Sugar Land, Texas facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Sugar Land, Texas
|
||
|---|---|---|
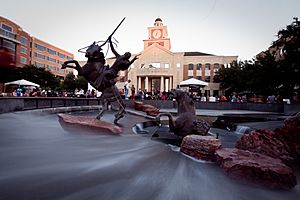
Sugar Land Town Square, First Colony in 2010
|
||
|
||
Location in Fort Bend County, Texas
|
||
| Country | United States | |
| State | Texas | |
| County | Fort Bend | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Council-Manager | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 42.90 sq mi (111.12 km2) | |
| • Land | 40.47 sq mi (104.81 km2) | |
| • Water | 2.44 sq mi (6.31 km2) | |
| Elevation | 100 ft (30 m) | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 111,026 | |
| • Density | 2,927.94/sq mi (1,130.49/km2) | |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central (CST)) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) | |
| ZIP codes |
77478-79, 77487, 77496, and 77498
|
|
| Area code(s) | Mostly 281 also 713, 832, and 346 | |
| Sales Tax | 8.25% | |
| GNIS feature ID | 1348034 | |
Sugar Land is a large city in Fort Bend County, Texas, in the Greater Houston area. It is about 19 miles (30 km) southwest of downtown Houston. The city is known for its many planned communities and fast growth.
In the 1800s, Sugar Land was a big sugar plantation near the Brazos River. Later, in 1908, the plantations joined to form the Imperial Sugar Company. Sugar Land grew as a "company town," meaning the company owned much of the town and provided for its workers. It became an official city in 1959. Since the 1980s, Sugar Land has grown very quickly. Many new neighborhoods have been built.
Sugar Land is one of the richest and fastest-growing cities in Texas. In 2020, the city's population grew by over 40% in just 10 years. This happened after the city added the communities of Greatwood and New Territory in 2017.
The Imperial Sugar Company still has its main office in Sugar Land. The company's crown logo is even part of the city's official seal.
History of Sugar Land
How Sugar Land Began
Sugar Land's history started with a land grant given to Stephen F. Austin by Mexico. One of the first settlers, Samuel M. Williams, called the area "Oakland Plantation." His brother, Nathaniel, bought the land in 1838. They grew cotton, corn, and sugarcane on the plantation.
This plantation was a key social spot along the Brazos River. In 1853, Benjamin Terry and William J. Kyle bought Oakland Plantation. Terry is famous for leading a group of Texas Rangers during the American Civil War. He also gave the town its name.
After Terry and Kyle died, Colonel E. H. Cunningham bought the 12,500-acre (5,100 ha) plantation. He built a sugar-refining plant in 1879. He also planned out the town and encouraged people to move there.
Sugar Land as a Company Town
In 1906, the Kempner family bought the 5,300-acre (2,100 ha) Ellis Plantation. This was one of the few plantations in Fort Bend County that survived the Civil War. In 1908, they also bought the 12,500-acre (5,100 ha) Cunningham Plantation, which had a sugar mill. They named their new company the Imperial Sugar Company.
Around 1900, a harsh winter destroyed most of the sugarcane crops. Logan J. Copenhaver moved to the area to manage the Imperial Sugar Company. He helped build Sugar Land as a company-owned town.
The train tracks in Sugar Land are part of the oldest railroad in Texas. They run next to the old sugar refinery. From the 1910s until 1959, Imperial Sugar Company provided homes for its workers. It also helped build schools and a hospital. Many of the first homes built by the company are still standing today.
In the 1950s, Imperial Sugar wanted to build more homes. They created a new neighborhood called Venetian Estates. It had homes along Oyster Creek and man-made lakes.
How Sugar Land Became a City
As the company town grew, people wanted to have their own city government. In 1959, voters decided to make Sugar Land a city. T. E. Harman became the first mayor.
In the 1960s, new neighborhoods like Covington Woods and Sugar Creek were built. Sugar Creek was a "master-planned community." This meant it was carefully designed with homes around golf courses, country clubs, and swimming pools. It even had private security.
The success of Sugar Creek, along with the building of U.S. Highway 59, made Sugar Land's farmlands attractive for new homes. In 1977, work began on First Colony, a huge master-planned community covering 10,000 acres (4,000 ha). First Colony offered beautiful landscaping, different types of homes, green spaces, and shopping areas.
Other master-planned communities like Sugar Mill, Greatwood, and New Territory also started to develop. Major companies like Fluor Daniel and Schlumberger began to open offices in Sugar Land. This helped the city's economy grow.
In 1981, voters approved a "home-rule" government for Sugar Land. This gave the city more control over its own laws. In 1986, the city changed its government to a "council-manager" system. This means a professional city manager runs the city's daily operations.
