Axis countries facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Axis powers
|
|
|---|---|
| 1936–1945 | |

Celebration of the signing of the Tripartite Pact in Tokyo
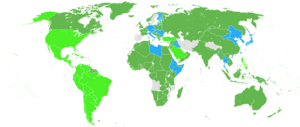
Major Axis powers:
Other Axis states:
|
|
| Status | Military alliance |
| Historical era | World War II |
| 25 November 1936 | |
| 22 May 1939 | |
| 27 September 1940 | |
|
• Defeated
|
2 September 1945 |
|
Footnotes
|
|
The Axis powers were a group of countries that formed a military alliance. They fought against the Allies during World War II. The main countries in this group were Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Imperial Japan.
Contents
How the Axis Powers Formed
The idea of the "Axis" started in the mid-1930s. Italian leader Benito Mussolini first used the word "Axis" in 1936. He said that Italy and Germany were like two poles around which other European countries would turn. This showed their strong connection.
Important Agreements and Pacts
The Axis powers became official through several key agreements:
- Anti-Comintern Pact (1936): This agreement was first signed by Germany and Japan. Its main goal was to stop the spread of communism, especially from the Soviet Union. Italy joined this pact in 1937.
- Pact of Steel (1939): This was a military and political alliance between Germany and Italy. It made their cooperation much stronger.
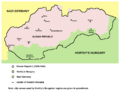
- Tripartite Pact (1940): Germany, Italy, and Japan signed this important pact. It created a promise to defend each other if attacked. This pact also brought other countries into the Axis group, like Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria.
Main Axis Countries
Germany's Role
Under Adolf Hitler, Germany wanted to expand its territory. They broke earlier agreements and took over areas like Austria and Czechoslovakia. Germany used a fast attack method called "blitzkrieg." This led to quick victories across Europe.
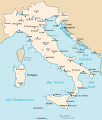
Italy's Role
Italy, led by Mussolini, also wanted to build a larger empire. They invaded countries like Ethiopia and Albania. However, Italy's military often struggled. Their plans were sometimes not well organized or carried out.
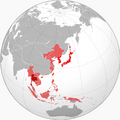
Japan's Role
Japan started expanding by invading Manchuria in 1931. This led to a full war with China in 1937. Japan aimed to control Asia and get important resources. They did this through military actions across the Pacific Ocean.
Other Countries in the Axis
Besides the three main powers, several other countries joined or helped the Axis.
Countries That Joined the Tripartite Pact
After the main three, these countries also signed the Tripartite Pact:
Other Allies and Controlled States
Some countries helped the Axis without officially being part of the main alliance:
- Finland fought against the Soviet Union. They were part of the Siege of Leningrad.
- Thailand also had ties with the Axis powers.
Other areas were controlled by the Axis powers, or were "client states":
The Defeat of the Axis Powers
At their strongest in 1942, the Axis powers controlled huge areas. These included parts of Europe, North Africa, and East Asia. Their military campaigns gained a lot of land. But they also faced strong resistance from the Allied forces.
The war started to turn against the Axis powers. A major defeat was the The Battle of Stalingrad (1942-1943). Here, Soviet forces strongly defeated German troops.
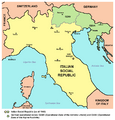
In July 1943, Mussolini was removed from power. Italy then surrendered to the Allies in September 1943. However, German forces continued fighting in northern Italy.
After many defeats, Hitler died on April 30, 1945. Germany surrendered completely on May 8, 1945. After atomic bombs were dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945, Japan surrendered on September 2, 1945. This officially ended World War II.
What Was the Axis Powers' Legacy?
The Axis powers had a huge impact on world history. Their desire for power and control led to widespread destruction during World War II. The war caused millions of deaths and major changes around the world. The defeat of the Axis powers also led to new international groups. These groups, like the United Nations, were created to help prevent future wars.
Images for kids
-
Germany's Führer Adolf Hitler (right) beside Italy's Duce Benito Mussolini (left)
-
Japan's Prime Minister Hideki Tojo (center) with fellow government representatives of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere. To the left of Tojo, from left to right: Ba Maw from Burma, Zhang Jinghui, Wang Jingwei from China. To the right of Tojo, from left to right, Wan Waithayakon from Thailand, José P. Laurel from the Philippines, and Subhas Chandra Bose from India
-
The signing of the Tripartite Pact by Germany, Japan, and Italy on 27 September 1940 in Berlin. Seated from left to right are the Japanese ambassador to Germany Saburō Kurusu, Italian Minister of Foreign Affairs Galeazzo Ciano, and Adolf Hitler.
-
Adolf Hitler, Führer and Reich Chancellor of the German People, 1933–1945
-
Engelbert Dollfuss, Chancellor of Austria, 1932–1934
-
German Führer Adolf Hitler along with General Walther von Brauchitsch, during the victory parade in Warsaw after the defeat of Poland, October 1939
-
German Heinkel He 111 bomber aircraft during the Battle of Britain
-
German vehicles advancing during the Second Battle of El Alamein in the North African campaign
-
German soldiers during the Battle of Stalingrad in the Eastern Front campaign
-
The Duce Benito Mussolini in an official portrait
-
Italian soldiers in the North African Campaign in 1941
-
IJN super-dreadnought battleships Yamashiro, Fusō, and battlecruiser Haruna, Tokyo Bay, 1930s
-
IJN Special Naval Landing Forces armed with the Type 11 Light Machine Gun during the Battle of Shanghai
-
Mitsubishi A6M Zero fighter aircraft and other aircraft preparing for takeoff on the aircraft carrier Shōkaku on 7 December 1941, for the attack on Pearl Harbor
-
IJA paratroopers are landing during the Battle of Palembang, February 13, 1942.
-
IJN Yamato-class Battleships Yamato and Musashi moored in Truk Lagoon, in 1943
-
Japanese Military Attaché, Makoto Onodera, visiting Fjell Fortress in Norway, 1943. Behind him is Lieutenant Colonel Eberhard Freiherr von Zedlitz und Neukrich (C-in-C Luftwaffe Feldregiment 502.), and to the right is Fregattenkapitän doktor Robert Morath (Seekommandant in Bergen). Behind Onoderas hand (raised in salute) is General Nikolaus von Falkenhorst (C-in-C German military forces in Norway).
-
Adolf Hitler meeting with NDH leader Ante Pavelić
-
Ion Antonescu and Adolf Hitler at the Führerbau in Munich (June 1941)
-
Mannerheim with Hitler
-
Front row in order from left to right: Karl Wolff, Heinrich Himmler, Francisco Franco and Spain's Foreign Minister Serrano Súñer in Madrid, October 1940
-
Francisco Franco (centre) and Serrano Súñer (left) meeting with Mussolini (right) in Bordighera, Italy in 1941. At Bordighera, Franco and Mussolini discussed the creation of a Latin Bloc.
-
Phraya Phahon (far left), Thawan Thamrong (left), and Direk Jayanama (right) with Hideki Tōjō (center) in Tokyo 1942
-
Philippe Pétain (left) meeting with Hitler in October 1940
-
An RAF officer investigates wrecked Iraqi artillery near Habbaniya.
-
RSI (Repubblica Sociale Italiana) soldiers, March 1944
See also
 In Spanish: Potencias del Eje en la Segunda Guerra Mundial para niños
In Spanish: Potencias del Eje en la Segunda Guerra Mundial para niños