Coconino County, Arizona facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
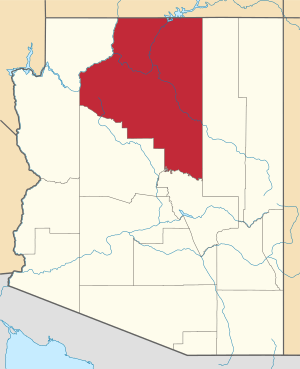
Coconino County
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

Old Coconino County Courthouse in Flagstaff
|
|||
|
|||
Location within the U.S. state of Arizona
|
|||
 Arizona's location within the U.S. |
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| Founded | February 18, 1891 | ||
| Named for | Hopi designation for the Havasupai, Hualapai, and/or Yavapai tribes | ||
| Seat | Flagstaff | ||
| Largest city | Flagstaff | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 18,661 sq mi (48,330 km2) | ||
| • Land | 18,619 sq mi (48,220 km2) | ||
| • Water | 43 sq mi (110 km2) 0.2% | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 145,101 | ||
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
144,472 |
||
| • Density | 7.77563/sq mi (3.00219/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−7 (Mountain) | ||
| Congressional district | 2nd | ||



Coconino County is a large county in the north-central part of Arizona. It is home to about 145,000 people. The main city and county seat is Flagstaff.
The county's name comes from Cohonino, a name for the Havasupai people. Coconino County is the second-largest county by land area in the contiguous United States. It covers over 18,600 square miles, which is bigger than nine smaller U.S. states combined!
This county includes famous places like Grand Canyon National Park. It also has parts of the lands belonging to the Navajo, Hualapai, and Hopi nations. Because of this, almost 30% of the people living here are Native American.
Did you know that Coconino County was the setting for the old Krazy Kat comic strip?
Contents
History of Coconino County
After the Atlantic & Pacific Railroad was finished in 1883, the northern part of Yavapai County started to grow quickly. People in the northern areas found it hard to travel all the way to Prescott for county business.
They wanted their own county. So, in 1887, they asked to create a new county called Frisco County. This didn't happen, but in 1891, Coconino County was officially formed. Flagstaff was chosen as its county seat.
Geography and Nature
Coconino County is huge! It covers about 18,661 square miles. Most of this is land, with a small amount of water. It's the largest county in Arizona and the second largest in the entire United States (not counting Alaska). It's bigger than states like Connecticut, Delaware, and Hawaii.
The highest point in Coconino County, and all of Arizona, is Humphreys Peak. It stands tall at 12,637 feet (3,852 meters). You can also find the famous Barringer Meteor Crater here, which was formed by a meteor impact.
Neighboring Counties
Coconino County shares borders with these other counties:
- Mohave County – to the west
- Yavapai County – to the south
- Gila County – to the south
- Navajo County – to the east
- San Juan County, Utah – to the northeast
- Kane County, Utah – to the north
Native American Reservations
Coconino County has a large area of federally recognized Indian reservations, covering over 7,100 square miles. These include lands for the Navajo, Hualapai, Hopi, Havasupai, and Kaibab tribes. The Havasupai Reservation is completely within Coconino County.
National Parks and Forests
Many beautiful and protected natural areas are found in Coconino County. These include:
- Apache-Sitgreaves National Forest (part)
- Coconino National Forest (part)
- Glen Canyon National Recreation Area (part)
- Grand Canyon National Park (part)
- Kaibab National Forest (part)
- Prescott National Forest (part)
- Sunset Crater Volcano National Monument
- Vermilion Cliffs National Monument
- Walnut Canyon National Monument
- Wupatki National Monument
People of Coconino County
Coconino County has grown a lot over the years. Here's how its population has changed:
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1900 | 5,514 | — | |
| 1910 | 8,130 | 47.4% | |
| 1920 | 9,982 | 22.8% | |
| 1930 | 14,064 | 40.9% | |
| 1940 | 18,770 | 33.5% | |
| 1950 | 23,910 | 27.4% | |
| 1960 | 41,857 | 75.1% | |
| 1970 | 48,326 | 15.5% | |
| 1980 | 75,008 | 55.2% | |
| 1990 | 96,591 | 28.8% | |
| 2000 | 116,320 | 20.4% | |
| 2010 | 134,421 | 15.6% | |
| 2020 | 145,101 | 7.9% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 144,472 | 7.5% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010–2020 |
|||
In 2010, about 134,421 people lived in the county. The population is quite diverse. Many people are White, and a large number are American Indian, especially from the Navajo tribe. Other groups include people of German, Mexican, English, and Irish backgrounds.
The average age of people in the county was about 31 years old.
Communities in Coconino County
Cities
- Flagstaff (This is the county seat, where the main government offices are)
- Page
- Sedona (most of this city is in Yavapai County)
- Williams
Towns
Census-Designated Places (CDPs)
These are areas that are like towns but are not officially incorporated as cities or towns.
- Bellemont
- Bitter Springs
- Blue Ridge
- Cameron
- Doney Park
- Forest Lakes
- Fort Valley
- Grand Canyon Village
- Greenehaven
- Kachina Village
- Kaibab Estates West
- Kaibito
- LeChee
- Leupp
- Moenkopi
- Mormon Lake
- Mountain View Ranches
- Mountainaire
- Munds Park
- Oak Creek Canyon
- Parks
- Red Lake
- Supai
- Timberline-Fernwood
- Tolani Lake
- Tonalea
- Tuba City
- Valle
- Winslow West (mostly in Navajo County)
Other Communities
- Big Springs
- Gray Mountain
- Happy Jack
- Jacob Lake
- Marble Canyon
- North Rim
- Rare Metals
- Robbers Roost
- Ryan
- Winona
Ghost Towns
These are towns that used to be active but are now mostly abandoned.