Sugar Land's Growth Continues
In 1990, the city council changed to include a mayor and two council members elected by all voters. Throughout the 1990s, Sugar Land grew very fast. Many residents are college-educated and work in Houston's energy industry.
More businesses came to Sugar Land, especially along Interstate 69/U.S. 59 and State Highway 6. In 1996, First Colony Mall opened. It was the first large shopping mall in Fort Bend County. In 1997, Sugar Land added more areas from the First Colony community, bringing the city's population to almost 60,000 people.
Sugar Land After 2000
In 2000, Sugar Land had the fastest growth among Texas's largest cities, with a population of 63,328. By 2003, Sugar Land was recognized as a "principal" city in the Houston metropolitan area.
To support its growth, Sugar Land attracted higher education facilities. In 2002, the University of Houston Sugar Land opened a new campus. The city helped fund one of its buildings.
In 2003, the Imperial Sugar Company's refinery closed. However, this did not hurt the local economy much. Sugar Land had become a rich suburb of Houston, not just a town focused on farming. The Imperial Sugar Company still has its headquarters in the city.
In 2003, the Texas Department of Transportation sold 2,018 acres (817 ha) of former prison land in Sugar Land to a developer. This land became the new master-planned community called Telfair. In 2004, Sugar Land added this land to its city limits to guide its development.
By 2017, Sugar Land had added the communities of Avalon, River Park, Greatwood, and New Territory. This brought the city's population to 117,869.
In the 2010s, the Imperial master-planned community began to develop. It includes Constellation Field, home to the Sugar Land Space Cowboys baseball team. The Smart Financial Centre, a large concert hall, opened in 2017.
Geography of Sugar Land
Sugar Land is in the northeast part of Fort Bend County. It is about 20 miles (32 km) southwest of downtown Houston. The city covers about 42.90 square miles (111.12 km2). Most of this is land, and about 5.7% is water. The city is generally 70 to 90 feet (21 to 27 m) above sea level.
Two main waterways flow through Sugar Land. The Brazos River runs through the southwestern and southern parts of the city. Oyster Creek flows from the northwest to the east. Many artificial lakes have been built in Sugar Land, connecting to these waterways.
Climate in Sugar Land
Sugar Land has a humid subtropical climate. This means it has two main seasons: a wet season from April to October, and a dry season from November to March. The city gets about 48 inches (120 cm) of rain each year. Winds usually come from the south and southeast, bringing heat and moisture from the Gulf of Mexico.
In summer, daily high temperatures are often around 95 °F (35 °C) in July and August. The air feels still, and high humidity makes it feel even hotter. Summer thunderstorms are common. The highest temperature ever recorded in the area was 109 °F (43 °C) in August 2023.
Winters are cool and mild. The average winter high is 62 °F (16 °C), and the low is 45 °F (7 °C). January is usually the coldest month. Snow is very rare and usually melts quickly.
| Climate data for Sugar Land, Texas | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 61.9 (16.6) |
65.7 (18.7) |
72.5 (22.5) |
79.2 (26.2) |
85.6 (29.8) |
90.7 (32.6) |
93.7 (34.3) |
93.6 (34.2) |
89.1 (31.7) |
81.7 (27.6) |
72.0 (22.2) |
64.2 (17.9) |
79.2 (26.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 41.5 (5.3) |
44.4 (6.9) |
51.4 (10.8) |
58.3 (14.6) |
66.4 (19.1) |
72.1 (22.3) |
74.5 (23.6) |
73.9 (23.3) |
69.4 (20.8) |
59.9 (15.5) |
50.9 (10.5) |
43.2 (6.2) |
58.8 (14.9) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 4.06 (103) |
2.98 (76) |
3.24 (82) |
3.48 (88) |
4.69 (119) |
5.51 (140) |
3.30 (84) |
4.29 (109) |
5.82 (148) |
4.03 (102) |
4.58 (116) |
3.36 (85) |
49.34 (1,253) |
People in Sugar Land
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1950 | 2,285 | — | |
| 1960 | 2,802 | 22.6% | |
| 1970 | 3,318 | 18.4% | |
| 1980 | 8,826 | 166.0% | |
| 1990 | 24,529 | 177.9% | |
| 2000 | 63,328 | 158.2% | |
| 2010 | 78,817 | 24.5% | |
| 2020 | 111,026 | 40.9% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
Population and Diversity
| Race / Ethnicity (NH = Non-Hispanic) | Pop 2000 | Pop 2010 | Pop 2020 | % 2000 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 38,526 | 35,014 | 42,305 | 60.84% | 44.42% | 38.10% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 3,242 | 5,744 | 7,969 | 5.12% | 7.29% | 7.18% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 112 | 135 | 150 | 0.18% | 0.17% | 0.14% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 15,042 | 27,672 | 42,639 | 23.75% | 35.11% | 38.40% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 18 | 26 | 30 | 0.03% | 0.03% | 0.03% |
| Some Other Race alone (NH) | 109 | 179 | 578 | 0.17% | 0.23% | 0.52% |
| Mixed race or Multiracial (NH) | 1,226 | 1,723 | 3,925 | 1.94% | 2.19% | 3.54% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 5,053 | 8,324 | 13,430 | 7.98% | 10.56% | 12.10% |
| Total | 63,328 | 78,817 | 111,026 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
As of the 2020 United States census, Sugar Land had 111,026 people. In 2010, the city's population was 78,817. Sugar Land has the highest number of Asian Americans in Texas. In 2010, about 10.7% were Indian, 11.5% Chinese, 4.5% Vietnamese, and 2.0% Filipino. There is also a large Pakistani community.
