Caborn-Welborn culture facts for kids
The Caborn-Welborn people were a group of Native Americans who lived in North America a long time ago. They were part of the Mississippian culture, which was a big group of ancient societies in the central and southeastern United States. The Caborn-Welborn culture developed around the year 1400. They lived in what is now southern Indiana, after an earlier group called the Angel chiefdom. This culture lasted until about 1700. They were the last Native American group to live in southern Indiana before Europeans arrived. We are not sure which Native American groups today are their direct descendants.
Contents
Where Did the Caborn-Welborn People Live?
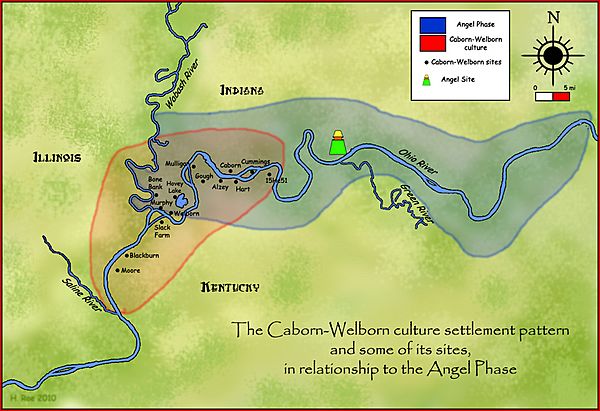
The Caborn-Welborn culture had more than 80 known sites. Most of these sites were located along the Wabash and Ohio rivers. Their territory stretched from Geneva, Kentucky to the Saline River in Illinois. Many of their settlements were found where the Ohio and Wabash rivers meet.
Caborn-Welborn Settlements
The sites where these people lived varied in size. Some were small, about 0.6 acres, while larger villages could be up to 35 acres. Most of their homes were built on higher ground, like ridges, in the river floodplains. They often chose spots near sloughs (small, swampy channels) and marshy areas. The Ohio River floodplain in this area has many natural levees (raised banks). These levees run alongside the river, with swampy areas in between them.
Some important Caborn-Welborn sites include:
- Bone Bank Site: This was a large village on the Wabash River. It got its name because many ancient burial sites were found there in the 1800s. It was one of the earliest Caborn-Welborn settlements, started around 1400.
- Hovey Lake-Klein Archeological Site (12 Po 10): This site is located near a lake that connects to the Ohio River. It was also established around 1400.
- Slack Farm: A large village located near where the Wabash River meets the Ohio River.
- Welborn Village Archeological Site (12 Po 19): Also known as Murphy's Landing Site, this village was in Posey County, Indiana.
Caborn-Welborn Timeline
Archaeologists have divided the Caborn-Welborn culture into three main time periods. These periods are based on the types of pottery found and if European trade goods were present.
| Period | Dates | What was happening |
|---|---|---|
| Early Caborn-Welborn | 1400–1450 | This was a time of change from older cultures to the Caborn-Welborn way of life. |
| Middle Caborn-Welborn | 1450–1600 | This was the main period for the Caborn-Welborn culture. |
| Late Caborn-Welborn | 1600–1700 | This period is called "Protohistoric." It means it was just before direct contact with Europeans. European trade goods started to appear. |
What Was Their Culture Like?
Pottery
The women of the Caborn-Welborn culture made pottery by hand. They built up pots from strips of clay, then smoothed them out. They did not use a potter's wheel, which was unknown in Eastern America. Common shapes included jars, bowls, pans, plates, and funnels. Many jars had rounded necks and handles.
Most of their pottery was called Mississippian Plain and Bell Plain. These types were common in many Mississippian cultures. This pottery was usually buff-colored and contained crushed mussel shells to make it stronger. It was not as smooth or shiny as some other types of pottery.
Some unique pottery styles help us identify the Caborn-Welborn people. These include Caborn-Welborn Decorated, Kimmswick Fabric Impressed, and Kimmswick Plain. They also made jars shaped like humans or animals. Some had heads and tails attached to the rim, while others were shaped entirely like heads with clay pieces for limbs. Caborn-Welborn Decorated pottery often had lines or dots carved into the shoulders of the jars.
Agriculture and Food
The Caborn-Welborn people were skilled farmers. They grew a lot of maize (corn), which was their main food. They also grew other important crops like beans, squash, sunflowers, and gourds. Adding beans to their diet was very important. Beans provided valuable protein, which balanced their diet that was rich in corn. Corn lacks certain amino acids, but beans have them. Together, corn and beans provide a complete and healthy diet.
They also gathered many wild foods from their local environment. These included different kinds of nuts like hickory, black walnuts, pecans, and acorns. They also collected fruits and berries such as persimmons, pawpaws, and plums.
Hunting was another important way they got food. They hunted animals like whitetail deer, bison, squirrels, rabbits, turkeys, opossums, and beavers. These animals provided much-needed protein. However, unlike some other Mississippian groups, the Caborn-Welborn people did not eat a lot of fish or waterfowl.
European Trade Goods and Their Impact
In the later years of the Caborn-Welborn culture, European trade items started to appear. These items were sometimes found in graves. They included things like copper and brass tubes, glass beads, and bracelets. This does not mean that Europeans had direct contact with the Caborn-Welborn people. Instead, these items likely traveled along old trade routes. Native traders had used these routes for centuries to bring special materials, like shells and native copper, from other regions.
However, these traders also unknowingly carried European diseases. Diseases like smallpox and measles often spread across the American continents long before European explorers arrived. Native American groups had little or no natural protection against these new diseases. As a result, many cultures suffered greatly or even disappeared before they ever met Europeans face-to-face. The Caborn-Welborn culture is believed to be one of these groups.