Antofagasta facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Antofagasta
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Top row: View of downtown Antofagasta
2nd row: Old Antofagasta Customs House building, Beach of Antofagasta, "Mano del Desierto" (Hand of the Desert) Sand Sculpture in Atacama Desert 3rd row: Sailboats, Plaza Colón clocktower Bottom row: La Portada Natural Monument, Panorama of North Antofagasta, Ruins of Huanchaca. |
|||||
|
|||||
| Nickname(s):
La perla del Norte ("Pearl of the North")
|
|||||
| Motto(s):
"Gloria, patria y tesón es tu lema y tu honor"
("Glory, homeland and tenacity is your motto and your honor") |
|||||
| Country | |||||
| Region | |||||
| Province | Antofagasta | ||||
| Settled | 22 October 1868 | ||||
| Capital | Antofagasta | ||||
| Government | |||||
| • Type | Municipal council | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • Total | 30,718.1 km2 (11,860.3 sq mi) | ||||
| Elevation | 40 m (130 ft) | ||||
| Population
(2017 Census)
|
|||||
| • Urban | 352,638 | ||||
| Demonym(s) | Antofagastian | ||||
| GDP (PPP, constant 2015 values) | |||||
| • Year | 2023 | ||||
| • Total (Metro) | $12.8 billion | ||||
| • Per capita | $28,100 | ||||
| Time zone | UTC−4 (CLT) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−3 (CLST) | ||||
| Postal code |
3580000
|
||||
| Area code(s) | +56 55 | ||||
| Climate | BWk | ||||
| Website | Municipality of Antofagasta | ||||
Antofagasta is a busy port city in northern Chile. It is located about 1,100 kilometers (680 miles) north of Santiago, the capital of Chile. This city is the main center for the Antofagasta Province and Antofagasta Region. In 2015, about 402,669 people lived here.
Antofagasta was once part of Bolivia after the Spanish American wars of independence. However, Chile took control of it on February 14, 1879. This event started the War of the Pacific (1879–83). Chile's ownership of the city was officially recognized in 1904. This happened with the Treaty of Peace and Friendship.
The city of Antofagasta is very important for mining. It serves as a port and a main service center for Chile's big mining areas. In the past, silver and saltpeter were key. But since the mid-1800s, copper mining has become the most important activity. This has helped the city grow a lot. There has been steady growth in building, shopping, hotels, and population. The city's skyline also changed a lot until 2013. Since the 2010s, Antofagasta has also become a center for lithium mining.
Antofagasta has the highest GDP per capita in Chile. This means its people earn more money on average than in other Chilean cities. It also ranks third in the Human Development Index.
Contents
Discovering Antofagasta's Past
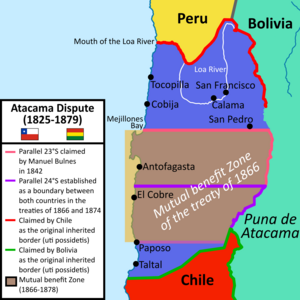
Antofagasta has a rich history. It was once part of maps of the Captaincy General of Chile in the 1700s. The land was disputed between Chile and Bolivia for many years. This changed with a treaty in 1866.
Early Days and Mining
In 1866, explorers found rich deposits of saltpeter (a mineral used in fertilizer) near Antofagasta. A company was formed to explore the Atacama Desert. This led to the growth of a settlement called "La Chimba."
In 1872, the Bolivian government declared Antofagasta a major port. This opened it up for trade around the world. A year later, the Municipality of Antofagasta was founded.
A Chilean mining company, "Compañía de Salitres y Ferrocarril de Antofagasta" (CSFA), signed a contract in 1873. This contract removed taxes on mineral mining for 15 years. However, the Bolivian Congress did not approve this contract right away.
The War of the Pacific
In 1873, Bolivia made a secret agreement with Peru to protect each other. This agreement would play a role in the War of the Pacific. In 1874, Chile and Bolivia signed a new border treaty. This treaty said no new taxes would be placed on Chilean businesses for 25 years.
However, Bolivia later tried to add a small tax (10 cents) on the saltpeter company. Bolivia said the 1873 contract was not yet official. Chile believed this tax broke the 1874 treaty.
Because of this disagreement, Chile took control of Antofagasta on February 14, 1879. This started the War of the Pacific. After the war, in 1884, a peace agreement was signed. It stated that the land around Antofagasta would be managed by Chile. Bolivia would still be able to use the ports of Arica and Antofagasta.
Antofagasta in the 20th Century
In 1904, Chile and Bolivia signed a permanent border treaty. In 1912, the British community built a clock tower in Plaza Colón. It looked like London's Big Ben and celebrated Chile's 100th birthday.
In 1937, Antofagasta got its own city anthem. A local doctor and poet, Antonio Rendic, wrote the words. Juan Bautista Quagliotto composed the music.
The Catholic University of the North was founded in 1956. Later, in 1968, the Antofagasta center of the University of Chile also opened.
The city faced natural disasters in the late 20th century. In 1991, a big mudslide caused a lot of damage. It destroyed many homes and left 92 people dead. In 1995, an earthquake hit the city. While it caused some deaths and injuries, the buildings held up well.
Antofagasta Today
Antofagasta continues to grow and develop. In 2008, the city elected its first female mayor, Marcela Hernando. She ran as an independent candidate.
Exploring Antofagasta's Geography
Antofagasta is located in the desert, which is the driest nonpolar desert in the world. The city itself is on the coast. It has an average elevation of 40 meters (130 feet) above sea level.
The Tropic of Capricorn passes just north of the city. A special monument was built there in 2000. It marks the Tropic of Capricorn and works like a solar calendar.
Antofagasta has very little natural plant life because of the dry desert. However, there are some important urban wetlands. These wetlands are home to reptiles, insects, birds, and even culpeo foxes. The city is working to protect these important natural areas.
Antofagasta's Climate
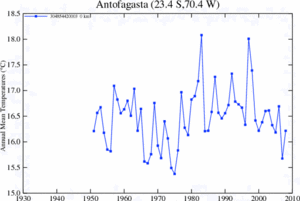
Antofagasta has a cold desert climate. It gets lots of sunshine but also has high humidity and morning fog. This fog is called "Camanchaca." The average yearly temperature is about 16.8°C (62.2°F).
January is the warmest month, with average highs around 23.2°C (73.8°F). July is the coldest, with average highs around 16.5°C (61.7°F). The highest temperature ever recorded was 30.0°C (86.0°F) in January 1998. The lowest was 3.0°C (37.4°F) in September 1978.
Antofagasta is known as one of the driest cities in the world. It receives very little rainfall, less than 0.1 mm per year on average. However, when it does rain heavily, the city can experience mudslides. This happened in 1940 and again in 1991.
| Climate data for Antofagasta (1991–2020, extremes 1950–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 31.8 (89.2) |
30.5 (86.9) |
30.6 (87.1) |
28.8 (83.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.0 (75.2) |
27.0 (80.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26.0 (78.8) |
29.8 (85.6) |
31.8 (89.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 23.6 (74.5) |
23.6 (74.5) |
22.6 (72.7) |
20.5 (68.9) |
18.8 (65.8) |
17.3 (63.1) |
16.5 (61.7) |
16.8 (62.2) |
17.4 (63.3) |
18.5 (65.3) |
20.1 (68.2) |
21.8 (71.2) |
19.8 (67.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 20.2 (68.4) |
20.2 (68.4) |
19.1 (66.4) |
17.3 (63.1) |
15.7 (60.3) |
14.5 (58.1) |
13.8 (56.8) |
14.0 (57.2) |
14.6 (58.3) |
15.6 (60.1) |
17.1 (62.8) |
18.7 (65.7) |
16.7 (62.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 17.4 (63.3) |
17.2 (63.0) |
16.2 (61.2) |
14.6 (58.3) |
13.3 (55.9) |
12.3 (54.1) |
11.7 (53.1) |
12.2 (54.0) |
12.9 (55.2) |
13.9 (57.0) |
15.1 (59.2) |
16.2 (61.2) |
14.4 (57.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
8.3 (46.9) |
9.0 (48.2) |
0.0 (32.0) |
5.3 (41.5) |
6.0 (42.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
3.6 (38.5) |
6.5 (43.7) |
7.0 (44.6) |
9.2 (48.6) |
7.5 (45.5) |
0.0 (32.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.8 (0.03) |
0.1 (0.00) |
0.2 (0.01) |
1.5 (0.06) |
0.4 (0.02) |
0.8 (0.03) |
0.2 (0.01) |
0.2 (0.01) |
0.1 (0.00) |
0.1 (0.00) |
4.4 (0.17) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74 | 75 | 77 | 77 | 76 | 76 | 75 | 75 | 74 | 74 | 73 | 73 | 75 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 312 | 294 | 289 | 249 | 228 | 200 | 207 | 210 | 220 | 250 | 270 | 303 | 3,032 |
| Source 1: Dirección Meteorológica de Chile | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (precipitation days 1991–2020) Ogimet (sun 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
Water Features
Antofagasta has about fifteen streams that collect sand and gravel. These streams can cause floods during heavy rains, like the one in 1991.
