Juba II facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Juba II |
|
|---|---|

Portrait bust of Juba II, Louvre Museum
|
|
| King of Numidia | |
| Reign | 30 BC – 25 BC (5 years) |
| Predecessor | Juba I |
| Successor | Annexed to the Roman Republic/Empire |
| King of Mauretania | |
| Reign | 25 BC – AD 23 (47 years) |
| Predecessor | Bocchus II |
| Successor | Ptolemy of Mauretania |
| Spouse | Cleopatra Selene II Glaphyra of Cappadocia |
| Issue | Ptolemy of Mauretania Julia |
| Father | Juba I |
Juba II (born around 48 BC, died AD 23) was a famous king from ancient times. He was the son of King Juba I. Juba II ruled two kingdoms: first Numidia (from 30 BC to 25 BC), then Mauretania (from 25 BC to AD 23). He was not only a successful ruler but also a respected writer and scholar. His first wife was Cleopatra Selene II, who was the daughter of the famous Queen Cleopatra VII of Egypt and the Roman leader Mark Antony.
Contents
The Life of King Juba II
Early Years and Education
Juba II was a Berber prince from Numidia, a kingdom in North Africa. He was the only son of King Juba I of Numidia. In 46 BC, his father was defeated by the Roman general Julius Caesar. Numidia then became a Roman province.
After his father's defeat, Juba II was taken to Rome by Julius Caesar. He even took part in Caesar's victory parade. In Rome, Juba II learned Latin and Greek. He became very Romanized and was given Roman citizenship.
Juba II loved to study. He became one of Rome's most educated citizens. By the time he was 20, he wrote a book called Roman Archaeology. Julius Caesar raised him, and later, Caesar's great-nephew Octavian took care of him. Octavian later became the first Roman Emperor, Augustus. Juba II went on military trips with Octavian. This helped him gain important experience as a leader. He even fought alongside Octavian in the Battle of Actium in 31 BC.
Becoming King of Numidia and Mauretania
In 30 BC, Octavian made Juba II the king of Numidia again. Juba II made Numidia a strong ally of Rome. Because of his help to Augustus in a war in Spain, Augustus arranged for Juba II to marry Cleopatra Selene II. She was given a large dowry and became queen.
Later, in 25 BC, Numidia became part of the Roman Empire. Juba II then received Mauretania as his new kingdom. This new kingdom was even larger than before.
Ruling Mauretania
When Juba II and Cleopatra Selene moved to Mauretania, they named their new capital Caesaria. This name honored Emperor Augustus. Today, Caesaria is known as Cherchell, Algeria. The buildings and statues in Caesaria and another city, Volubilis, showed a mix of Egyptian, Greek, and Roman styles.
Cleopatra Selene had a big influence on Juba II's decisions. Juba II supported the arts, science, and natural history. He also helped Mauretania's trade grow. Mauretania was very important to the Roman Empire. It traded goods all over the Mediterranean Sea, especially with Spain and Italy.
Mauretania exported fish, grapes, pearls, figs, grain, wooden furniture, and purple dye. This dye came from shellfish and was used for important Roman robes. Juba II even sent people to the Iles Purpuraires to restart the old way of making this dye. Tingis (modern Tangier) became a major trade center.
The coins made in Mauretania were highly valued. The Greek historian Plutarch called Juba II "one of the most gifted rulers of his time." In AD 21, Juba II made his son Ptolemy a co-ruler. Juba II died in AD 23. He was buried next to his first wife in the Royal Mausoleum of Mauretania. His son Ptolemy then became the sole ruler of Mauretania.
Family Life
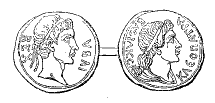
Juba II had two marriages and several children.
- First marriage: He married Cleopatra Selene II (40 BC – 6 AD). She was a Ptolemaic princess from Greek Egypt. Their children were:
- Ptolemy of Mauretania, born around 10 BC or 5 BC.
- A daughter whose name is not known.
- Second marriage: He married Glaphyra, a princess from Cappadocia. She was the widow of Alexander, son of Herod, who was the son of Herod the Great. Glaphyra married Juba II in 6 AD or 7 AD. She later divorced Juba to marry Herod Archelaus, another son of Herod the Great.
Juba II's Writings and Discoveries
Books and Knowledge
Juba II wrote many books in Greek. His books covered history, natural history, geography, grammar, painting, and theater. He wrote a comparison of Greek and Roman ways of life called Resemblances. His guide to Arabia was very popular in Rome.
Sadly, only small parts of his works still exist today. He had a huge library with many different topics. Pliny the Elder, a famous Roman writer, mentioned Juba II as an expert 65 times in his book Natural History. In Athens, a monument was built to honor Juba II's writings.
Some of his known works include:
- Roman Archaeology
- Resemblances
- On Painting
- Theatrical History
- The Wanderings of Hanno (possibly a translation)
- On Arabia
- On Assyria
His writings are known to us only because other ancient writers quoted or mentioned them.
Contributions to Science
Juba II was a big supporter of the arts and sciences. He paid for several trips and scientific studies. According to Pliny the Younger, Juba II sent a trip to the Canary Islands and Madeira. He named them the Canary Islands because of the fierce dogs found there. The word canarius means "of the dogs" in Latin.
Juba II's Greek doctor, Euphorbus, found a succulent plant in the High Atlas mountains. He said it was a strong laxative. In 12 BC, Juba II named this plant Euphorbia after Euphorbus. This was to honor his doctor, just as Augustus had honored his own doctor. Later, the botanist Carl Linnaeus named the whole group of these plants Euphorbia. One type is even called Euphorbia regis-jubae, meaning "King Juba's euphorbia."
The palm tree group Jubaea is also named after Juba II. This shows his important contributions to natural history.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Juba II para niños
In Spanish: Juba II para niños







