Virgo (constellation) facts for kids
| Constellation | |
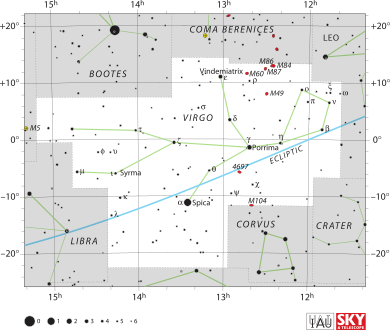
List of stars in Virgo
|
|
| Abbreviation | Vir |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Virginis |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Symbolism | the Maiden |
| Right ascension | 13h |
| Declination | −4° |
| Quadrant | SQ3 |
| Area | 1294 sq. deg. (2nd) |
| Main stars | 9, 15 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars |
96 |
| Stars with planets | 29 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 3 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 10 |
| Brightest star | Spica (α Vir) (0.98m) |
| Messier objects | 11 |
| Meteor showers |
|
| Bordering constellations |
|
| Visible at latitudes between +80° and −80°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of May. |
|
Virgo is a large constellation in the night sky. Its name means "maiden" in Latin. You can find it between the Leo constellation to its west and Libra to its east. Virgo is the second-largest constellation overall and the biggest one in the zodiac.
The Sun appears to pass through Virgo during the September equinox. This is when the Sun crosses the celestial equator. The brightest star in Virgo is called Spica, which makes it easy to spot.
Contents
Where to Find Virgo
You can see Virgo clearly in the spring sky if you are in the Northern Hemisphere. It is visible all night during March and April. Since Virgo is the largest zodiac constellation, the Sun takes about 44 days to pass through it. This is longer than for any other zodiac constellation. From 1990 until 2062, the Sun will be in Virgo from September 16 to October 30.
Virgo is located in the southern part of the sky, in a section called SQ3. You can see it from most places on Earth, between 80 degrees north and 80 degrees south latitude.
To find Virgo, first locate the Big Dipper. Follow the curve of its handle to find Arcturus in the Boötes constellation. If you continue that same curve, you will "speed on to Spica," the bright star in Virgo.
Due to a slow wobble of Earth called precession, the point where the Sun crosses the celestial equator in autumn (the autumn equinox point) is currently within Virgo. This point will move into the Leo constellation around the year 2440.
Stars and Planets in Virgo
Bright Stars
The brightest star in Virgo is Spica. Other bright stars include:
- Beta Virginis (also called Zavijava)
- Gamma Virginis (Porrima)
- Delta Virginis (Auva)
- Epsilon Virginis (Vindemiatrix)
Some fainter stars also have names, like Zeta Virginis (Heze) and Eta Virginis (Zaniah).
Star Patterns
Five stars – Beta, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Eta Virginis – form a shape known as "The Bowl of Virgo." When you add Spica and Theta Virginis, these stars together create a "Y" shape in the sky.
Planets Beyond Our Solar System
Scientists have found many planets orbiting stars in Virgo. These are called exoplanets.
- The star 70 Virginis has one of the first exoplanets ever discovered. This planet is about 7.5 times bigger than Jupiter.
- Another star, Chi Virginis, has a very massive planet, about 11.1 times the size of Jupiter.
- The star 61 Virginis is similar to our Sun. It has three planets: one is a "super-Earth" (bigger than Earth but smaller than Neptune), and two are about the size of Neptune.
- SS Virginis is a special star that changes its brightness over about a year. It also has a noticeable red color.
In total, astronomers have confirmed 35 exoplanets orbiting 29 different stars in the Virgo constellation.
Deep-Sky Objects


Virgo is famous for having many galaxies. This is because a huge group of galaxies, called the Virgo Cluster, is located within its borders.
Famous Galaxies
Some well-known galaxies in Virgo include:
- Messier 49 (an elliptical galaxy)
- Messier 58 (a spiral galaxy)
- Messier 87 (a large elliptical galaxy and a strong source of radio waves)
- The Sombrero Galaxy (M104), which is an unusual spiral galaxy. It looks like a sombrero hat!
Interesting Galaxy Facts
- Messier 87 (M87) is the largest galaxy in the Virgo Cluster. It is about 60 million light-years away. M87 is known for a powerful jet of particles shooting out from its center. This jet is caused by a supermassive black hole at the galaxy's core. In 2019, scientists captured the first direct image of this black hole's shadow. It is one of the most massive black holes near our Milky Way galaxy, weighing at least 7.2 billion times the mass of our Sun.
- Messier 84 (M84) is another elliptical galaxy about 60 million light-years away. Scientists believe it also has a black hole at its center, about 300 million times the mass of the Sun.
- The Sombrero Galaxy (M104) is about 28 million light-years away. It is a spiral galaxy seen edge-on, meaning we see it from the side. It has a large central bulge of older stars and a very clear dust lane.
- NGC 4261 has a black hole about 20 light-years from its center. This black hole is 1.2 billion times the mass of the Sun.
- Virgo is also home to the quasar 3C 273. This was the very first quasar ever found, and it's the brightest one we can see with telescopes. Quasars are extremely bright objects powered by supermassive black holes at the centers of distant galaxies.
Mythology and Stories
Many ancient cultures had stories about the Virgo constellation.
In ancient Babylonia, part of this constellation was called "The Furrow." It represented the goddess Shala and her ear of grain. The star Spica gets its name from the Latin word for "ear of grain," linking Virgo to farming and fertility.
Early Greek astronomy connected Virgo to their goddess of wheat and agriculture, Demeter. The Romans later associated it with their goddess Ceres.
Sometimes, Virgo was seen as the virgin goddess Iustitia or Astraea, who held the scales of justice. These scales are now a separate constellation called Libra.
Another Greek myth tells of Erigone, the daughter of Icarius. After her father was killed, Erigone was so sad that she took her own life. The god Dionysus is said to have placed them in the stars as Boötes (Icarius) and Virgo (Erigone).
Virgo is also linked to Persephone, the goddess of spring. She was the daughter of Zeus and Demeter and spent part of the year in the Underworld with Hades.
During the Middle Ages, some people connected the Virgo constellation with the Blessed Virgin Mary.
In Greek mythology, Virgo is also associated with Dike, the goddess of justice, who is shown holding the scales of justice.
Images for kids
-
The elliptical galaxy Messier 87
-
This image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows two of the galaxies in the galactic triplet Arp 248.
-
James Webb Space Telescope peers behind the bars to image the bright tendrils of gas and stars of the barred spiral galaxy NGC 5068. The galaxy lies around 17 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo.
See also
 In Spanish: Virgo (constelación) para niños
In Spanish: Virgo (constelación) para niños