Nuclear power facts for kids
Nuclear power is a way to make electricity using the powerful energy found inside tiny parts of atoms. This energy comes from a special metal called uranium. We release this energy in a machine called a nuclear reactor. Then, this energy is turned into electricity to power our homes and devices. In 2007, about 14% of the world's electricity came from nuclear power. Nuclear power plants also create radioactive waste. This waste needs to be stored very carefully because it can be harmful. Interestingly, nuclear power plants actually produce less radioactive material than power stations that burn coal.
Contents
How Nuclear Power Started
The first nuclear reactor was built by Enrico Fermi in 1941. Many reactors were built in the United States during World War II as part of the Manhattan Project. The very first nuclear power plant that generated electricity started working in 1954 in Obninsk, near Moscow. Most nuclear power plants in the U.S. were built between the 1960s and 1970s. Nuclear reactors are also used to power some large military ships and submarines.
Important Nuclear Accidents
Some serious nuclear accidents have happened over time. To help measure how dangerous these accidents are, a special scale was created. It is called the International Nuclear Event Scale. This scale has 8 levels, from 0 to 7, where level 7 is the most serious.
Here are some of the most serious accidents:
- The Chernobyl disaster happened in 1986 and was classified as a level 7 accident.
- The Fukushima nuclear disaster happened in 2011 and was also classified as level 7.
- The Mayak accident happened in 1957. It released a lot of radiation, even more than Chernobyl, but the affected area was smaller. It was classified as level 6.
- The Windscale fire in 1957 and the Three Mile Island accident in 1979 were both level 5 accidents.
- The Tokaimura nuclear accident was a level 4 accident.
Nuclear-powered submarines have also had accidents. These include the Soviet submarine K-19 reactor accident in 1961, the Soviet submarine K-27 reactor accident in 1968, and the Soviet submarine K-431 reactor accident in 1985.
Money and Nuclear Power
Building and running nuclear power plants can be quite expensive. After the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, the costs for both existing and new nuclear power plants are expected to go up. This is because more money is needed for safely storing used nuclear fuel and for making the plants even safer.
Debates About Nuclear Power
There are different opinions about using nuclear power.
- Supporters like the World Nuclear Association and the IAEA say that nuclear power is a good way to get energy that lasts a long time. They also argue that it helps reduce carbon emissions, which are gases that contribute to climate change.
- Opponents like Greenpeace International and the Nuclear Information and Resource Service believe that nuclear power can be dangerous for people and the environment.
Recent Updates in Nuclear Power
In 2007, nuclear power plants produced about 2600 TWh of electricity. This provided 14 percent of the world's electricity, which was a small drop compared to 2006. As of May 9, 2010, there were 438 (372 GW) nuclear reactors working around the world. The highest number of operating reactors was in 2002, with 444.
The nuclear emergencies at Japan's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant and other nuclear sites made people think more about the future of nuclear power. After the Fukushima nuclear disaster, the International Energy Agency cut its prediction for how much more nuclear power would be built by 2035 by half.
Images for kids
-
The launching ceremony of the USS Nautilus in January 1954. In 1958 it became the first vessel to reach the North Pole.
-
The town of Pripyat abandoned since 1986, with the Chernobyl plant and the Chernobyl New Safe Confinement arch in the distance.
-
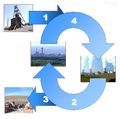
The nuclear fuel cycle begins when uranium is mined, enriched, and manufactured into nuclear fuel (1), which is delivered to a nuclear power plant. After use, the spent fuel is delivered to a reprocessing plant (2) or to a final repository (3). In nuclear reprocessing 95% of spent fuel can potentially be recycled to be returned to use in a power plant (4).
-
Nuclear waste flasks generated by the United States during the Cold War are stored underground at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) in New Mexico. The facility is seen as a potential demonstration for storing spent fuel from civilian reactors.
-
Nuclear fuel assemblies being inspected before entering a pressurized water reactor in the United States.
-
The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG), used in several space missions such as the Curiosity Mars rover.
-
Following the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, the world's worst nuclear accident since 1986, 50,000 households were displaced after radiation leaked into the air, soil and sea. Radiation checks led to bans of some shipments of vegetables and fish.
-
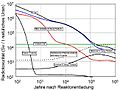
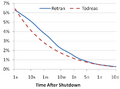
Reactor decay heat as a fraction of full power after the reactor shutdown, using two different correlations. To remove the decay heat, reactors need cooling after the shutdown of the fission reactions. A loss of the ability to remove decay heat caused the Fukushima accident.
-
The Ikata Nuclear Power Plant, a pressurized water reactor that cools by utilizing a secondary coolant heat exchanger with a large body of water, an alternative cooling approach to large cooling towers.
-
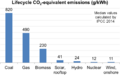
Life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions of electricity supply technologies, median values calculated by IPCC.
-
Schematic of the ITER tokamak under construction in France.
See also
 In Spanish: Energía nuclear para niños
In Spanish: Energía nuclear para niños