Soviet Union in World War II facts for kids

The Soviet Union played a huge role in World War II, especially on the Eastern Front. This was where most of the fighting happened against Nazi Germany. Before the war, the Soviet Union signed a special agreement with Germany called a non-aggression pact. This meant they promised not to attack each other. However, Germany broke this promise and invaded the Soviet Union in 1941. This led to some of the biggest and deadliest battles in history.
The Soviet Union fought hard and pushed back the German army. They received help from countries like the United States and Britain. Soviet leaders also met with Allied leaders to plan how to defeat Germany. After many years of fierce fighting, the Soviet army marched all the way to Berlin, the capital of Germany. Germany surrendered in May 1945. The Soviet Union also joined the war against Japan in August 1945, which helped end World War II. The war caused a lot of suffering and loss for the Soviet people, but it also made the Soviet Union a very powerful country.
Contents
The Start of the War: A Surprising Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact Explained
In the 1930s, the Soviet Union tried to work with Western countries like France and Czechoslovakia. They wanted to stop Adolf Hitler and Nazi Germany from expanding. But after the Munich Agreement, which allowed Germany to take parts of Czechoslovakia, the Soviet Union changed its mind. They decided to try to make a deal with Germany instead.
On August 23, 1939, the Soviet Union and Germany signed a non-aggression pact. This was a secret agreement where they promised not to attack each other. It also secretly divided parts of Eastern Europe between them. The Soviet Union would get eastern Poland, Latvia, Estonia, and Finland. Later, Lithuania and parts of Bessarabia (in Romania) were also added to the Soviet side.
This pact was signed after talks between the Soviet Union, Britain, and France failed. Germany offered the Soviets better terms. German officials even said that Germany and the Soviet Union shared a common idea: being against the capitalist countries of the West. Some historians believe that Soviet leader Joseph Stalin signed the pact to gain time. He wanted to make his army stronger before a possible war with Hitler. He also wanted to move Soviet borders further west.
Dividing Eastern Europe and Other Invasions
On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. This started World War II. On September 17, the Red Army (Soviet army) invaded eastern Poland. They took the land that was secretly agreed upon in the pact. Later, the pact was changed. Germany got more of Poland, and the Soviet Union got most of Lithuania.
The Soviets also took many Polish prisoners. Some of these prisoners, especially military officers and intellectuals, were later killed in what is known as the Katyn massacre.
In August 1939, Stalin decided to take control of the Baltic states: Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia. He forced them to sign "mutual assistance" treaties. In November 1939, the Soviet Union invaded Finland in the Winter War. Finland fought back bravely, and the Soviets suffered heavy losses. Eventually, Finland had to give up some land to the Soviet Union.
In June 1940, while Germany was invading France, Soviet troops raided border posts in the Baltic countries. Stalin claimed the treaties were broken. He gave these countries only six hours to form new governments chosen by the Soviets. Many people were deported or killed. New elections were held with only pro-Soviet candidates. These countries then joined the Soviet Union. In June 1940, the Soviets also took Bessarabia and northern Bukovina from Romania.
Stalin even considered joining the Axis Powers (Germany, Japan, Italy) in 1940. He sent his foreign minister to Berlin to discuss it. But the talks broke down because Stalin wanted control over too many areas. Hitler then secretly planned to invade the Soviet Union.
To show peaceful intentions towards Germany, Stalin signed a neutrality pact with Japan in April 1941. He knew this pact was important for political reasons. He wanted to make Germany think the Soviets were friendly. But Stalin also knew that a war with Hitler was likely.
Germany Attacks: Operation Barbarossa
The Pact Ends
On June 22, 1941, Hitler broke the pact and launched Operation Barbarossa. This was a massive invasion of the Soviet Union. It started the war on the Eastern Front. Before the invasion, Stalin thought Germany would not attack until Britain was defeated. But Soviet generals and spies warned him that Germany was gathering forces on the border.
Even with these warnings, Stalin did not order a full army mobilization. He thought it might provoke Hitler to attack sooner. He wanted to delay the war until 1942 to make his forces stronger.
When the German attack began, Stalin was unsure if it was a full invasion or just a rogue general's action. Some accounts say he was in despair for days. But other records show he was still giving orders. Stalin quickly took charge of the entire Soviet war effort. He became the highest military leader.
