Orinoco facts for kids
The Orinoco River is a very important river in northern South America. It's one of the longest rivers on the continent, stretching about 2,140 kilometers (1,330 miles). The area it drains, called the Orinoquia, is huge! It covers about 880,000 square kilometers (340,000 square miles). Most of this area (about 76%) is in Venezuela, and the rest is in Colombia.
The Orinoco and its smaller rivers (called tributaries) are like a main highway for eastern and central Venezuela, and for the flat grasslands (called llanos) in Colombia. The Orinoco area is also super important for nature and animals. It's the only place where the rare Orinoco crocodile lives. There are fewer than 250 of these crocodiles left in the wild, making them one of the rarest reptiles on Earth. You can also find Amazon river dolphins swimming in its waters.
Quick facts for kids Orinoco |
|
| Río Orinoco | |
| River | |
|
Panorama of the Orinoco River
|
|
| Countries | Venezuela, Colombia |
|---|---|
| District | South America |
| Source | |
| - location | Cerro Delgado-Chalbaud, Parima Mountains, Venezuela & Brazil |
| - elevation | 1,047 m (3,435 ft) |
| - coordinates | 02°19′05″N 63°21′42″W / 2.31806°N 63.36167°W |
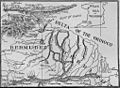
| Mouth | Delta Amacuro |
| - location | Atlantic Ocean, Venezuela |
| - elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| - coordinates | 8°37′N 62°15′W / 8.617°N 62.250°W |
| Length | 2,140 km (1,330 mi) |
| Basin | 880,000 km² (339,770 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 33,000 m³/s (1,165,384 cu ft/s) |
Contents
History of Exploration
The place where the Orinoco River meets the sea (its mouth) was first seen by Christopher Columbus. He recorded it on August 1, 1498.
However, the very beginning of the river (its source) was not explored by non-native people until much later. A team from France and Venezuela finally explored it in 1951, which was 453 years after Columbus saw the mouth!
In the 1500s, German explorers like Ambrosius Ehinger explored the delta area. They also explored the smaller rivers in the eastern grasslands. Later, in 1800, a famous explorer named Alexander von Humboldt explored the Orinoco basin. He wrote a lot about the plants and animals he found, and he even mentioned the river dolphins.
Geography of the Orinoco
The Orinoco River flows in a wide curve that goes around the Guiana Shield. The river starts high up in the Parima Mountains. This spot is called Cerro Delgado-Chalbaud, and it's right on the border between Venezuela and Brazil. It's about 1,047 meters (3,435 feet) high.
The river can be divided into four main parts:
- Upper Orinoco — This part is about 242 kilometers (150 miles) long. It flows through mountains in a northwest direction. It ends at the rapids called Raudales de Guaharibos.
- Middle Orinoco — This section is about 750 kilometers (466 miles) long. At first, it flows west until it meets the Atabapo and Guaviare rivers. Then, it turns north and flows along the border between Venezuela and Colombia. This part of the river is surrounded by the mountains of the Guiana Shield. It ends at the Atures rapids, near where the Meta joins it.
- Lower Orinoco — This part is about 959 kilometers (596 miles) long. It has a wide, flat area made of river deposits. It flows northeast from the Atures rapids down to a town called Piacoa.
- Delta Amacuro — This is the last part, about 200 kilometers (124 miles) long. Here, the river splits into hundreds of smaller rivers and waterways, forming a huge delta. This delta empties into the Gulf of Paría and the Atlantic Ocean.
The Orinoco delta is a massive area of swampy forests, covering about 41,000 square kilometers (15,800 square miles). At its widest, the delta is about 370 kilometers (230 miles) across. During the rainy season, the Orinoco River can get very wide, up to 22 kilometers (14 miles) across, and very deep, sometimes 100 meters (328 feet) deep!
The islands of Trinidad and Tobago are located off the coast of the delta. They are separated from the mainland by the Columbus Channel.
Major Rivers in the Orinoco Basin
Most of the important rivers in Venezuela are tributaries (smaller rivers that flow into a larger one) of the Orinoco. The largest one is the Caroní, which joins the Orinoco at Puerto Ordaz.
The Orinoco River is actually connected to the Amazon River! This happens through a natural canal called the Casiquiare canal. This canal is a "distributary" of the Orinoco, meaning it's a branch that flows away from the main river. The Casiquiare canal flows into the Rio Negro, which then flows into the Amazon.
Here are some other important rivers that flow into the Orinoco:
- Apure: Flows from Venezuela east into the Orinoco.
- Arauca: Flows from Colombia to Venezuela, then east into the Orinoco.
- Atabapo: Flows from the Guiana Highlands in Venezuela north into the Orinoco.
- Caroní: Flows from the Guiana Highlands in Venezuela north into the Orinoco.
- Caura: Flows from eastern Venezuela (Guiana Highlands) north into the Orinoco.
- Guaviare: Flows from Colombia east into the Orinoco.
- Inírida: Flows from Colombia southeast into the Guaviare.
- Meta: Flows from Colombia, along the border with Venezuela, then east into the Orinoco.
- Ventuari: Flows from eastern Venezuela (Guiana Highlands) southwest into the Orinoco.
- Vichada: Flows from Colombia east into the Orinoco.
Economics and Resources
Boats can travel on the Orinoco River for most of its length. Large ocean ships can travel as far as Ciudad Bolívar, which is about 435 kilometers (270 miles) upstream from the mouth. Smaller river steamers carry cargo even further, all the way to Puerto Ayacucho.
There are rich iron ore deposits in the Orinoco delta. Iron ore is a rock from which we get iron. This deposit was discovered in 1926, south of the town of San Felix, on a mountain called El Florero. Mining for iron began there after World War II. In the early 1950s, about 10,000 tons of soil containing iron ore were being mined every day!
The Orinoco area also has large amounts of tar sands. These are sands that contain a very thick, heavy form of oil. These tar sands in the Orinoco Belt could be an important source of oil in the future.
Images for kids
-
Orinoco River at its confluence with the Caroní River (lower left)
-
Union of the Orinoco with the Caroní River
See also
 In Spanish: Río Orinoco para niños
In Spanish: Río Orinoco para niños
 | Valerie Thomas |
 | Frederick McKinley Jones |
 | George Edward Alcorn Jr. |
 | Thomas Mensah |