Great Rift Valley facts for kids
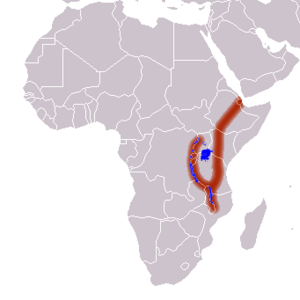
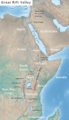
The Great Rift Valley is a huge, long trench on Earth's surface. It stretches for about 6,000 kilometers (3,700 miles). This amazing geographical feature runs from northern Syria in Southwest Asia all the way to central Mozambique in East Africa. The valley is surrounded by mountains and active volcanoes. It's a place where the Earth's crust often cracks (these are called faults) and where earthquakes happen.
Basically, the western part of Africa is slowly pulling away from the eastern part. This movement causes all the geological activity you see in the Valley. Far in the future, a new sea might even form between these two parts of Africa! The Arabian Peninsula is already almost separated. This whole process is part of how Earth's giant plates move, known as plate tectonics. In eastern Africa, the valley splits into two main parts: the Western Rift Valley and the Eastern Rift Valley.
About 20 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, which are special places protected for their importance, were formed because of the unique geography and geology of the Great Rift Valley.
The Rift Valley in Asia
The northernmost parts of the Great Rift Valley are part of what's called the Dead Sea Transform (DST). This middle section of the DST forms the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon. It separates the Lebanon Mountains from the Anti-Lebanon Mountains. Further south, it's known as the Hula Valley, which separates the Galilee mountains and the Golan Heights.
The Jordan River starts here and flows south through Lake Hula into the Sea of Galilee in Israel. The Rift then continues south through the Jordan Rift Valley into the Dead Sea, which is on the border between Israel and Jordan. From the Dead Sea southwards, the Rift is filled by the Wadi Arabah, then the Gulf of Aqaba, and finally the Red Sea.
Near the southern tip of Sinai in the Red Sea, the Dead Sea Transform meets the Red Sea Rift. This rift runs along the entire length of the Red Sea. The Red Sea Rift then joins the East African Rift and the Aden Ridge in a place called the Afar Triangle in East Africa. This spot where three rifts meet is known as the Afar Triple Junction.
The Rift Valley in Africa
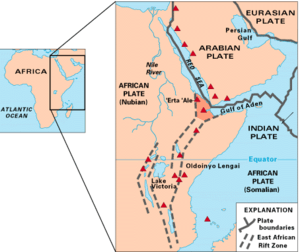
The East African Rift follows the Red Sea before turning inland into the Ethiopian Highlands. It divides Ethiopia into two large, separate mountainous regions. In Kenya, Uganda, and parts of South Sudan, the Great Rift runs along two separate branches. These branches only join together at their southern end, in Southern Tanzania near its border with Zambia. These two branches are called the Western Rift Valley and the Eastern Rift Valley.
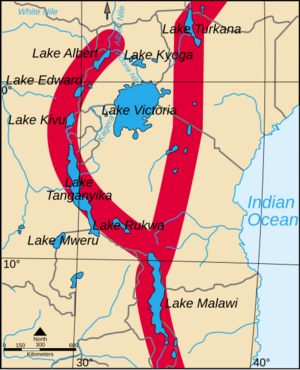
The Western Rift, also known as the Albertine Rift, is bordered by some of Africa's highest mountains. These include the Virunga Mountains, Mitumba Mountains, and Ruwenzori Range. It contains the Rift Valley lakes, which are some of the deepest lakes in the world. For example, Lake Tanganyika is up to 1,470 meters (4,820 feet) deep!
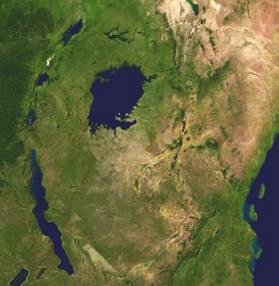
Much of this area is protected within national parks. These include Virunga National Park in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwenzori National Park and Queen Elizabeth National Park in Uganda, and Volcanoes National Park in Rwanda. Lake Victoria is considered part of the rift valley system, even though it lies between the two main branches. All of the African Great Lakes were formed because of the rift, and most are located within its boundaries.
In Kenya, the valley is deepest north of Nairobi. The lakes in the Eastern Rift usually don't have an outlet to the sea and tend to be shallow. Because of this, they have a high mineral content. As water evaporates, salts are left behind. For example, Lake Magadi has lots of soda (sodium carbonate). Lake Elmenteita, Lake Bogoria, and Lake Nakuru are all very alkaline (meaning they have a high pH). However, freshwater springs supply Lake Naivasha, which helps support its wide variety of plants and animals.
The southern part of the Rift Valley includes Lake Malawi. This is the third-deepest freshwater body in the world, reaching 706 meters (2,316 feet) deep. It separates the Nyassa plateau of Northern Mozambique from Malawi. The Rift Valley finally ends in the Zambezi River valley.
Images for kids
-
Satellite image of a graben (a sunken block of Earth's crust) in the Afar Triangle.
See also
 In Spanish: Gran Valle del Rift para niños
In Spanish: Gran Valle del Rift para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |