Lake Maracaibo facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lake Maracaibo |
|
|---|---|

Lake Maracaibo, seen from space. The green swirls in the lake are patches of duckweed, which is infesting the lake. North is at the top of the image.
|
|
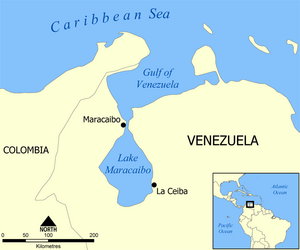
Map
|
|
| Coordinates | 09°48′57″N 71°33′24″W / 9.81583°N 71.55667°W |
| Type | Coastal saltwater, bay |
| Primary inflows | Catatumbo River |
| Primary outflows | Gulf of Venezuela |
| Basin countries | Venezuela |
| Max. length | 99 miles (159 km) |
| Max. width | 67 miles (108 km) |
| Surface area | 13,210 km2 (5,100 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 60 m (200 ft) |
| Water volume | 280 km3 (230,000,000 acre⋅ft) |
| Surface elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Islands | 467 |
| Settlements | Maracaibo, Cabimas, Ciudad Ojeda |
Lake Maracaibo (Spanish: Lago de Maracaibo) is a very large body of water in Venezuela. It is often called a lake, but it is actually a brackish tidal bay. This means its water is a mix of fresh water and salty ocean water. It is connected to the Caribbean Sea.
A channel about 55 kilometers (34 miles) long links the lake to the Caribbean Sea. The city of Maracaibo is located on the west side of this channel. The channel is about 8.5 kilometers (5.3 miles) wide near the city. The General Rafael Urdaneta Bridge, one of the longest bridges in the world, crosses this channel.
Lake Maracaibo is about 160 kilometers (99 miles) long and 110 kilometers (68 miles) wide. Many rivers flow into the lake, about 135 in total. The longest river is the Catatumbo River, which is 500 kilometers (310 miles) long. Other important rivers include the Escalante River and the Chama River.
The water in the northern part of the lake is brackish, meaning it is a bit salty. The southern part of the lake has freshwater. There are also many islands within the lake.
Contents
How Lake Maracaibo Helps People
Most parts of Lake Maracaibo are quite shallow. To allow large ships to reach the ports of Maracaibo and Cabimas, a special canal was built. This canal helps ships carry goods and people.
In 1914, crude oil was discovered in the lake, near the city of Cabimas. The area around the lake, called the Maracaibo Basin, holds huge amounts of oil. This makes the lake a very important place for Venezuela's economy. Almost a quarter of Venezuela's population lives in the area around the lake.
Amazing Thunderstorms at Lake Maracaibo
Lake Maracaibo is not very deep, usually only about 5 meters (16 feet) on average. Its deepest point is about 45 meters (148 feet). The water in the lake is very warm, often around 30 degrees Celsius (86 degrees Fahrenheit).
During the day, a lot of water turns into vapor and rises from the lake. At night, the air over the land around the lake cools down faster than the air over the warm lake water. This difference in temperature causes clouds to form. Because of this, thunderstorms happen very often.
This unique weather event is called Catatumbo lightning. It happens regularly over Lake Maracaibo and produces more lightning than almost any other place on Earth. Sometimes, lightning can strike oil facilities in the lake, which can cause fires.
Protecting the Lake's Environment
The environment of Lake Maracaibo faces several challenges. One big problem is a tiny plant called duckweed (Lemna). These plants float freely on the water and can spread incredibly fast, doubling their coverage in just 48 hours. In 2004, about 18% of the lake was covered by duckweed.
Duckweed is not harmful to fish directly. However, when it dies and breaks down, it uses up oxygen in the water. This can make it hard for fish to breathe and survive. The duckweed also causes problems for local fishers because it can clog the motors of their small boats, making it impossible to go fishing.
The duckweed also affects the lake's ecosystem by blocking sunlight. Other plants in the lake do not get enough light and can die. In some conditions, duckweed can also collect harmful substances like heavy metals and certain bacteria.
Besides duckweed, the lake also suffers from other types of pollution. Untreated sewage (wastewater from homes) is released into the lake. Also, oil drilling operations can cause pollution with crude oil.
Images for kids
-
This image uses False color to show pollution in the lake. The dark patches in the bluish area are oil spills.
See also
 In Spanish: Lago de Maracaibo para niños
In Spanish: Lago de Maracaibo para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |




