Biomolecule facts for kids
A biomolecule is a molecule that is made and used by living things, like plants, animals, and even tiny bacteria. Think of them as the "building blocks of life." They are essential for processes like growing, getting energy, and storing information.
Biomolecules include large molecules like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids (fats), and nucleic acids (like DNA). They also include smaller ones like vitamins and hormones. The study of these molecules is a big part of biochemistry and molecular biology.
Almost all biomolecules are organic compounds, which means they are built around the element carbon. Just four elements—oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen—make up 96% of the human body's mass.
Even though there are millions of different species on Earth, many of them use the exact same types of biomolecules to live. This is one of the amazing, unifying ideas in biology, along with the cell theory and the theory of evolution.
Contents
The Four Main Types of Biomolecules
Living things rely on four main groups of biomolecules to function.
- Carbohydrates (sugars and starches) are the main source of energy.
- Lipids (fats and oils) are used to store energy and build cell membranes.
- Proteins are the "workers" of the cell, carrying out many different jobs.
- Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) store and carry genetic information.
Nucleic Acids: The Cell's Code
Nucleic acids are like the instruction manual for a cell. They tell the cell what to do and how to build everything it needs. The two main types are DNA and RNA. They are made of smaller units called nucleotides.
Each nucleotide has three parts: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
- In DNA, the bases are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
- In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil (U).
Nucleotides do more than just build DNA and RNA. They also help carry energy around the cell. For example, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the main energy currency of the cell.
DNA and RNA Structure
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) stores the genetic blueprint for an organism. Its structure is a famous shape called a double helix, which looks like a twisted ladder. The "rungs" of the ladder are made of pairs of bases. Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G). This specific pairing is how genetic information is stored so accurately.
RNA (ribonucleic acid) has several important jobs. One type, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries a copy of the instructions from the DNA in the cell's nucleus out to the main part of the cell where proteins are made. Unlike DNA, RNA is usually a single strand, which allows it to fold into complex 3D shapes to perform different tasks.
Carbohydrates: Energy for Life
Carbohydrates are biomolecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and they are the main source of fuel for most living things. They are also known as saccharides, or sugars.
Simple Sugars
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates, made of just one sugar unit. The most important one is glucose, which your cells use for energy. Other examples include fructose (found in fruits) and galactose (found in milk).
Disaccharides are made when two simple sugars join together. The most common example is sucrose, which is regular table sugar. It is made of one glucose and one fructose molecule joined together. Lactose, the sugar in milk, is another example.
Complex Carbohydrates
Polysaccharides are long chains made of many simple sugars linked together. They are great for storing energy or building structures.
- Starch is how plants store extra glucose. When you eat potatoes or bread, you are eating starch.
- Glycogen is how animals store extra glucose. It is stored in your liver and muscles.
- Cellulose is a strong polysaccharide that plants use to build their cell walls. It gives plants their structure and is what we call fiber in our diet.
Lipids: Fats, Oils, and More
Lipids are a group of biomolecules that do not mix well with water. They are commonly known as fats, oils, and waxes. Their main jobs are storing energy for long-term use and forming the outer membranes of cells.
Most lipids are amphiphilic, meaning they have a "head" that is hydrophilic (water-loving) and a "tail" that is hydrophobic (water-fearing). This property is key to how they form cell membranes. The tails hide from the water, while the heads face the water, creating a protective barrier.
Lipids include:
- Fatty acids: Long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. They can be saturated (with only single bonds, like butter) or unsaturated (with one or more double bonds, like olive oil).
- Phospholipids: The main component of cell membranes. They have a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails.
- Sterols: A type of lipid with a ring structure. Cholesterol is an important sterol that is also part of cell membranes.
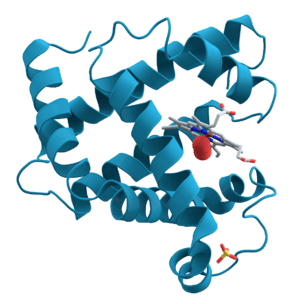
Proteins: The Workers of the Cell
Proteins are the most versatile biomolecules. They do almost everything in a cell. They act as enzymes to speed up chemical reactions, provide structural support (like collagen in your skin), transport substances (like hemoglobin carrying oxygen in your blood), and much more.
Amino Acids: The Building Blocks of Proteins
Proteins are polymers made from smaller units called amino acids. There are 20 common types of amino acids. The order in which these amino acids are linked together determines what the protein's shape and function will be.
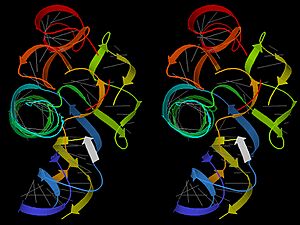
Protein Structure
A protein's function depends entirely on its unique 3D shape. This shape is built in four levels:
- Primary structure: This is simply the sequence, or order, of amino acids in the chain.
- Secondary structure: The amino acid chain begins to fold and twist into simple patterns, such as an alpha helix (a spiral) or a beta sheet (a pleated, flat sheet).
- Tertiary structure: The helixes and sheets fold up further to form a compact, overall 3D shape. This is the final working shape for many proteins.
- Quaternary structure: Some proteins are made of more than one amino acid chain. This level describes how the different chains fit together to form a larger protein complex. Hemoglobin is an example of a protein with a quaternary structure.
See also
 In Spanish: Biomolécula para niños
In Spanish: Biomolécula para niños
- Biomolecular engineering
- List of biomolecules
- Metabolism
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |