Rocket facts for kids
A rocket is a special kind of vehicle. It can be a missile, a spacecraft, or even an aircraft. What makes a rocket special is how it moves: it's pushed forward by a powerful rocket engine.
Some very large rockets are called launch vehicles. These are used to send things into space. Some rockets carry people, like the famous Saturn V rocket that went to the Moon. These are called "manned" rockets, meaning a person is inside. Other rockets, like many missiles, do not have people in them. They are called "unmanned" rockets.
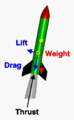
Most rockets can take off right from the ground. This is because the force from their engine, called thrust, is stronger than the rocket's weight on Earth. Many rockets are used to carry satellites into orbit around Earth. Some special rockets, like ion thrusters, are not strong enough to lift themselves from Earth. They start working only after other rockets carry them into outer space.
The idea of rockets first came from the Chinese. They used gunpowder to make the first rockets. These early rockets looked like arrows and were not very fast. Today, most rockets still work in a similar way. They create a lot of fire and hot gases. These hot gases expand and shoot out from the back of the rocket. This push makes the rocket move forward.
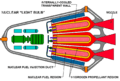
Rockets can use different kinds of fuel. Many rockets use solid fuel to create their fire. The largest and most powerful rockets often use liquid fuel. Liquid fuel makes a much hotter fire, which gives the rocket more power. However, handling liquid fuel can be tricky and costly. Some rockets that launch satellites use both solid and liquid fuels.
Rockets are also used for other things, like fireworks and weapons. In outer space, small rockets help spacecraft move and change direction.
Manned rockets, which carry people, are built to be very smooth. They limit how fast they speed up (their acceleration) and how much they shake (their vibration). This keeps the people inside safe and comfortable. Unmanned rockets, however, don't need to worry about human limits. They can speed up and shake much more.
Some rockets fly incredibly fast. They can go faster than the speed of sound. This speed is also known as Mach 1 or 1,200 km/h or 760 mph. Rockets that go into Low Earth orbit travel at speeds of about 30,000 km/h (19,000 mph).
Yuri Gagarin was a Soviet cosmonaut. On April 12, 1961, he made history by becoming the first human to fly into outer space. He traveled in an R-7 rocket, launched by the Soviet Union.
Famous Rocket Pioneers
Many smart people helped make rockets what they are today. Here are some of the most famous:
Images for kids
-
A Soyuz-FG rocket launches from "Gagarin's Start" (Site 1/5), Baikonur Cosmodrome
-
Rocket arrows depicted in the Huolongjing: "fire arrow", "dragon-shaped arrow frame", and a "complete fire arrow"
-
Mysorean rockets and rocket artillery used to defeat an East India Company battalion during the Battle of Guntur.
-
William Congreve at the bombardment of Copenhagen (1807) during the Napoleonic Wars
-
A battery of Soviet Katyusha rocket launchers fires at German forces during the Battle of Stalingrad, 6 October 1942
-
V-2 rocket launched from Test Stand VII, summer of 1943
-
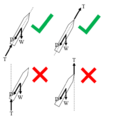
Illustration of the pendulum rocket fallacy. Whether the motor is mounted at the bottom (left) or top (right) of the vehicle, the thrust vector (T) points along an axis that is fixed to the vehicle (top), rather than pointing vertically (bottom) independent of vehicle attitude, which would lead the vehicle to rotate.
-
Workers and media witness the Sound Suppression Water System test at Launch Pad 39A.
-
Apollo 6 while dropping the interstage ring
-
Space Shuttle Atlantis during launch phase
-
Space Shuttle Challenger torn apart T+73 seconds after hot gases escaped the SRBs, causing the breakup of the Shuttle stack
See also
 In Spanish: Cohete para niños
In Spanish: Cohete para niños