Shiva Temple (Grand Canyon) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Shiva Temple |
|
|---|---|

South aspect, from South Rim
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 7,646 ft (2,331 m) |
| Prominence | 1,351 ft (412 m) |
| Isolation | 2.65 mi (4.26 km) |
| Parent peak | Dragon Head (7,765 ft) |
| Geography | |
| Location | Grand Canyon Coconino County, Arizona, US |
| Parent range | Kaibab Plateau Colorado Plateau |
| Topo map | USGS Shiva Temple |
| Type of rock | Kaibab Limestone Coconino Sandstone |
| Climbing | |
| Easiest route | class 4 climbing |
Shiva Temple is a tall mountain peak in the Grand Canyon. It stands 7,646 feet (2,331 meters) high. You can find it in Coconino County, Arizona, in the southwestern United States.
This impressive peak is about six miles north of Hopi Point, a popular viewpoint on the canyon's South Rim. It rises an amazing 5,200 feet (1,585 meters) above the Colorado River below.
Shiva Temple got its name from Shiva, a powerful Hindu god. Clarence Dutton started the tradition of naming Grand Canyon features after gods and goddesses. He thought Shiva Temple was the biggest and most majestic of all the canyon's peaks. Its top is wide, flat, and covered in trees. The name was officially approved in 1906.
In 1937, scientists from the American Museum of Natural History explored Shiva Temple. They thought that because these peaks were isolated for a very long time, new kinds of animals might have evolved there. The scientists found old ruins from the Anasazi people. They also found deer antlers and an empty film box left by an explorer named Emery Kolb. However, they did not find any new animal species.
Shiva Temple has a Cold semi-arid climate. This means it is generally dry, but not extremely hot.
What is Shiva Temple Made Of?
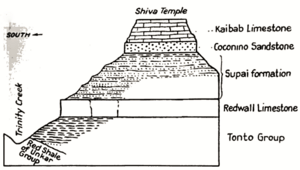
The very top of Shiva Temple is made of a rock called Kaibab Limestone. This rock formed during the Permian period. Below it is a cream-colored rock called Coconino Sandstone. This sandstone forms tall cliffs.
The Coconino Sandstone is one of the younger rock layers in the Grand Canyon. It was formed about 265 million years ago from ancient sand dunes. Below this sandstone are reddish layers of rock called the Supai Group. These formed during the Pennsylvanian and Permian periods.
Even further down, you can find Redwall Limestone, which formed during the Mississippian period. The lowest layers are part of the Tonto Group, which formed during the Cambrian period. Rainwater flows off Shiva Temple and drains into the Colorado River through smaller streams.
Plants and Animals on the Plateau
The flat top of Shiva Temple is like a small plateau. It has a forest of Ponderosa Pine trees. You can also find other pines, juniper trees, shrubs, and cacti growing there.
During the 1937 expedition, scientists saw several animals. These included chipmunks, cottontail rabbits, pack rats, different types of mice, and rock squirrels.
Gallery
Images for kids