Gudea facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Gudea𒅗𒌤𒀀 |
|
|---|---|
| Ruler of Lagash | |

Diorite statue of Gudea, prince of Lagash, dedicated to the god Ningishzida, Louvre Museum.
|
|
| Ruler of Lagash | |
| Reign | c. 2144–2124 BC |
| Predecessor | Ur-Baba |
| Successor | Ur-Ningirsu |
| Spouse | Ninalla |
| Issue | Ur-Ningirsu |
| Dynasty | Kings of Lagash |
Gudea (pronounced Goo-dee-ah) was an important ruler of an ancient city-state called Lagash. This city was located in Southern Mesopotamia, a region now mostly in modern-day Iraq. He ruled around 2144 to 2124 BC.
Gudea likely wasn't born into the royal family of Lagash. He married Ninalla, the daughter of the previous ruler, Ur-Baba. This marriage helped him become the next leader. After Gudea, his son, Ur-Ningirsu, took over.
During Gudea's time, a group called the Gutian dynasty controlled much of the area. However, Lagash, under Gudea, seemed to be quite independent. This period is often called a "golden age" for Lagash because it was a time of peace and prosperity.
Contents
Who Was Gudea?
Gudea chose the title ensi. This meant "town-king" or "governor." He did not call himself lugal, which meant "king" in a grander sense. He also wasn't seen as a god during his lifetime. This title was given to him after he died, which was a common tradition in Mesopotamia for many rulers.
Historians know about 20 years of Gudea's rule. Each year had a special name. One important event happened in his sixth year. It was called the "Year when Anshan was smitten with weapons." This suggests a military victory.
Building for the Gods
Even though Gudea might have won battles, most of his writings talk about peaceful projects. He focused on building irrigation channels to help farms. He also built many beautiful temples for the gods. He created valuable gifts to honor them.
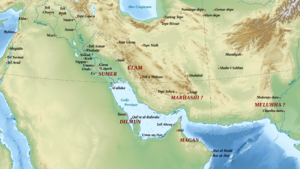
To build these temples and statues, Gudea brought materials from far away lands.
- He got cedar wood from the Amanus mountains.
- Quarried stones came from Lebanon.
- Copper was brought from northern Arabia.
- Gold and precious stones came from the desert between Canaan and Egypt.
- Diorite, a very hard stone, was from Magan (modern-day Oman).
- Timber (wood) came from Dilmun (modern-day Bahrain).
This shows that Lagash had strong trade connections with many distant places.
Gudea's Devotion to Religion

Gudea was very religious. He dedicated many statues and items to the gods. One famous inscription is on a statue of Gudea as an architect. This statue was for the temple of Ningirsu, a powerful god.
The inscription warns people not to change the words. It describes terrible things that would happen to anyone who dared to alter it. The curses were very detailed and creative, showing how serious Gudea was about honoring the gods and his work.
Trade and International Connections
Gudea's kingdom, Lagash, traded with many distant places. His records mention people from a land called Meluhha. They came to Sumer to sell valuable goods like gold dust and carnelian stones.
Gudea also recorded victories over territories like Magan, Meluhha, Elam, and Amurru. This shows his influence reached far.
In some of Gudea's writings, known as the Gudea cylinders, he talks about his temple. He hoped that "the whole universe will gather in it." He even mentioned that Magan and Meluhha would come from their mountains to visit. He also wrote about getting "blocks of lapis lazuli and bright carnelian from Meluhha."
Some historians believe that "Meluhha" might refer to the Indus Valley Civilization in ancient India. This suggests that Gudea's kingdom had trade links with India as early as 2200 BC.
Important Art and History
Many statues and artifacts from Gudea's reign have been found. These items help us understand his time. They show his devotion to the gods and his importance as a ruler.
Images for kids
-
The "Libation vase of Gudea" with the dragon Mušḫuššu, dedicated to Ningishzida (21st century BC short chronology). The caduceus (right) is interpreted as depicting god Ningishzida. Inscription; "To the god Ningiszida, his god, Gudea, Ensi (governor) of Lagash, for the prolongation of his life, has dedicated this"
-
Head of Gudea in polished diorite, reign of Gudea (Boston Museum of Fine Arts).
See also
 In Spanish: Gudea para niños
In Spanish: Gudea para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |