65803 Didymos facts for kids
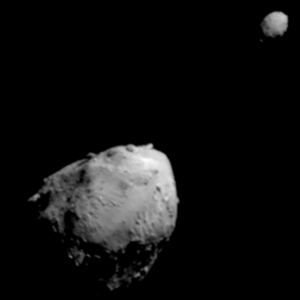
Didymos (bottom left) and Dimorphos (top right) photographed by the DART space probe
|
|
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Spacewatch |
| Discovery site | Kitt Peak National Observatory |
| Discovery date | 11 April 1996 |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | (65803) Didymos |
|
Named after
|
Greek word for "Twin" |
| 1996 GT | |
| NEO · PHA Apollo (2022) |
|
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch 21 January 2022 (JD 2459600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 24.82 years (9,066 days) |
| Aphelion | 2.2753 AU |
| Perihelion | 1.0131 AU |
| 1.6442 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.38385 |
| 2.11 yr (770 days) | |
| 232.01 | |
|
Mean motion
|
0° 28m 2.28s / day |
| Inclination | 3.4079° |
| 73.196° | |
| 319.32° | |
| Known satellites | 1 (Dimorphos) |
| Earth MOID | 0.0403 AU (15.7 LD) |
| Mars MOID | 0.02 AU (7.8 LD) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 851 × 849 × 620 m (± 15 × 15 × 15 m) |
|
Mean diameter
|
765±15 m |
| Mass | (5.4±0.4)×1011 kg (system) ≈ 5.2×1011 kg (primary) |
|
Mean density
|
2.40±0.30 g/cm3 |
| 2.2600±0.0001 2.2593±0.0002 h |
|
| 174°±20° | |
|
Pole ecliptic latitude
|
−84°±20° |
|
Pole ecliptic longitude
|
310°±20° |
| 0.15±0.04 | |
| S · SMASS = Xk · X | |
| 18.0 · 18.16 18.16±0.03 |
|
65803 Didymos (also called 1996 GT) is a space rock, or asteroid, that is less than one kilometer wide. It's special because it's a binary system, meaning it has its own small moon. This moon is named Dimorphos. Didymos is also known as a potentially hazardous asteroid and a near-Earth object. This means its orbit can bring it close to Earth, but it's carefully watched.
Scientists discovered Didymos in 1996 using the Spacewatch survey. Its tiny moon, Dimorphos, was found later in 2003. Because it's a pair, the asteroid was named Didymos, which is the Greek word for 'twin'. Dimorphos was the target of the DART mission. This mission tested if a spacecraft could push an asteroid off course. The impact was even watched by a small satellite called LICIACube.
Contents
Discovering Didymos

Didymos was first seen on April 11, 1996. It was found by the Spacewatch survey in Arizona, USA. They used a special telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory. At first, scientists didn't know Didymos had a moon. But in 2003, they suspected it was a binary system. Radar images from the Arecibo Observatory confirmed it on November 23, 2003.
How Didymos Orbits the Sun
Didymos travels around the Sun. It orbits at a distance of 1.0 to 2.3 AU. One AU is the distance from the Earth to the Sun. It takes Didymos about 770 days, or 2 years and 1 month, to complete one orbit. Its path is not a perfect circle; it's a bit stretched out.
Didymos can come quite close to Earth. The closest it gets is about 0.04 AU (6.0 million km). This distance can change over time. In November 2003, it passed 7.18 million kilometers from Earth. It won't come that close again until November 2123. Then, it will be 5.86 million kilometers away. Didymos also sometimes passes near Mars. In July 2144, it will fly by Mars at 4.68 million kilometers.
Didymos spends about one-third of its time in the near-Earth asteroid (NEA) region. This is where impacts are more likely to happen. Over millions of years, Didymos has probably been hit many times.
What Didymos is Like

Didymos is classified as an Xk-type asteroid. This means it's a mix of different types of asteroids. Later studies showed it's made of silicate rock, like many stony asteroids. Didymos spins very fast. It completes one full spin in about 2.26 hours. Because it spins so quickly, it's not perfectly round. It's a bit flattened, like a squashed ball.
Didymos's Moon: Dimorphos
Didymos has a small moon, which is called Dimorphos. This moon orbits Didymos in a nearly circular path. It takes Dimorphos about 11.9 hours to go around Didymos once. Dimorphos is much smaller than Didymos. It is about 160 meters (520 ft) across. Didymos, the main asteroid, is about 780 meters (2,560 ft) wide. Before it got its official name, Dimorphos was sometimes called "Didymoon".
Naming the Asteroids
The main asteroid was named "Didymos." This name comes from the Greek word for "twin." It was chosen because Didymos is a binary system, meaning it has a moon. Joseph L. Montani, an astronomer, suggested the name. The International Astronomical Union approved it in 2004.
The moon, Didymos B, was officially named "Dimorphos." This Greek word means "having two forms." The name was chosen because Dimorphos's orbit would change after the DART mission. It would have a "new form" of orbit. This name also shows that Dimorphos is both a test target and a model for protecting Earth from asteroids. A scientist named Kleomenis Tsiganis suggested this name.
Two large rocks on Didymos have also been named. They are called Carillon Saxum and Gong Saxum. These names come from types of traditional drums.
| Name | Pronunciation | Feature | Named after | Date approved |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carillon Saxum | boulder | carillon | 14 Nov 2023 | |
| Gong Saxum | boulder | gong | 14 Nov 2023 |
Exploring Didymos

In the early 2010s, space agencies planned a mission to Didymos's moon, Dimorphos. It was called the Asteroid Impact & Deflection Assessment (AIDA) mission. This mission did not happen as planned.
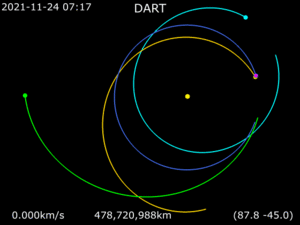
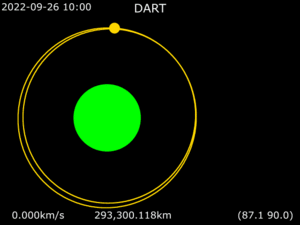
Later, NASA decided to go ahead with a similar mission. This mission was called the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART. The goal of DART was to see if a spacecraft could hit an asteroid. This would test if we could change an asteroid's path if it were heading for Earth. The DART spacecraft launched on November 24, 2021. It successfully crashed into Dimorphos on September 26, 2022. A small satellite called LICIACube traveled with DART. LICIACube watched the impact from close by.
Didymos is the easiest asteroid of its size to reach from Earth. It takes less energy for a spacecraft to get there than to reach the Moon!
After the impact, NASA studied the results. They found that the collision changed Dimorphos's orbit around Didymos. Its orbital period became 32 minutes shorter. This was much more than the scientists hoped for. It proved that this method could work for planetary defense.
Another mission to Didymos is planned for the future. The ESA's Hera mission will arrive at Didymos in 2026. Hera will study the changes made by the DART impact. It will also measure the crater DART created on Dimorphos.
See also
 In Spanish: (65803) Dídimo para niños
In Spanish: (65803) Dídimo para niños
- 66391 Moshup – a similar near-Earth asteroid binary system
- List of asteroids visited by spacecraft
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |