Hotspot (geology) facts for kids
In geology, a hotspot is a special place on Earth's surface where volcanoes form. These volcanoes are often far away from the edges of tectonic plates. Hotspots can be caused by something called a mantle plume, which is a super-hot column of rock rising from deep inside the Earth.
When magma (molten rock) pushes up from the mantle at a hotspot, it creates a volcano. As the Earth's tectonic plates slowly move over this fixed hotspot, new volcanoes can form in a line. This creates a chain of volcanoes, like the famous Hawaiian Islands.
How Hotspots Work
Volcanoes and Plate Edges
Most volcanoes on Earth are found where tectonic plates either crash into each other or pull apart. For example, the long mountain ranges along the western side of the Americas have many volcanoes because plates are colliding there. Also, huge valleys like the East African Rift are formed where plates are splitting apart. Most scientists agree that these big features are caused by plate tectonics.
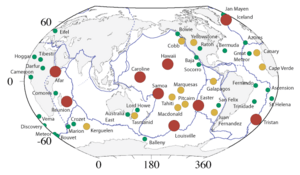
However, some volcanoes are not found at the edges of these plates. This is where hotspots come in. For example, Yellowstone in the United States is a very active area. It has geysers (hot springs that shoot water and steam) because of constant geothermal energy (heat from inside the Earth). The ground in the crater at Yellowstone even moves up and down by many meters over a few years!
In the Pacific Ocean, there are also several chains of islands that were formed by volcanoes. Most of these island chains, like Hawaii, cannot be easily explained by just being at the edge of tectonic plates.
The Hotspot Idea
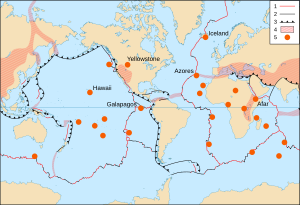
In 1963, a scientist named J. Tuzo Wilson suggested an idea to explain these mysterious volcanoes. He thought that volcanic chains, like the Hawaiian Islands, are formed because a tectonic plate slowly moves over a fixed "hot spot" deep inside the planet.
Scientists believe these hotspots are caused by a narrow stream of very hot rock. This hot rock rises from the deep mantle, near the Earth's core. This rising stream is called a mantle plume. Imagine a slow-moving lava lamp inside the Earth!
Some other geologists have a different idea. They think that it's not super-high temperatures that cause the volcanoes. Instead, they believe that the lithosphere (the Earth's outer rigid layer) stretches and thins out. This stretching allows molten rock to rise from shallower depths.
Scientists have found about 40 to 50 hotspots around the world. The ones under Hawaii, Réunion, Yellowstone, and the Galápagos Islands are some of the most active ones right now.
Images for kids
-
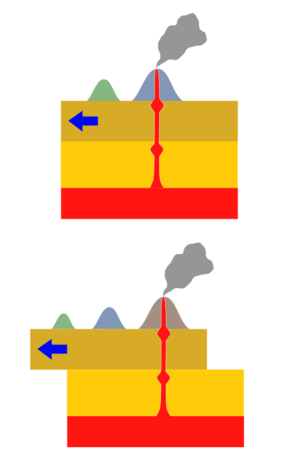
This diagram shows a cross section through Earth at the Hawaii hotspot. Magma from the mantle rises into the asthenosphere and lithosphere. As the lithosphere moves over the magma source, a chain of volcanoes is created.
-
Over millions of years, the Pacific Plate has moved over the Hawaii hotspot. This created a trail of underwater mountains that stretches across the Pacific Ocean.
-
Kilauea is the most active shield volcano in the world. It erupted almost constantly from 1983 to 2018 and is part of the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain.
-
Mauna Loa is a very large shield volcano. Its last eruption was in 1984. It is also part of the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain.
-
Bowie Seamount is a sleeping underwater volcano. It is part of the Kodiak-Bowie Seamount chain.
-
Mauna Kea is the tallest volcano in the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain. Many small cone-shaped hills (cinder cones) are found near its top.
-
Hualalai is a huge shield volcano in the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain. Its last eruption was in 1801.
-
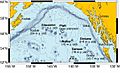
Over millions of years, the Pacific Plate has moved over the Bowie hotspot. This created the Kodiak-Bowie Seamount chain in the Gulf of Alaska.
See also
 In Spanish: Punto caliente (geología) para niños
In Spanish: Punto caliente (geología) para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |