Colonial colleges facts for kids
The colonial colleges are nine special schools that were started in the Thirteen Colonies before the United States became its own country after the American Revolution. These schools have been studied together for a long time, especially since a big survey in 1907.
Seven of these nine colonial colleges grew up to become seven of the eight famous Ivy League universities. These are Harvard, Yale, Princeton, Columbia, University of Pennsylvania, Brown, and Dartmouth. The eighth Ivy League school, Cornell University, was founded much later in 1865. All these schools are private universities, meaning they get most of their money from tuition and donations, not from the government.
The two colonial colleges that are not part of the Ivy League are now public universities. These are The College of William & Mary in Virginia and Rutgers University in New Jersey. William & Mary started as a royal school in 1693, meaning the King or Queen of England approved its creation. After the American Revolution, it became a private school. It faced tough times during the American Civil War and started getting money from the government in the 1880s. William & Mary officially became a public college in 1906.
Rutgers was founded in 1766 as Queen's College, named after Queen Charlotte. For many years, it was connected to the Dutch Reformed Church, a religious group. It changed its name to Rutgers University in 1825. After World War II, it was named the State University of New Jersey, becoming a public school.
What are the Nine Colonial Colleges?
Most of the nine colonial colleges started as places for higher education right away. However, two of them grew out of schools that were already teaching younger students.
Dartmouth College began in 1768 as the college part of Moor's Charity School. This was a secondary school started in 1754 by Dartmouth's founder, Eleazar Wheelock. Dartmouth officially considers its founding year to be 1769, when it received its special college charter.
The University of Pennsylvania started in 1751 as a secondary school called the Academy of Philadelphia. It added a higher education part in 1755 when it received a charter to become the College of Philadelphia.
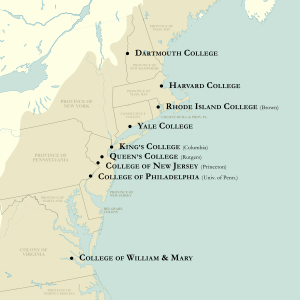
Here is a list of the nine colonial colleges:
| Image | Colonial College (Current Name, if different) |
Colony | Founded | Chartered | First Classes (Degrees) | Main Religious Connection | Ivy League |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
New College (Harvard University) |
Massachusetts Bay Colony | 1636 | 1650 | 1642 (1642) | Puritan (Congregational) | Yes |
 |
College of William & Mary | Colony of Virginia | 1693 | 1693 | 1694 | Church of England (Episcopalian) | No |
 |
Collegiate School (Yale University) |
Connecticut Colony | 1701 | 1701 | 1702 (1702 honorary MA) (1703 BA) | Puritan (Congregational) | Yes |
 |
College of New Jersey (Princeton University) |
Province of New Jersey | 1746 | 1746 | 1747 (1748) | Presbyterian (but officially non-religious) | Yes |
 |
King's College (Columbia University) |
Province of New York | 1754 | 1754 | 1754 (1758) | Church of England (but allowed religious freedom) | Yes |
 |
College of Philadelphia (University of Pennsylvania) |
Province of Pennsylvania | 1740 (college) | 1755 | 1755 (1757) | Church of England (but officially non-religious) | Yes |
 |
College of Rhode Island (Brown University) |
Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations | 1764 | 1764 | 1765 | Baptist (but no religious rules for students) | Yes |
 |
Queen's College (Rutgers University) |
Province of New Jersey | 1766 | 1766 | 1771 (1774) | Dutch Reformed (Calvinist) | No |
 |
Dartmouth College | Province of New Hampshire | 1769 | 1769 | 1768 (1771) | Puritan (Congregational) | Yes |