Many people of Indian origin are drawn to Sugar Land because of the good jobs, schools, and parks. The city has Indian grocery stores, temples, and mosques.
In 2010, about 40.7% of households had children under 18. Most households (70.0%) were married couples living together. The average household had 2.90 people. The median age in the city was 41.2 years.
In 2014, the average income for a household in Sugar Land was $115,069. About 6.4% of families and 9.9% of the population lived below the poverty line.
Religions in Sugar Land
Catholicism
Catholics make up over 30% of Sugar Land's population. The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Galveston-Houston runs three churches in the city:
- St. Laurence Church: Its main building was opened in 1992. By 2006, it had 4,600 families.
- St. Theresa Church: The Imperial Sugar Company gave the land for this church, which opened in 1924.
- St. Thomas Aquinas Church
Hinduism
The BAPS Shri Swaminarayan Mandir Houston, a Hindu temple, is near Sugar Land. The Sri Saumyakasi, a Sugar Land Chinmaya Hindu temple, opened in 2007. It is the only Hindu temple in the city dedicated to Shiva. The Chinmaya Mission Houston started in 1982.
Islam
The Islamic Society of Greater Houston has two mosques in the area: Masjid Maryam and Masjid At-Taqwa.
Economy of Sugar Land
Like the rest of the Houston area, Sugar Land has a big energy industry, especially in oil and gas. Sugar Land is home to the headquarters of CVR Energy, Inc., Western Airways, and NalcoChampion's Energy Services. CVR Energy was listed as a Fortune 500 company in 2012.
Sugar Land also has many international energy, software, and engineering companies. The Imperial Sugar Company's headquarters are in Sugar Land, even though its refinery closed in 2003.
Schlumberger, an oil services company, moved its Houston-area offices to Sugar Land in 1995. In 2015, Schlumberger announced it would move its U.S. corporate headquarters to Sugar Land. Fluor Daniel also has a large office in the city.
Minute Maid opened its headquarters in Sugar Land Town Square in 2009.
Top Employers in Sugar Land
Here are the largest employers in Sugar Land as of 2019:
| No. | Employer | No. of employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Methodist Sugar Land Hospital | 2,400 |
| 2 | Fluor Enterprises, Inc | 1,980 |
| 3 | Schlumberger | 1,900 |
| 4 | Nalco Champion | 1,216 |
| 5 | Memorial Hermann Sugar Land | 800 |
| 6 | St. Luke's Hospital Sugar Land | 473 |
| 7 | Accredo Packaging | 425 |
| 8 | Baker Hughes | 422 |
| 9 | Applied Optoelectronics | 396 |
| 10 | AmerisourceBergen Drug Company | 380 |
Culture and Sports in Sugar Land
Many people in Sugar Land work in office jobs and have college degrees. They often work in Houston's energy industry.
In 2004, Sugar Land was named one of the top 100 places to live by HomeRoute. Cities were chosen based on schools, crime rates, jobs, and housing. Sugar Land was also named the "Fittest City in Texas" for its size in 2004, 2005, and 2006.
Sports are popular in Sugar Land. The city's first community swim team, the Sugar Land Sharks, started in 1967 and still competes today.
Sugar Land is home to the Smart Financial Centre, an indoor concert hall. It can hold 6,400 people for concerts and other events. There are also plans for an outdoor arts plaza and new developments around the center.
The city is also home to the Sugar Land Space Cowboys Minor League Baseball team. They play at Constellation Field. The team started in 2012 as the Sugar Land Skeeters. They won championships in 2016 and 2018. In 2021, they became a Triple-A team for the Houston Astros and changed their name to the Space Cowboys.
In 2014, the Sugar Land Youth Cricket Club was formed for children.
Fun Places to Visit in Sugar Land
Sugar Land Town Square is the main entertainment area in Sugar Land. It has many restaurants, cafes, shops, a hotel, offices, and Sugar Land City Hall. Festivals and important events often happen in the public plaza there.