In the first three weeks, the Soviet Union suffered huge losses. They lost many soldiers, tanks, and aircraft. Stalin completely reorganized the military. He took direct control of many military groups. He had more control over his country's war effort than any other leader in World War II.
The Germans made huge advances. They killed millions of Soviet soldiers. For example, in the Battle of Kiev, over 600,000 Soviet troops were killed or captured. By the end of 1941, the Soviet military had lost 4.3 million soldiers. The Germans captured 3 million Soviet prisoners. Many of these prisoners died in German camps.
Stopping the German Advance
Even though the Germans advanced far, Stalin made sure the Red Army protected Leningrad. This city was under siege for a very long time. More than a million Soviet soldiers and civilians died there, many from starvation. But the city held.
Stalin was confident that the Allies would eventually win. In September 1941, he told British diplomats he wanted two things: a mutual assistance pact and recognition that the Soviet Union would keep the lands it took from the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact. The British agreed to help but not to the land gains at first.
Stalin correctly guessed that Hitler would try to capture Moscow. He moved many divisions from the east to defend the city. By December, Hitler's troops were very close to Moscow. But on December 5, the Soviets launched a counterattack. They pushed the Germans back about 80 kilometers. This was the first major defeat for the German army in the war.
In early 1942, the Soviets launched more attacks. But these got stuck in the mud from spring rains. Stalin's attempt to retake Kharkov in Ukraine ended badly. Over 200,000 Soviet soldiers were lost. Stalin blamed his generals.
Hitler then changed his main goal. He wanted to secure the southern Soviet Union to get oil fields. Stalin thought this was just a trick to take Moscow. The German southern campaign began with a push to capture Crimea. This was another disaster for the Red Army. The Germans captured 625,000 Soviet prisoners in July and August 1942 alone.

The Germans then started another southern operation in autumn 1942: the Battle of Stalingrad. Hitler split his forces to besiege Stalingrad and attack Baku for oil. Stalin ordered his generals to defend Stalingrad at all costs. The Soviets suffered over 2 million casualties there. But their victory, which included surrounding 290,000 Axis troops, was a major turning point in the war.
After a year of war, Stalin reopened churches in the Soviet Union. He might have done this to motivate the Christian population to support the war effort. He allowed the Moscow Patriarchate to be reestablished.
Life as a Soviet Soldier: The Frontoviki
Most Soviet soldiers were called frontoviki, meaning "front fighters." These were the infantrymen who fought on the front lines. Most were young men, aged 19-24, born in the 1920s. They had grown up only knowing the Soviet system.
When called to duty, they reported to a collection point, usually a school. They brought a bag with clothes and tobacco. Then they went to a military center. There, they got uniforms, had their heads shaved, and were given a steam bath to get rid of lice.
Training was tough. It lasted 10-12 hours a day, six days a week. Before 1941, training was six months long. But during the war, it was shortened to just a few weeks. After training, every soldier took an oath to protect the Motherland.
Soviet soldiers were known for their strong defense. They were good at hiding their positions. They would wait until enemy forces were very close before firing. This surprised the enemy. When attacking, they would charge while shouting "Urra!" They would fire their rifles and submachine guns, throw grenades, and then fight hand-to-hand.
The typical frontovik was an ethnic Russian. Their uniforms were simple and practical. They wore olive-brown helmets or side caps. Their weapons were known for being simple, tough, and reliable. The standard rifle was the Mosin-Nagant, which worked well even in the cold. Many soldiers also had the PPSh-41 submachine gun.
Life for a frontovik was very hard. They carried all their belongings in a simple bag. They rarely had soap or toothbrushes. They often slept outdoors, even in winter. Food was usually bad and often in short supply, especially in 1941 and 1942. They ate black rye bread, canned meats, cabbage soup (shchi), and porridge (kasha). Hot sugared tea and vodka were popular drinks. They smoked cheap tobacco rolled into handmade cigarettes.
Medical care was poor. Many wounded soldiers died because there weren't enough doctors or medicines. Diseases like malaria and pneumonia were common. In winter, frostbite was a big problem. In spring and fall, muddy conditions caused trench foot.
