Lower seaboard theater of the American Civil War facts for kids
The lower seaboard theater of the American Civil War was a big area where important military and naval battles happened. These events took place near the coasts of the Southeastern United States. This included parts of Alabama, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina, and Texas. It also covered the southern part of the Mississippi River, especially around Port Hudson.
Battles that happened further inland were part of the western theater or trans-Mississippi theater. This depended on whether they were east or west of the Mississippi River. Coastal battles in Georgia, like the end of Sherman's March to the Sea, are usually grouped with the western theater.
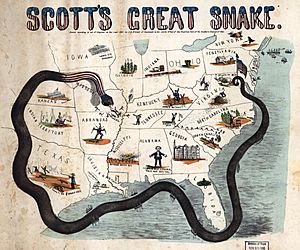
The Union Navy had a main plan called the Anaconda Plan. This plan aimed to "strangle" the South by blocking its ports. The goal was to stop supplies from getting in or out. Later, the Union Navy also attacked and took control of important port cities. These included New Orleans, Mobile, and Galveston.
The Confederate forces mostly tried to run the blockade. They used fast ships called blockade runners to get past Union ships. The Confederate Navy mostly defended against Union attacks. They had some successes but also faced many challenges.
Contents
Coastal Battles in South Carolina
Many battles along the South Carolina coast focused on capturing Charleston. This city was important for two reasons. It was a major port for blockade runners. It was also a symbol because the war started there.
One of the first battles of the war happened at Port Royal Sound. This was south of Charleston. The Union Navy wanted to use this spot to refuel their ships.
The Union army tried to capture Charleston in two ways. They tried attacking by land across James or Morris Islands. They also tried to attack through the harbor. But the Confederates fought hard and stopped every Union attack.
One famous land attack was the Second Battle of Fort Wagner. The brave 54th Massachusetts Infantry took part in this battle. The Union army lost many soldiers, about 1,500 men. The Confederates lost far fewer, only 175.
Something amazing happened on February 23, 1864. The CSS Hunley was a Confederate submarine. It became the first submarine to successfully sink an enemy warship. Sadly, the Hunley also sank shortly after its victory. The Confederates also used other small boats like the David, but they were not as successful.
Georgia's Coastal Forts
Fort Pulaski on the Georgia coast was an early target for the Union Navy. After capturing Port Royal, Union engineers led by Captain Quincy A. Gillmore planned an attack.
For a month, they set up 36 cannons and mortars on nearby Tybee Island. On April 10, 1862, Gillmore began firing at the fort. The Confederates surrendered the next day. Their gunpowder storage was in danger from the Union shells. The Union army then took over the fort and held it for the rest of the war.
Florida's Role in the War
Florida left the Union in January 1861. After that, Florida troops took control of most federal property in the state. However, they could not capture Fort Zachary Taylor at Key West or Fort Pickens at Pensacola.
The Union Navy quickly set up a blockade along Florida's coast. The South Atlantic Blockading Squadron covered the Atlantic side. The East Gulf Blockading Squadron covered the Gulf side.
Many small fights happened in Florida, but no very large battles. In 1864, the Union tried to set up a pro-Union government in Florida. A Union force led by Brigadier General Truman Seymour moved inland from Jacksonville. But they were defeated at the Battle of Olustee on February 20. This was the biggest Civil War battle in Florida.
The Union army also tried to capture the state capital, Tallahassee. But they were defeated at the Battle of Natural Bridge on March 8, 1865. Florida was one of only two Confederate states whose capital was not captured during the war.
Louisiana and the Mississippi River
One major goal for the Union was to control the Mississippi River. This would cut the Confederacy in half. The most important place on the river was New Orleans. It was the South's largest port and a big industrial center.
In April 1862, a Union naval force attacked Forts Jackson and St. Philip. These forts guarded the river approach to New Orleans from the south. While some Union ships fired at the forts, others broke through river defenses. This allowed the rest of the fleet to sail upriver to the city. A Union army force then landed near the forts and forced them to surrender.
The next year, the Union Army of the Gulf began a siege of Port Hudson. This siege lasted almost eight weeks. It was one of the longest sieges in U.S. military history. To cut off supplies to Port Hudson, the Union army first moved up Bayou Teche. They captured areas along the Atchafalaya and Red rivers.
The Confederates defending Port Hudson surrendered on July 9. They had heard that Vicksburg had also surrendered. These two surrenders gave the Union control over the entire Mississippi River. This successfully split the Confederacy in half.
For the rest of the war, the Confederates tried to get back the areas they had lost. From June to September 1863, Major General Richard Taylor tried to recapture Union gains. He wanted to cut off Union supplies to New Orleans and maybe even take the city back. While he won some battles, the Confederates did not achieve their main goals.

