Guaynabo, Puerto Rico facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Guaynabo
Municipio Autónomo de Guaynabo
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
City and municipality
|
|||
|
San Pedro de Mártir Church
Guaynabo City Hall
San Patricio Mall
Guaynabo skyline
|
|||
|
|||
| Nicknames:
"Ciudad de los Conquistadores", "Pueblo del Carnaval Mabó", "Primer Poblado de Puerto Rico"
|
|||
| Anthem: "Guaynabo, Pueblo Querido" | |||
Map of Puerto Rico highlighting Guaynabo Municipality
|
|||
| Sovereign state | |||
| Commonwealth | |||
| Settled | 1508 | ||
| Founded | April 9, 1769 | ||
| Founded by | Pedro R. Dávila | ||
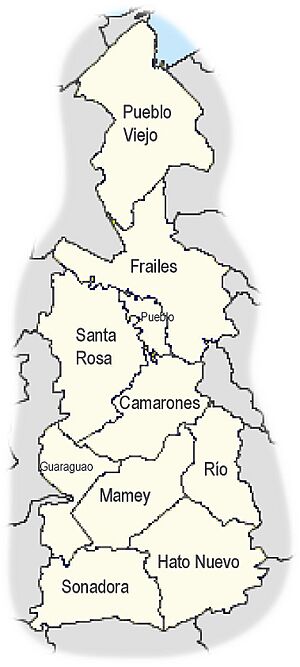
| Barrios | |||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 27.1 sq mi (70.2 km2) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 89,780 | ||
| • Rank | 6th in Puerto Rico | ||
| • Density | 3,312.4/sq mi (1,278.9/km2) | ||
| Demonym(s) | Guaynabeño (masculine) Guaynabeña (feminine) |
||
| Time zone | UTC−4 (AST) | ||
| ZIP Codes |
00965, 00966, 00968, 00969, 00971, 00970
|
||
| Area code(s) | 787/939 | ||
| Major routes | |||
| Website | guaynabocity.gov.pr | ||
Guaynabo is a city and municipality located on the northeastern coast of Puerto Rico. It is west of the capital city, San Juan. To its east is Bayamón, and to its south is Aguas Buenas. Guaynabo is home to about 89,780 people, according to the 2020 census. It is part of the larger San Juan metropolitan area. The main studios for WAPA-TV, a very popular television station in Puerto Rico, are also found here.
Contents
- History of Guaynabo
- Exploring Guaynabo's Geography
- Population and Demographics
- Fun Places to Visit in Guaynabo
- Guaynabo's Economy
- Climate in Guaynabo
- Culture and Traditions
- Symbols of Guaynabo
- Getting Around Guaynabo
- Famous People from Guaynabo
- Education in Guaynabo
- International Connections
- Images for kids
- See also
History of Guaynabo
The very first European settlement in Puerto Rico was called Caparra. It was started in 1508 by Juan Ponce de León in what is now Guaynabo. Ponce de León was the first Spanish governor of Puerto Rico and lived there. However, this settlement was later moved to San Juan in 1521.
The old ruins of Caparra are still there today. They are a U.S. National Historic Landmark. You can also visit the Museum of the Conquest and Colonization of Puerto Rico. This museum shows artifacts from Caparra and other places in Puerto Rico.
The municipality of Guaynabo was officially founded in 1769. Pedro R. Davila helped create it after it separated from the municipality of Bayamón. Before this, the area was known as "Buinabo." This name means "Here is another place of fresh water" in the Taíno language.
Exploring Guaynabo's Geography
Guaynabo is located on the northern side of Puerto Rico.
Understanding Guaynabo's Barrios
Like all municipalities in Puerto Rico, Guaynabo is divided into smaller areas called barrios. The main government buildings, the central town square, and a large Catholic church are all located in a barrio known as "el pueblo". This area is usually found near the center of the municipality.
Here are the barrios that make up Guaynabo:
Special Communities in Guaynabo
Some areas in Puerto Rico are called "Special Communities." These are neighborhoods where people might face challenges like social exclusion. In 2014, several areas in Guaynabo were on this list. These included Amelia, Buen Samaritano, Corea, El Polvorín, Honduras, Jerusalén, Los Filtros, Sector El Laberinto, Sector La Pajilla, Sector Los Ratones (Camino Feliciano), Sector San Miguel, Trujillo, Sector Tomé, Vietnam, and Villa Isleña.
Population and Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1920 | 10,800 | — | |
| 1930 | 13,502 | 25.0% | |
| 1940 | 18,319 | 35.7% | |
| 1950 | 29,120 | 59.0% | |
| 1960 | 39,718 | 36.4% | |
| 1970 | 67,042 | 68.8% | |
| 1980 | 80,742 | 20.4% | |
| 1990 | 92,886 | 15.0% | |
| 2000 | 100,053 | 7.7% | |
| 2010 | 97,924 | −2.1% | |
| 2020 | 89,780 | −8.3% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1920-1930 1930-1950 1960-2000 2010 2020 |
|||
The population of Guaynabo has changed over the years. In 1920, about 10,800 people lived there. By 2020, the population grew to 89,780. People from Guaynabo are called Guaynabeño (for males) or Guaynabeña (for females).
Fun Places to Visit in Guaynabo
To encourage people to explore Puerto Rico, the Puerto Rico Tourism Company created a "Voy Turistiendo" (I'm Touring) campaign. Guaynabo has many interesting places to visit.
Landmarks and Attractions
Some popular spots include:
- Caparra Ruins: See the remains of the first European settlement.