Soldiers got paid once a month, but often didn't receive their wages. They were exempt from taxes. Units that fought very well were given the title "Guards." This brought better pay and food.
Discipline was very strict. Soldiers could be executed for deserting or retreating without orders. To keep spirits up, soldiers watched films outdoors and enjoyed musical performances.
Soldiers lived and fought in small foxholes dug into the ground. They usually didn't have blankets or sleeping bags, even in winter. They slept in their coats and shelter-capes. Winter temperatures could drop to -50°C, making the cold as dangerous as the enemy. Spring and fall brought heavy rains, turning battlefields into muddy swamps.
The Soviet Union had over 150 languages. But most soldiers were Russian, and Russian was the language of command. Soldiers from different ethnic groups were usually mixed into units with Russian majorities. Despite differences, combat often brought them together. Jewish soldiers reported little anti-Semitism.
During the war, the Soviet government eased up on anti-religious propaganda. Eastern Orthodox priests blessed units before battle. Many soldiers carried lucky charms or wore crosses, even though the official policy was atheism.
Political officers, called politruks or kommissars, spent time teaching soldiers about Communism. They never used the term "Nazi" for the enemy. Instead, they called them "fascists" or "Hitlerites." These officers also watched soldiers for any signs of disloyalty. In 1942, the system changed. Officers gained full command power, and politruks became deputy commanders for political affairs. They still evaluated loyalty and could order executions for cowardice or treason. But military success became more important than political enthusiasm. Officers and soldiers usually had good relationships. Junior officers were seen as "comrades in arms" because they shared the same dangers.
The Soviet Push to Germany
Turning the Tide

After the victory at Stalingrad, the Soviets went on the offensive for most of the rest of the war. This was a huge turning point.
In 1943, Stalin listened to his generals. They suggested taking a defensive stance because of heavy losses. They predicted that the Germans would attack at Kursk. The Soviets prepared strong defenses there. The Germans did attack at Kursk, but the Soviets successfully pushed them back. This battle was another major victory for the Soviets. After Kursk, Stalin became more willing to listen to his generals' advice.
By the end of 1943, the Soviets had taken back half the land Germany had captured. Soviet factories also greatly increased their production. Stalin had moved many factories to the east, away from German attacks. This helped the Soviets produce more weapons and supplies. Even though the Soviets lost many soldiers, their army grew to 11 million members by the end of 1942.
Meeting the Allies and Advancing West
In November 1943, Stalin met with Churchill and Roosevelt at the Tehran Conference. Roosevelt hoped that Britain and America opening a second front in Western Europe would draw German soldiers away from the Eastern Front. Stalin and Roosevelt pushed for a cross-channel invasion of France. Churchill preferred attacking Italy and the Balkans. They agreed that Britain and America would invade France in May 1944. Stalin also insisted that the Soviet Union would keep the parts of Poland it had taken in the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.
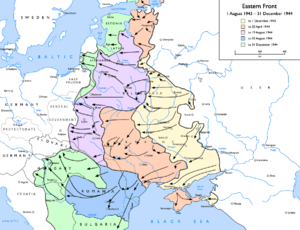
In 1944, the Soviet Union made big advances across Eastern Europe. This included Operation Bagration in Belarus. This massive attack happened around the same time as the American and British invasion of Western Europe (D-Day). Operation Bagration was a huge success. The Soviets retook Belarus and western Ukraine. They also destroyed a large German army group. This came at a cost of over 750,000 Soviet casualties.
The successes in 1944 were due to the Red Army learning from past mistakes. They planned attacks better, used artillery well, and moved more efficiently. The German army was also weaker. They lacked fuel and weapons. The Allies' attacks on the Western Front also helped by forcing Germany to divide its forces.

In late 1944, the Soviets invaded Romania and Bulgaria. They installed communist governments in these countries. Stalin and Churchill met again and agreed on "spheres of influence" in the Balkans. The Red Army also pushed German forces out of Lithuania and Estonia.
The Soviets also fought hard in Finland. They pushed Finnish forces back from land they had gained. Finland and the Soviets signed an armistice in September 1944, ending the Continuation War.
