Nanotyrannus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Nanotyrannus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
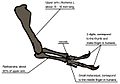
| Holotype skull | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Tyrannosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Tyrannosaurinae |
| Genus: | †Nanotyrannus Bakker, Currie & Williams, 1988 |
| Species: |
†N. lancensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Nanotyrannus lancensis Gilmore, 1946
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Genus synonymy
Stygivenator?
Olshevsky, 1995 Species synonymy
Gorgosaurus lancensis
Gilmore, 1946 Deinodon lancensis (Gilmore, 1946) Aublysodon lancensis (Gilmore, 1946) Albertosaurus lancensis (Gilmore, 1946) Tyrannosaurus lancensis? (Gilmore, 1946) Stygivenator molnari? (Paul, 1988) |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Nanotyrannus means "dwarf tyrant." It was a type of tyrannosaurid dinosaur. These dinosaurs lived at the very end of the Upper Cretaceous period. This was about 67 million years ago.
For a long time, scientists debated if Nanotyrannus was a separate dinosaur. Some thought it might just be a young Tyrannosaurus. However, many scientists now believe it was its own unique species.
Contents
What We Know About Nanotyrannus
Only a few fossil bones of Nanotyrannus have been found. These rare finds help us learn about this ancient creature.
Size and Appearance
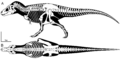
Nanotyrannus was smaller than its famous cousin, Tyrannosaurus rex. It likely grew to about 5 to 6 meters (16 to 20 feet) long. This is roughly the length of a small bus. It probably weighed around 1,000 kilograms (2,200 pounds). Like other tyrannosaurids, it walked on two strong legs. It had short arms with two fingers.
Where Nanotyrannus Lived
The fossils of Nanotyrannus have been found in North America. They come from the same time and place as Tyrannosaurus rex. This means they might have lived in the same areas.
Its Environment
During the Late Cretaceous, North America had a warm climate. There were vast forests and swamps. This environment was home to many different dinosaurs. These included plant-eaters and other predators.
What Nanotyrannus Ate
As a tyrannosaurid, Nanotyrannus was a carnivore. This means it ate meat. It had sharp teeth, perfect for tearing flesh. It likely hunted smaller dinosaurs. It might also have scavenged, eating animals that were already dead.
The Debate: Separate Species or Young T. rex?
The main debate about Nanotyrannus is whether it's a distinct species. Or if it's a juvenile Tyrannosaurus rex.
Arguments for a Separate Species
Scientists who believe Nanotyrannus is its own species point to differences in its skull. The shape of its skull and the number of its teeth are unique. These features don't seem to change as a Tyrannosaurus grows. This suggests it's a different kind of dinosaur.
Arguments for a Young T. rex
Other scientists argue that the differences are due to age. They say young Tyrannosaurus rex dinosaurs looked different from adults. As they grew, their skulls changed shape. This is a common process in many animals.
Ongoing Research
Scientists continue to study the available fossils. They use new technologies to examine the bones. This research helps them understand how dinosaurs grew. It also helps them decide if Nanotyrannus is truly unique.
Images for kids
-
Type specimen (AMNH 3982) of Manospondylus gigas
-
Dynamosaurus imperiosus holotype, Natural History Museum
-
Specimen "Sue", Field Museum of Natural History, Chicago
-
Probable footprint from New Mexico
-
Adult T. rex skeleton (the specimen AMNH 5027) at American Museum of Natural History.
-
Fossilized skin impressions from the tail region of a Tyrannosaurus, Houston Museum of Natural Science
-
Outdated reconstruction (by Charles R. Knight), showing upright pose
-
T. rex femur (MOR 1125) from which demineralized matrix and peptides (insets) were obtained
-
Only known tyrannosaurid trackway (Bellatoripes fredlundi), from the Wapiti Formation, British Columbia
-
The eye-sockets faced mainly forwards, giving it good binocular vision (Sue specimen).
-
Cast of the braincase at the Australian Museum, Sydney.
-
Mounted skeletons of different age groups (skeleton in lower left based on the juvenile formerly named Stygivenator), Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County
See also
 In Spanish: Nanotyrannus lancensis para niños
In Spanish: Nanotyrannus lancensis para niños