |
14.2 (57.6) |
15.6 (60.1) |
15.5 (59.9) |
14.5 (58.1) |
14.5 (58.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 116 (4.6) |
102 (4.0) |
205 (8.1) |
292 (11.5) |
285 (11.2) |
90 (3.5) |
25 (1.0) |
26 (1.0) |
221 (8.7) |
457 (18.0) |
306 (12.0) |
109 (4.3) |
2,234 (87.9) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 9 | 8 | 14 | 16 | 17 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 16 | 24 | 18 | 10 | 147 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 201.5 | 192.1 | 173.6 | 177.0 | 189.1 | 147.0 | 142.6 | 142.6 | 114.0 | 114.7 | 141.0 | 186.0 | 1,921.2 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 6.5 | 6.8 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 6.1 | 4.9 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 4.7 | 6.0 | 5.3 |
| Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst | |||||||||||||
Land and Environment
| Land Use (2012 est.) | |
|---|---|
| Arable land: | 4.28% |
| Permanent crops: | 2.14% |
| Other: | 93.58% |
The land in Equatorial Guinea changes from flat coastal plains to hills further inland. The islands are formed by volcanoes.
The country has about 26 cubic kilometers of fresh water available each year (as of 2011).
Natural dangers in Equatorial Guinea include strong windstorms and sudden floods.
Some environmental problems the country faces are that tap water is not safe to drink, and there is a lot of deforestation (trees being cut down).
Equatorial Guinea is part of many international agreements to protect the environment. These include agreements on:
- Biodiversity (protecting different types of plants and animals)
- Desertification (stopping land from becoming desert)
- Endangered Species (protecting animals and plants that are at risk)
- Hazardous Wastes (managing dangerous trash)
- Law of the Sea (rules for using the ocean)
- Marine Dumping (stopping pollution in the ocean)
- Ozone Layer Protection (protecting the Earth's ozone layer)
- Ship Pollution (reducing pollution from ships)
- Wetlands (protecting important wet areas)
It's interesting to note that the islands and the mainland parts of Equatorial Guinea are quite far apart from each other.
Extreme Points
Here are the most extreme points of Equatorial Guinea:
- Northernmost point: Punta Europa, located on Bioko Island.
- Easternmost point: The entire eastern border with Gabon, which is a straight line.
- Southernmost point: A Dyibó, found on Annobón Island.
- Westernmost point: Punta Dyiscoj, also on Annobón Island.
See also
 In Spanish: Geografía de Guinea Ecuatorial para niños
In Spanish: Geografía de Guinea Ecuatorial para niños