- Caribe Recreational Center: A great place for fun activities.
- Iglesia Parroquial de San Pedro Mártir: A beautiful church.
- La Marquesa Forest Park: Enjoy nature and outdoor adventures.
- Mario Morales Coliseum: A famous sports arena.
- San Patricio Plaza: A large shopping mall.
- Museum of Transportation: Learn about different ways people travel.
- Museo del Deporte: A sports museum.
- Fort Buchanan: A military base.
Guaynabo's Economy
Many important businesses and companies have their main offices or branches in Guaynabo. These include major news organizations like El Nuevo Día. Car companies like Chrysler and banks like Santander Securities also have a presence.
Big international companies such as Microsoft and Toshiba have their Puerto Rican headquarters here. The main studios for popular TV channels like WAPA-TV and Univision Puerto Rico are also located in Guaynabo.
Climate in Guaynabo
| Climate data for Guaynabo, Puerto Rico | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 93 (34) |
93 (34) |
94 (34) |
96 (36) |
99 (37) |
67 (19) |
101 (38) |
99 (37) |
104 (40) |
102 (39) |
98 (37) |
92 (33) |
104 (40) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 77 (25) |
78 (26) |
84 (29) |
88 (31) |
89 (32) |
90 (32) |
91 (33) |
92 (33) |
92 (33) |
90 (32) |
82 (28) |
79 (26) |
86 (30) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 65 (18) |
64 (18) |
67 (19) |
70 (21) |
72 (22) |
75 (24) |
76 (24) |
76 (24) |
75 (24) |
73 (23) |
71 (22) |
67 (19) |
71 (22) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 53 (12) |
52 (11) |
56 (13) |
62 (17) |
66 (19) |
— | 69 (21) |
69 (21) |
64 (18) |
66 (19) |
61 (16) |
59 (15) |
52 (11) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 1.89 (48) |
1.51 (38) |
1.52 (39) |
2.39 (61) |
9.36 (238) |
4.35 (110) |
2.42 (61) |
5.50 (140) |
8.34 (212) |
5.57 (141) |
5.28 (134) |
3.74 (95) |
51.87 (1,317) |
| Source: weather.com | |||||||||||||
Guaynabo has a warm climate throughout the year. The temperatures are generally mild, with average highs in the 80s and 90s Fahrenheit. Even the lowest temperatures rarely drop below the 60s. The area receives a good amount of rain, especially in certain months like May and September.
Culture and Traditions
Festivals and Events in Guaynabo
Guaynabo celebrates its patron saint festival in April. This event is called the Fiestas Patronales de San Pedro Martir. It's a fun religious and cultural celebration. You can often see parades, play games, buy crafts from local artists, and enjoy amusement rides. There's also delicious regional food and live entertainment.
Other exciting festivals and events in Guaynabo include:
- Three Kings Festival: Celebrated in January.
- Mabó Carnival: A lively carnival in February.
- Mothers’ Day Celebration: Held in May to honor mothers.
- National Salsa Day: A celebration of Salsa music in June.
- Fine Arts Camp and Recreation and Sports Camp: Summer camps in June.
- Bomba and Plena Festival: A festival in October featuring traditional folkloric music and dance.
- Official Lighting of Christmas Lights: Kicking off the holiday season in November.
Sports in Guaynabo
Guaynabo has a rich sports history and is home to several sports teams. The city's old basketball team, the Guaynabo Mets, won national championships in 1980, 1982, and 1989. These teams were led by a famous player named Mario "Quijote" Morales. The Mario Morales Coliseum is named after him.
Today, the Guaynabo Conquistadores are the city's basketball team, and they also play at the Mario Morales Coliseum. The Mets de Guaynabo is the local women's volleyball team. They have won three titles in their league.
Guaynabo also has a professional soccer team called Guaynabo Fluminense FC. They play in the Puerto Rico Soccer League. Their matches used to be at the Jose Bonano Stadium, which was originally for baseball.
Here are some of Guaynabo's sports teams:
- Mets de Guaynabo (women's volleyball)
- Mets de Guaynabo (men's volleyball)
- Guaynabo Conquistadores (basketball)
- Mets de Guaynabo (basketball)
- Mets de Guaynabo (baseball)
- Guaynabo Fluminense FC (soccer)
Symbols of Guaynabo
The municipality of Guaynabo has its own official flag and coat of arms. These symbols represent the history and identity of the city.
Guaynabo's Flag
The flag of Guaynabo is an important symbol for the municipality.
Guaynabo's Coat of Arms
The coat of arms of Guaynabo also represents the city's unique heritage.
Getting Around Guaynabo
Guaynabo has a public transportation system. The Tren Urbano (Urban Train) has one station in the municipality, called Torrimar Station. Guaynabo also has its own bus network, known as “Guaynabo City Transport.” There are 63 bridges located throughout Guaynabo.
Famous People from Guaynabo
Many talented individuals have come from Guaynabo, including:
- Iván DeJesús Jr. (born 1987), a baseball player who played for the Cincinnati Reds.
- Carlos (born 1965), Oscar (born 1966), and Ricky Meléndez (born 1967), singers from the famous group Menudo.
- Tomas Nido (born 1994), a baseball catcher for the New York Mets.
Education in Guaynabo
Guaynabo is home to Atlantic University. This university specializes in new media art, which involves using digital tools to create art.
International Connections
Guaynabo hosts the offices for several foreign consulates. These consulates help with business and other matters for their home countries in Puerto Rico. The countries with consulates in Guaynabo include:
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Guaynabo para niños
In Spanish: Guaynabo para niños