Cloverly Formation facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Cloverly FormationStratigraphic range: Aptian-Albian |
|
|---|---|

Brightly colored strata of the Himes Member of the Cloverly Formation near Shell, Wyoming
|
|
| Type | Geological formation |
| Sub-units | Pryor Conglomerate, Little Sheep Member, Himes Member |
| Underlies | Thermopolis Shale |
| Overlies | Morrison Formation |
| Thickness | 150–400 ft (46–122 m) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Mudstone |
| Other | Conglomerate, sandstone |
| Location | |
| Region | |
| Country | |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Cloverly post office, Wyoming |
| Named by | Nelson Horatio Darton, 1904 |
The Cloverly Formation is a special rock layer found in parts of the western United States. You can find it in Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, and Utah. This rock layer formed during the Early Cretaceous period, which was about 125 to 100 million years ago.
It was named in 1904 after a post office in Wyoming by a scientist named N.H. Darton. The rocks in the Cloverly Formation were laid down in ancient floodplains. They are famous for containing many fossils of vertebrate animals, especially dinosaurs! Because it's so important for understanding Earth's past, the Cloverly Formation Site was made a National Natural Landmark in 1973.
Contents
How the Cloverly Formation is Layered
The Cloverly Formation sits on top of another rock layer called the Morrison Formation. It is covered by a layer called the Thermopolis Shale. Think of it like a sandwich of rock layers.
Scientists have divided the Cloverly Formation into different sections, or "members," depending on where you are. In one area, the Bighorn Basin, it's divided into three main parts:
- The Pryor Conglomerate is the very bottom layer. It's made of a type of rock called conglomerate, which is like natural concrete with lots of pebbles and black chert pieces. It's named after the Pryor Mountains.
- The Little Sheep Member is the middle layer. It's mostly pale purple, gray, or almost white mudstone. This mudstone has a lot of bentonite, which is a type of clay that can swell up when wet.
- The Himes Member is the top layer. It has some coarse-grained sandstone from ancient river channels. But it's mostly made of brightly colored, varied mudstones.
How Old is the Cloverly Formation?
Scientists use a method called radiometric dating to figure out how old rocks are. This is like a very accurate clock that uses tiny amounts of radioactive materials in the rocks.
Using this method, they found that the lower part of the Little Sheep Member is about 115 million years old. The top part of that same member is about 108.5 million years old. This confirms that the Cloverly Formation formed during the Aptian to Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous period.
What the Environment Was Like
The rocks in the Cloverly Formation tell us about the ancient environment where they formed. It was a land of rivers and floodplains.
- The thick conglomerate layers at the bottom were likely left behind by braided rivers. These are rivers that split into many smaller channels.
- The sandstone layers were formed in the main channels of these ancient rivers.
- The mudstone layers, where most of the fossils are found, were formed in areas away from the main river channels. These could be overbank deposits (from floods), lake deposits, or ancient soils.
Amazing Animals Found in the Cloverly Formation
The Cloverly Formation is famous for its incredible vertebrate fossils, especially dinosaurs! Here are some of the animals that have been found:
- The fierce Deinonychus
- The smaller Microvenator
- The plant-eating Tenontosaurus
- The speedy Zephyrosaurus
- The armored Sauropelta
- Large Titanosaurs (a type of long-necked dinosaur)
- Ornithomimids (dinosaurs that looked a bit like ostriches)
- Two types of turtles: Naomichelys and Glyptops
- The ancient lungfish Ceratodus
Scientists have even found Dinosaur eggs in Montana from this formation!
Ornithischian Dinosaurs
These are dinosaurs with hips like birds.
| Ornithischian Dinosaurs from the Cloverly Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | What was found | Cool Facts | Images | |
|
A. americanus |
|
This was a small, early horned dinosaur. |
||||
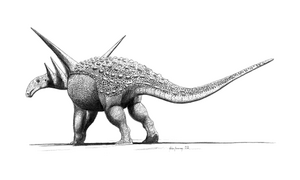
|
S. edwardsorum |
|
Several full skeletons and many armor plates. |
Its armor plates are very common fossils. Scientists often use acid to safely remove the rock around its bones. |
|||
|
T. tilleti |
|
Many remains, making it the most common dinosaur found here. |
Young Tenontosaurus might have lived in groups. Deinonychus teeth are often found near Tenontosaurus bones, suggesting Deinonychus hunted them. |
|||
|
Z. schaffi |
|
Very rare remains. |
This was a small, fast-running dinosaur. |
|||
Saurischian Dinosaurs
These are dinosaurs with hips like lizards.
| Saurischian Dinosaurs from the Cloverly Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | State | What was found | Cool Facts | Images | |
| Acrocanthosaurus | A. atokensis |
|
This was a large, powerful meat-eating dinosaur. |
|||
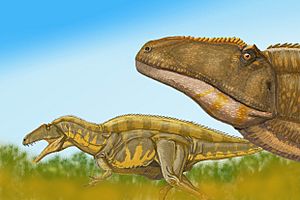
|
D. antirrhopus |
|
Very rare remains. |
This dinosaur had a large, sickle-shaped claw on each foot. It likely hunted Tenontosaurus. |
|||
|
M. celer |
|
Extremely rare, only a partial skeleton. |
Its name means "tiny hunter." The first bones were found in 1933. |
|||
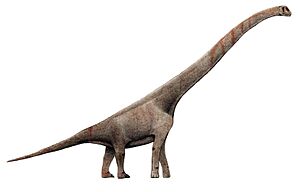
|
Rugocaudia |
R. cooneyi |
|
This was a type of long-necked dinosaur (sauropod). |
|||
| Sauroposeidon | S. proteles |
|
This was one of the tallest dinosaurs ever, with a very long neck. |
|||
Ancient Mammals
Small, early mammals also lived alongside the dinosaurs.
| Mammals from the Cloverly Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | What was found | Cool Facts | Images | ||
|
Corviconodon |
C. montanensis |
|||||
|
Gobiconodon |
G. ostromi |
This mammal was a predator, eating other small animals. |
||||
|
Montanalestes |
M. keeblerorum |
This was a very early type of mammal. |
||||
Turtles
Two types of ancient turtles have been found.
| Turtles from the Cloverly Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | What was found | Cool Facts | |||
|
Glyptops |
G. pervicax |
This turtle lived in freshwater environments. |
||||
|
Naomichelys |
N. speciosa |
This turtle had a unique shell pattern. |
||||
Bony Fish
Ancient fish also swam in the waters of the Cloverly Formation.
| Bony Fish from the Cloverly Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | What was found | Cool Facts | Images | ||
|
Ceratodus |
C. frazieri |
This was a type of lungfish, able to breathe air. |
||||
|
C. nirumbee |
||||||
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Formación Cloverly para niños
In Spanish: Formación Cloverly para niños