In late 1944, Soviet forces fought fiercely to capture Hungary in the Budapest Offensive. The Germans held out until February 1945. After taking Budapest, the Red Army launched the Vienna Offensive in April 1945. To the northeast, the Soviets launched the huge Vistula–Oder Offensive. They advanced from the Vistula River in Poland to the Oder River in Germany.
Stalin's leadership had its flaws. His early decisions led to huge Soviet losses. But he eventually learned to rely on his professional generals. He also used strong appeals to patriotism and the Russian Orthodox Church to motivate his army.
Final Victory and Its Aftermath
The Fall of Germany

By April 1945, Nazi Germany was collapsing. The Red Army was fighting 1.9 million German soldiers in the East. Western Allied soldiers were fighting 1 million Germans in the West. At the Yalta Conference in February 1945, Stalin successfully argued that Eastern Germany should be in the Soviet "sphere of influence." So, the Western Allies did not plan to capture Berlin by ground.
Stalin remained suspicious. He worried that Western Allied forces might try to take Berlin. He ordered the Red Army to move quickly into Germany. Capturing Berlin became the main goal. After taking Eastern Prussia, three Soviet army groups moved towards Berlin. By April 24, Soviet forces had surrounded Berlin. On April 20, a massive shelling of Berlin began. It continued until the city surrendered.
On April 30, 1945, Hitler and Eva Braun committed suicide. Soviet forces found their remains. German forces officially surrendered on May 7, 1945. Even though the Soviets had Hitler's remains, Stalin did not believe he was truly dead. This belief lasted for years after the war.
The Cost of Victory and War Against Japan
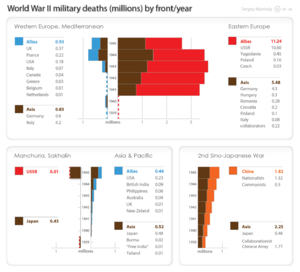
The Soviet Union paid a huge price to defeat Nazi Germany. Around 27 million Soviet people died. This included about 18 million civilians. Millions of soldiers and civilians were taken to German camps or forced to work. Many more suffered permanent physical and mental harm.
The war also caused terrible economic damage. About 70,000 Soviet cities, towns, and villages were destroyed. This included millions of houses, farms, factories, schools, and hospitals.
On August 9, 1945, the Soviet Union invaded Japanese-controlled Manchukuo and declared war on Japan. Experienced Soviet troops quickly conquered Japanese territories in Manchuria, southern Sakhalin, the Kuril Islands, and parts of Korea. Japan was already struggling after the United States dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Faced with the Soviet invasion, Japan surrendered on August 15, 1945. This officially ended World War II.
In June 1945, Stalin was given the new highest military rank: Generalissimus of the Soviet Union. His leadership was celebrated, and his "cult of personality" grew.
Repressions and Hardship
Maintaining Control During War

During the war, Stalin issued harsh orders to keep the Soviet defense system strong. On August 16, 1941, he issued Order No. 270. This order stated that any commanders who deserted or surrendered would be considered traitors. They could be shot on the spot. Their families could also be arrested. The order also said that units surrounded by the enemy must fight to the last.
Stalin also ordered a "scorched earth" policy. As the Red Army retreated, they destroyed infrastructure and food supplies. This was to prevent the Germans from using them. This caused starvation and suffering for the civilians left behind.
Stalin worried that Hitler might use unhappy Soviet citizens against him. So, he ordered the NKVD (Soviet secret police) to deal with the situation. They killed about 100,000 political prisoners in the western Soviet Union. Many others were sent to the east.
In July 1942, Stalin issued Order No. 227, known as "Not a Step Back!" This order said that any commander who allowed retreat without permission would face a military trial. Soldiers found guilty of breaking rules were sent to "penal battalions." These units were sent to the most dangerous parts of the front lines. The order also created "blocking detachments" to shoot fleeing troops. While these measures had some effect at first, they hurt troop morale. So, the idea of regular blocking detachments was later stopped.
Soviet prisoners of war (POWs) and forced laborers who survived German captivity were sent to special "filtration" camps. The Soviets wanted to find out if they were potential traitors. Many were sent home, but others were forced into the army or work battalions. Some were sent to the Gulag (labor camp) system for punishment.