Organ (music) facts for kids


In music, an organ is a keyboard instrument. It makes sound by pushing air through pipes or by using electronics. Organs are often found in churches. You might also see them in old movie theatres. A person who plays the organ is called an organist.
There are different kinds of organs:
- Pipe organs: These are the oldest type. They use real pipes and air.
- Water organs: Similar to pipe organs, but they use water flow to make air move.
- Mechanical organs: These are powered by a crank. Examples include street organs and fairground organs.
- Electric organs: A newer type that uses an electric motor to move air.
- Electronic organs: The newest type. They use electronics to create sounds.
Contents
Pipe Organs: The King of Instruments

The pipe organ is often called the "King of instruments." It is known for its huge size and amazing sound. Pipe organs have been around in their current form since the 1300s. Some older designs, like the hydraulic organ, existed even in ancient times. Before the Industrial Revolution, the pipe organ was one of the most complex things people had ever built.
Pipe organs can be small, with just one keyboard. Or they can be massive, with over 10,000 pipes! A big modern organ usually has three or four keyboards. These are called manuals. Each manual has 61 notes. There is also a pedalboard for the feet. It usually has 32 notes.
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart gave the organ its "King of instruments" nickname. Some very large organs have pipes that are 64 feet long. These pipes can make incredibly deep sounds. What makes the organ special is its huge range of sound. It can play the softest whisper or a powerful, full sound. An organist can hold these sounds for a long time. For example, the Wanamaker Organ in Philadelphia, USA, sounds like three symphony orchestras playing at once!
Another cool thing about pipe organs is how their sounds mix. Each set of pipes can play at the same time as others. The sounds blend together in the room, not inside the instrument. This is different from digital organs, where the sound comes from speakers.
Church Organs

repaired in Jerusalem (2009).
Most organs in places like North America and Europe are used in Christian and Jewish religious services. These are called church organs. Organs started being used in churches around the 600s. The organ is perfect for supporting human voices. It can play low notes, support singing voices, and add bright sounds. This helps congregations, choirs, or solo singers. Church services often include solo organ music too. This is played at the start (prelude) and end (postlude) of the service.
Chamber Organs
A chamber organ is a small pipe organ. It often has only one keyboard. Sometimes, it doesn't have separate pipes for the foot pedals. These organs are made for small rooms. They can fill a small space with sound. Chamber organs are usually played with music made just for them. This is because they don't have as many sound options as bigger pipe organs. They have a unique, more personal sound.
Theatre Organs
The theatre organ was made to play music for silent movies. It was designed to sound like a whole orchestra. But it also has many extra features. These include percussion sounds and special effects. This gives the theatre organist more options. Theatre organs usually take up less space than regular organs. They use special techniques to make a bigger sound from fewer pipes.
One technique is called "unification." This means that instead of having a separate pipe for every single note at every pitch, some pipes are shared. For example, a classical organ might have 183 pipes for certain sounds. A theatre organ might get the same sounds from only 85 pipes. This makes the organ smaller but still powerful.
Other Pipe Organs
The bamboo organ, called Bambuso sonoro, is a special instrument. It was designed by Hans van Koolwijk. This instrument has 100 flutes, all made from bamboo.
Reed Organs
Before electronic organs, reed organs were very common. These include the harmonium. They make sound using reeds, like a piano accordion. Reed organs were smaller and cheaper than pipe organs. They were also easier to move. Many small churches and homes used them. However, their sound volume and variety were limited. Most had only one or two keyboards. Foot pedals were very rare.
Chord Organs
The chord organ was invented in 1950 by Laurens Hammond. It had special buttons for the left hand to play chords. This was similar to an accordion. Other companies also made chord organs.
Electronic Organs

Since the 1930s, electric organs have been made without pipes. They create similar sounds to pipe organs. They also play similar roles. Many churches and musicians bought them. They were much smaller and cheaper than pipe organs. Many were even portable. This allowed organ music to be played in homes and dance bands. Electronic organs have mostly replaced reed organs.
Hammond Organs