The coast of Antofagasta is mostly rocky. This means most of its beaches are man-made. North of the city, you can find natural beaches like "La Portada."
The area also has several dry lakes, called "salar." These include Salar de Pajonales and Salar Punta Negra.
How Antofagasta is Governed
Antofagasta is a commune, which is a local government area in Chile. It is run by a municipal council. The head of the council is the alcalde (mayor), who is elected every four years. As of 2021, the mayor is Jonathan Velásquez.
The city also has local police courts. The Municipality of Antofagasta has different offices to help with community needs.
Antofagasta's Economy
Antofagasta's economy mainly relies on mining. This includes copper mining and other minerals like nitrate and iodine. There are also factories that process copper and make cement and lime.
A second industrial area is in the north of the city. Many companies have their offices and operations there. Since the 2010s, Antofagasta has also become a center for lithium mining. Chile has the largest lithium reserves in the world. Lithium is shipped from Antofagasta.
Shopping in Antofagasta is mostly in the city center, around Plaza Colón. Many big national stores are located there. There are also large supermarkets like "Líder" and "Jumbo" throughout the city. In 2006, a large shopping mall, "Mall Plaza," was built. The "Casino Enjoy Antofagasta" was also built in the south of the city.
Business and Tourism
Antofagasta is an important city for business, especially in mining. It produces 54% of Chile's copper. Because of this, many business events are held here.
One of the biggest events is Exponor. This show helps connect mining companies from around the world. It promotes new business ideas and sharing knowledge.
In 2024, Antofagasta was the fifth most expensive city to live in Chile.
People of Antofagasta
According to the 2002 census, Antofagasta had 296,905 people. Most of them (99.6%) lived in urban areas. The population grew by 30% between 1992 and 2002. By 2009, it was estimated that about 360,473 people lived in the city.
Learning in Antofagasta

Antofagasta has many universities, both public and private. The main public university is the University of Antofagasta. The main private one is the Catholic University of the North. Several other private universities have opened since 2002.
Public schools are found all over the city. Private schools are mostly in the central and southern parts. Some private schools, like The Antofagasta British School, are among the top schools in Chile.
Antofagasta is also unique because it has a municipal school inside a military base.
Sports in Antofagasta
Football
The city's main football team is Deportes Antofagasta. They play in the Chilean First Division A. Their home games are played at the Antofagasta Regional Stadium. Other local football clubs include Club Deportivo Ormazábal.
Other Sports
Antofagasta hosted part of the 1959 Basketball World Cup. Chile won the bronze medal in that tournament.
Baseball is also popular in the city. Local teams play against teams from other cities like Tocopilla.
Getting Around Antofagasta
Roads
The main road connecting Antofagasta to the rest of Chile is Route 5-CH. This road is part of the Panamerican Highway. Other routes connect to the city from the north and south. Route 1-CH leads to the Andrés Sabella Gálvez International Airport and the natural monument La Portada.
Traffic in the city is mainly on the coastal road, called Avenida Costanera. This long road goes from north to south. It passes by important places like the Mall Plaza Antofagasta and the University of Antofagasta.
Airport
The only airport in Antofagasta is Andrés Sabella Gálvez International Airport. It is located north of the city. While it is an international airport, most flights are domestic. One international airline, LATAM Peru, flies to Lima.
Port
Antofagasta has a large port with seven docks. It was opened in 1943. The port handles about 5,000,000 tons of cargo each year. It is also a stop for cruise ships.
Escondida, a big private mining company, has its own private port south of the city.
Public Transport
The main public transport uses minibuses. These buses can carry fewer than thirty people. This system is called TransAntofagasta. It started in 2005. The buses travel along fixed routes throughout the city.
There are also shared taxis, which are black cars that follow specific routes.
Railways
The most important railway is the Ferrocarril de Antofagasta a Bolivia (FCAB). It was founded in 1888. This railway was very important during the saltpeter mining boom. Today, it transports mining products like copper and sulfuric acid. Its network is 900 kilometers (560 miles) long. It connects to railways in Bolivia and Argentina.
Future Train Plans
Because Antofagasta has grown so much, there are plans for a commuter train. This train would use the existing FCAB line. It would help reduce traffic by connecting the north and south parts of the city.
Sister Cities
Antofagasta is connected with other cities around the world. These are called sister cities:
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Antofagasta para niños
In Spanish: Antofagasta para niños