Graphic design facts for kids
Graphic design is a cool way to communicate using pictures and words. It's like telling a story or sharing information without just using spoken words. Graphic designers arrange images, text, and colors to create messages that grab your attention. You see graphic design everywhere, from the books you read to the websites you visit and even the signs on the road!
Graphic design can be found in many places. This includes things printed on paper, videos, product labels, and even websites. It uses many different skills and techniques to make sure the right information gets across clearly. It's a mix of art and how people understand messages.
Contents
What is Graphic Design Used For?
Graphic design has tons of uses! Think about road signs that tell you where to go, or instruction manuals that show you how to use something. It's also super important for making products look good. This includes things like company logos, the colors a brand uses, packaging, labelling, and even the text on a product.
From science magazines to news reports, graphic design makes facts and opinions easier to understand. It helps present visual information in a clear way. This is sometimes called information design. With the internet, designers who know about interactive tools are often used to help explain news stories. Information design can also involve using computer programs to turn data into cool visuals, like infographics.
Skills You Need in Graphic Design
A graphic design project often involves taking existing text, decorations, and pictures and making them look great together.
One way to think about design is like a conversation. It focuses on how messages are sent and received. Another way is to see messages as a collection of signs that create meaning when people interact with them.
What is Typography?
Typography is all about working with text. It includes designing new letter styles (called glyphs), changing existing ones, and arranging text on a page. When you arrange text, you choose the font style, how big the letters are, the space between all characters, the space between two specific characters (kerning), and the space between lines.
Many people work with typography, including typesetters, graphic artists, and art directors. Before computers, typography was a very special job. Different fonts can make you think of different things. For example, a font called "1942 Report" looks like text from an old typewriter.
What is Page Layout?
Page layout is about how you arrange everything on a page. This includes where pictures go, how text is placed, and the overall style. Page design has always been important for printed materials like books and magazines. Now, it's also key for digital displays like web pages. The elements usually include text, images, and sometimes special graphics for things that aren't printed with ink, like cutting shapes or raising parts of the paper.
Using Grids in Design
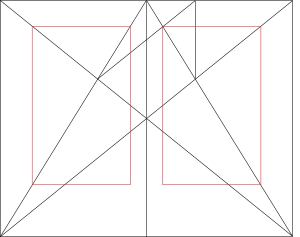
A grid is like an invisible guide that helps you arrange things on a page. It makes it easier for people to understand what they're looking at. Grids help keep things organized and tidy. Even though grids have been used for hundreds of years, many designers connect them with Swiss design from the 1940s. Back then, designers wanted a very organized way to show information. Later, some thought grids were boring, but today, they are seen as super important tools for designers, whether they are just starting or have lots of experience.
Tools for Graphic Designers
In the mid-1980s, computers started to change graphic design. Programs for desktop publishing and graphic art software made it possible to create and change images digitally. Before this, everything was done by hand. Computers let designers quickly see how changes to layout or text would look. They could also make things look like they were made with traditional art supplies. Even with computers, tools like pencils are still useful. Designers often sketch out many ideas first as part of their creative process. You can also use special pens (styluses) with tablet computers to draw digitally.
Computers and Software for Design
Designers sometimes disagree about whether computers make the creative process better. Some say computers help them try out many ideas quickly and in more detail than they could by hand. Others feel that having too many choices with digital design can make it hard to decide or lead to endless changes without a clear end.
Most designers use a mix of old and new methods. They might first sketch ideas by hand to get approval. Then, they create the final polished design on a computer.
Graphic designers are expected to be good at using software programs for making images, working with text, and creating layouts. Many of the most popular programs used by designers are made by Adobe Inc. Adobe Photoshop is great for editing photos, and Adobe Illustrator is used for drawing vector graphics (which can be scaled to any size without losing quality). CorelDraw is another popular program for vector graphics. Designers often use ready-made raster images and vector graphics from online libraries. Photos might be edited in Adobe Photoshop, logos in Adobe Illustrator or CorelDraw, and then everything is put together in programs like Adobe InDesign, Serif PagePlus, or QuarkXPress.
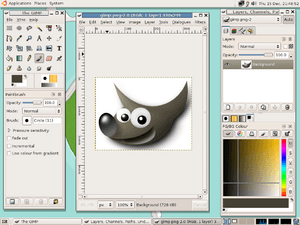
There are also many free and open-source programs that designers use. Inkscape is a free program for vector graphics. Other open-source tools include GIMP for photo editing, Krita for digital painting, and Scribus for page layout.
Other Design Jobs
What is Interface Design?
Since personal computers became popular, many graphic designers have started working on interface design. This is about creating the look and feel of things you interact with, like a Graphical User Interface (GUI). This includes web design and software design, where how a user interacts with the design is important. Graphic designers combine their visual communication skills with an understanding of how users interact with things online. They often work with software developers and web developers to create the overall look of a website or software application. A key part of interface design is creating icons.
What is User Experience Design?
User experience design (often called UX design) is about making products that are meaningful and helpful for people to use. It involves thinking about the whole process of getting and using a product, including its brand, design, how easy it is to use, and what it does. UX design creates the way you interact with a website or app. This job needs a mix of skills, like visual design, understanding how people think, development, project management, and most importantly, being able to understand what users need.
Jobs in Graphic Design

Graphic design jobs cover many parts of the creative world and often overlap. People in this field do specialized tasks like design services, publishing, advertising, and public relations. In 2023, the average pay was about $50,710 per year. Job titles can be different depending on the country. They might include graphic designer, art director, creative director, animator, or production artist. Sometimes, the job title might be "DTP associate" or "Graphic Artist" if it's for a specific industry. These jobs might also involve special skills like illustration, photography, animation, visual effects, or interactive design.
Jobs in online design projects are expected to grow a lot, by about 35% by 2026. However, jobs in traditional media, like newspaper and book design, are expected to decrease by 22%. Graphic designers will need to keep learning new techniques, programs, and methods all the time.
Graphic designers can work for companies that focus only on design, like design agencies. Others might work for publishing, marketing, or communication companies. Since computers became common, many graphic designers also work inside companies that aren't mainly about design. Graphic designers can also work freelance, which means they work for themselves and set their own terms and prices.
A graphic designer usually reports to an art director, creative director, or senior media creative. As designers get more experienced, they spend less time actually designing and more time leading and guiding other designers on bigger creative projects, like developing a brand's look and feel. They are also often expected to talk directly with clients, for example, to understand what the client needs.
The Future of Graphic Design
The future of graphic design will likely be greatly shaped by new technologies and social trends. Advances in things like artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and automation will probably change how graphic designers work and create. Social trends, such as caring more about the environment and including everyone, will also affect graphic design.
One big way new technologies will impact graphic design is by automating some tasks. For example, AI programs can look at lots of data and create designs based on patterns. This can free up designers to focus on more complex and creative work. VR and AR technologies might also let designers create amazing, interactive experiences for users, blurring the lines between the digital and real worlds.
Social trends will also help shape the future of graphic design. As people care more about environmental issues, there might be a greater demand for designs that are sustainable and create less waste. Similarly, there will likely be a growing focus on making designs that are inclusive and represent many different people and communities.
Images for kids
-
This Boeing 747 aircraft, known as Air Force One, shows how different designs can come together. The blue shapes, the US flag, the presidential seal, and the lettering were all designed at different times by different people. Designer Raymond Loewy combined them into this single aircraft exterior design.
See also
 In Spanish: Diseño gráfico para niños
In Spanish: Diseño gráfico para niños
 | George Robert Carruthers |
 | Patricia Bath |
 | Jan Ernst Matzeliger |
 | Alexander Miles |