The Hammond organ was the first successful electric organ. It came out in the 1930s. It used spinning metal wheels, called tonewheels, to make sounds. It had special sliders called drawbars. These let you change the volume of different sounds. You could also create vibrato effects. The drawbars let players choose sound levels for different parts of the sound.
The most popular Hammond models were the B-3, C-3, and A-100. They all had the same sound parts inside. The B-3 had legs. The C-3 was a church model. The A100 had built-in speakers.
Hammond organs were first made for churches. But the B-3 model became very popular in jazz, especially soul jazz. It was also big in gospel music. Since these styles influenced rock and roll, the Hammond organ became a key part of rock music. Bands like The Doors, Pink Floyd, and Deep Purple used it a lot in the 1960s and 1970s. Its popularity grew again around 2000. This was partly because new, lighter versions became available.
Other Electronic Organs
Some organs used oscillators instead of mechanical parts to make sound. These were even cheaper and easier to carry than the Hammond. They could also bend pitches.
From the 1940s to the 1970s, small organs were sold. They made traditional organ sounds simpler. These instruments were like early versions of modern portable keyboards. They had one-touch chords, rhythms, and other electronic helpers. Lowrey was a top maker of these smaller organs.
In the 1960s and 1970s, a simple, portable electronic organ called the combo organ was popular. Rock and pop bands loved them. They had a unique sound that was famous in that era's music. Bands like The Doors and Led Zeppelin used them. The most popular combo organs were made by Farfisa and Vox.
Digital Organs
New computer chips changed electronic keyboard instruments. Digital organs have been sold since the 1970s. They use advanced technology to create sound. This includes sampling (using recordings of real sounds) and physical modelling synthesis (creating sounds by copying how instruments work).
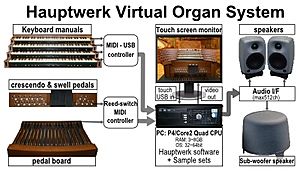
Virtual Pipe Organs are played using MIDI. They use samples (recorded sounds) of real pipe organs. These samples are stored on a computer. This is different from other digital organs. Those organs use special computer parts inside the instrument to make sounds.
With stereo sound systems, virtual organs can sound very much like real pipe organs. For example, virtual organs that have deep 16-foot or 32-foot pipe sounds need a subwoofer. This helps create the powerful low-frequency sounds. For personal use, small studio speakers with a subwoofer are often used.
Steam Organ: The Calliope
The calliope is a special organ. It uses pressurized steam instead of air to make sound. It was invented in the United States in the 1800s. Calliopes usually have a very loud and clear sound. They are often used outdoors. Many calliopes have been built on wheels, so they can be moved around.
Historical Organs
Other Instruments Like Organs
Reed Organs (More Types)
- Harmonium: Also called a parlor organ. It's a reed instrument. It usually has many stops and two foot pedals to pump air.
- American reed organ: Similar to the harmonium. It uses foot pedals or electricity to suck air through reeds.
- Melodeon: A reed instrument with an air tank and foot pedals. It was popular in the USA in the mid-1800s.
Squeezeboxes
- Squeezeboxes: These are free reed instruments. They include the accordion, concertina, and Bandoneón. The player squeezes bellows to make sound.
Mechanical Organs
- Barrel organ: Made famous by organ grinders. The smaller ones are portable. Larger ones sometimes have keyboards for people to play.
- Other special instruments work in similar ways:
- Orchestrion, fairground organ (or band organ in the USA), Dutch street organ, and Dance organ. These pipe organs use a "piano roll" or other mechanical parts to play pre-recorded songs instead of a keyboard.
-
A barrel organ.
-
An Orchestrion from Germany.
-
A band organ from the USA.
Images for kids
-
An old drawing of an organ from the Utrecht Psalter.
-
A harmonium. You pump the pedals at the bottom to make air move.
-
The organ in St Giles' Cathedral.
See also
 In Spanish: Órgano (instrumento musical) para niños
In Spanish: Órgano (instrumento musical) para niños