Native American Reservations (Communities)
- Havasupai Indian Reservation
- Hopi Reservation
- Hualapai Indian reservation
- Kaibab Indian Reservation
- Navajo Nation
Population Ranking of Communities
This table shows how many people lived in the main communities in 2010.
| Rank | City/town/etc. | Population (2010 Census) | Municipal type | Incorporated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | † Flagstaff | 65,870 | City | 1928 |
| 2 | Sedona (mostly in Yavapai County) | 10,031 | City | 1988 |
| 3 | Tuba City | 8,611 | CDP | |
| 4 | Page | 7,247 | City | 1975 |
| 5 | Doney Park | 5,395 | CDP | |
| 6 | Williams | 3,023 | City | 1901 |
| 7 | Kachina Village | 2,622 | CDP | |
| 8 | Grand Canyon Village | 2,004 | CDP | |
| 9 | Kaibito | 1,522 | CDP | |
| 10 | LeChee | 1,443 | CDP | |
| 11 | Fredonia | 1,314 | Town | 1956 |
| 12 | Parks | 1,188 | CDP | |
| 13 | Mountainaire | 1,119 | CDP | |
| 14 | Moenkopi | 964 | CDP | |
| 15 | Leupp | 951 | CDP | |
| 16 | Cameron | 885 | CDP | |
| 17 | Valle | 832 | CDP | |
| 18 | Fort Valley | 779 | CDP | |
| 19 | Munds Park | 631 | CDP | |
| 20 | Tusayan | 558 | Town | 2010 |
| 21 | Tonalea | 549 | CDP | |
| 22 | Bitter Springs | 452 | CDP | |
| 23 | Winslow West (mostly in Navajo County) | 438 | CDP | |
| 24 | Tolani Lake | 280 | CDP | |
| 25 | Supai | 208 | CDP | |
| 26 | Kaibab (mostly in Mohave County) | 124 | CDP |
Economy and Jobs
Many people in Coconino County work in different areas. Some of the biggest employers include:
- Northern Arizona University
- W. L. Gore & Associates (a manufacturing company)
- Flagstaff Medical Center (a hospital)
- Flagstaff Unified School District (schools)
- Aramark (food and facility services)
- Coconino County government
- City of Flagstaff government
- National Park Service (managing national parks)
- Page Unified School District 8
- State of Arizona government
- Grand Canyon Railway (a tourist train)
- Haven of Flagstaff (healthcare)
- Salt River Project (utility company)
- United States Forest Service (managing national forests)
- Walmart
Many jobs in the county are related to tourism, like hotels and restaurants, because of the Grand Canyon and other natural attractions. Healthcare, education, and government jobs are also very important.
Transportation
Coconino County is an important place for travel. Major highways cross through it, connecting different parts of Arizona and other states.
Major Highways
 I-17
I-17 I-40
I-40 I-40 BL
I-40 BL US 66
US 66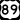 US 89
US 89 US 89A
US 89A US 160
US 160 US 180
US 180 State Route 64
State Route 64 State Route 87
State Route 87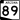 State Route 89
State Route 89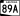 State Route 89A
State Route 89A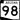 State Route 98
State Route 98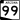 State Route 99
State Route 99 State Route 260
State Route 260 State Route 264
State Route 264
Airports
- The Grand Canyon National Park Airport is a public airport near the South Rim of the Grand Canyon in Tusayan.
- Flagstaff Pulliam Airport is another public airport south of Flagstaff. It's used for general flights and has some commercial airlines.
Bus and Train Services
- Greyhound Bus Lines has a station in Flagstaff, offering bus trips across the country.
- Amtrak has a train station in Flagstaff. You can take the Southwest Chief train east towards Chicago or west towards Los Angeles.
- The Grand Canyon Railway is a special tourist train that connects Williams to the Grand Canyon's South Rim. It runs almost every day.
- The Mountain Line provides local bus service in the Flagstaff area.
Education
Coconino County has many schools and colleges.
School Districts (K-12)
- Ash Fork Joint Unified School District
- Flagstaff Unified School District
- Fredonia-Moccasin Unified School District
- Grand Canyon Unified School District
- Page Unified School District
- Sedona-Oak Creek Unified School District
- Tuba City Unified School District
- Williams Unified School District
Elementary School Districts
- Chevelon Butte School District
- Maine Consolidated School District
Some areas on Native American reservations are in "Unorganized School Districts." This means they don't have a high school within that specific district.
Charter Schools
- Flagstaff Arts and Leadership Academy
- Northland Preparatory Academy
Bureau of Indian Education (BIE) Schools
These schools are run by or connected to the Bureau of Indian Education.
- Greyhills Academy High School
- Havasupai Elementary School
- Kaibeto Boarding School
- Leupp Schools, Inc.
- Tuba City Boarding School
Colleges and Universities
- Coconino County Community College
- Diné College (Tuba City Center)
- Northern Arizona University
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Coconino para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Coconino para niños