Afrotropic facts for kids
The Afrotropic is one of Earth's eight main natural regions, called ecozones. These zones are huge areas with similar plants and animals. This ecozone used to be known as the Ethiopian Zone.
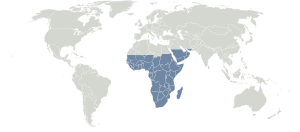
The Afrotropic ecozone includes a large part of Africa south of the Sahara Desert. It also covers the southern and eastern parts of the Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, southern Iran, a tiny bit of southwestern Pakistan, and islands in the western Indian Ocean. Most of this land was once part of a giant ancient supercontinent called Gondwana. Gondwana started to break apart about 150 million years ago.
Contents
Different Natural Areas in the Afrotropic
Africa is a very big continent that stretches from north to south across the equator. Because of this, the Afrotropic ecozone has many different climates and natural homes, called habitats. Most of the Afrotropic has a tropical climate, meaning it's warm all year round.
A wide belt of deserts separates the Afrotropic from the Palearctic ecozone. The Palearctic ecozone includes northern Africa and the cooler parts of Eurasia.
Sahel and Sudan Grasslands
South of the Sahara Desert, you'll find two long belts of grasslands and savannas. These areas stretch from the Atlantic Ocean to the Ethiopian Highlands.
Right next to the Sahara is the Sahel belt. This is a dry area with short grasslands and Acacia trees. As you go further south, the rainfall increases. This leads to the Sudan belt, which has taller grasslands and savannas. The Sudanian savanna is home to two large flooded grasslands. These are the Sudd wetland in Sudan and the Niger Inland Delta in Mali.
Southern Arabian Woodlands
Southern Arabia, which includes most of Yemen and parts of Oman and Saudi Arabia, doesn't have many permanent forests. Instead, you'll find small groups of trees, mostly Juniper or Acacia forests, scattered across the land.
African Forest Zone
A wide belt of tropical moist forests runs across much of central Africa, near the equator. These are called broadleaf forests because their trees have wide, flat leaves.
The biggest tropical forest area in Africa is found in the Congo Basin in Central Africa. Another belt of tropical moist forest stretches along the Indian Ocean coast, from southern Somalia all the way to South Africa.
East Africa's Unique Landscapes
East Africa is special because of the Great Rift Valley. This area has a unique mix of deep lakes, high mountains, volcanoes, and grasslands.
- Serengeti (famous for its wildlife)
- Lake Victoria (one of the largest lakes in Africa)
- Olduvai Gorge (an important place for human history)
Southern African Areas
Southern Africa has a mix of woodlands, savannas, grasslands, and deserts.
- Namib Desert (one of the oldest deserts in the world)
- Kalahari Desert (a large semi-arid sandy savanna)
Madagascar and Indian Ocean Islands
Madagascar and the islands nearby are a very special part of the Afrotropic ecozone. They have many unique plants and animals that are found nowhere else. For example, lemurs live only on Madagascar.
Madagascar and the Seychelles islands are not connected to the African continent. This is why you don't find monkeys or apes in Madagascar, even though they are common in Africa. Madagascar separated from Africa when Gondwana broke apart. Lemurs fill the same natural roles, or niches, that monkeys do in Africa.
Other Indian Ocean islands, like the Comoros and Mascarene Islands, are volcanic islands that formed more recently. Madagascar has amazing biodiversity, meaning a huge variety of life. It has many unique species.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ecozona afrotropical para niños
In Spanish: Ecozona afrotropical para niños