Next to Town Square is First Colony Mall, a large shopping mall. It has grown to include outdoor shops and parking garages.
Sugar Land also has the Sugar Land Ice and Sports Center. Here, you can go ice skating and take hockey lessons. It used to be the practice place for the Houston Aeros hockey team. Olympic medalist Tara Lipinski even trained there!
New developments are planned for the former Imperial Sugar refinery area, called Imperial Market. This will include a hotel and other businesses. The Smart Financial Centre is also part of new development plans.
Neighborhoods and Communities
Sugar Land has many "master-planned communities." These are large neighborhoods that are carefully designed with homes, green spaces, and amenities. Some of these communities include First Colony, Greatwood, New Territory, Telfair, Sugar Creek, River Park, Imperial, and Riverstone. Many have golf courses, country clubs, and lakes. Sugar Creek was the first master-planned community built in Sugar Land. There are now 13 such communities in and around the city.
The northern part of Sugar Land is sometimes called "Old Sugar Land." This area includes the original city limits from 1959. Here you'll find the former Imperial Sugar Company refinery. The Sugar Land Business Park is also in this area, with many electronic and energy companies. The Imperial master-planned community, with Constellation Field, is also in north Sugar Land.
The largest business and entertainment areas are in south and southeastern Sugar Land. Most of the city's population lives here. This area is full of master-planned communities like First Colony, Sugar Creek, Sugar Lakes, and Telfair. This is where you'll find First Colony Mall, Sugar Land Town Square, and the new Sugar Land City Hall. There are also many fun activities, including golf courses and the Sugar Land Ice & Sports Center.
The southwestern part of Sugar Land was recently added to the city. It is separated from the rest of Sugar Land by the Brazos River. This area has two master-planned communities: Greatwood and River Park.
The western part of Sugar Land was also fully added to the city in 2017. It includes New Territory and Telfair. A new highway, Texas State Highway 99 (the "Grand Parkway"), opened in this area in 1994. The Sugar Land Regional Airport is also in this western part of the city.
Historic Buildings
Lakeview Auditorium, located at Lakeview Elementary School, is the oldest public building still standing in the area. It was once one of 11 buildings that made up the old Sugar Land Independent School District. The auditorium was a central place for the growing community. Today, it is a Recorded Texas Historic Landmark.
In 1912, Imperial Sugar Company built a small building to be a school. The original school had 11 buildings in a semicircle, with the auditorium in the middle. The buildings were connected by a covered walkway with large white columns. All the buildings were white and had big windows for fresh air. The auditorium was a very active place for the community.
Education in Sugar Land
Colleges and Universities
Sugar Land has branch campuses of Wharton County Junior College and the University of Houston.
Wharton County Junior College offers many programs, including associate degrees and courses for students who want to transfer to a four-year university.
Schools for Kids
Public Schools
The Texas Education Agency (TEA) oversees all public schools in Texas. Most of Sugar Land is served by the Fort Bend Independent School District (FBISD). This district was formed in 1959. A small part of Sugar Land is in the Lamar Consolidated Independent School District (LCISD).
High schools in Fort Bend ISD that serve Sugar Land include Clements High School, Dulles High School, Kempner High School, Austin High School, and Travis High School. In Lamar Consolidated ISD, Lamar Consolidated High School and George Ranch High School serve parts of Sugar Land.
Dulles, Clements, and Austin high schools have been named among the top high schools in Texas by Texas Monthly magazine. They were also ranked among the top 1000 schools in the U.S. by Newsweek in 2009.
Before 1959, Sugar Land High School served the city. When FBISD was formed, it combined schools for different groups of students. After schools became desegregated in 1965, Dulles High School became the main high school for all students in FBISD.
Also, Harmony Public Schools runs three charter schools in Sugar Land: Harmony Science Academy (K–5), Harmony School of Excellence (6–8), and Harmony School of Innovation (9–12).
Private Schools
Sugar Land and the nearby areas have many private schools. These include non-religious schools, Catholic schools, and Protestant schools. The Texas Education Agency does not control private schools.
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Galveston-Houston runs two Catholic schools in Sugar Land for grades K–8: St. Theresa Catholic School and St. Laurence School. St. Laurence opened in 1992, and St. Theresa opened in 2008.
Fort Bend Christian Academy has been named the "Best Private School" in Fort Bend County. Logos Preparatory Academy is also in Sugar Land. The Honor Roll School serves grades PK-8 and offers advanced classes.
Public Libraries
Residents of Sugar Land can use the Fort Bend County Libraries system, which has 11 libraries. Three of these libraries are in Sugar Land: the Sugar Land Branch, the First Colony Branch, and the University Branch (on the University of Houston Sugar Land campus).
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sugar Land para niños
In Spanish: Sugar Land para niños