Dolphin facts for kids
Dolphins are amazing mammals that live in the water. They are part of a group called toothed whales, which means they have teeth instead of baleen plates. Dolphins are usually smaller than other whales. Most dolphins live in the salty oceans, but some kinds, like the river dolphins, live in fresh water rivers. Dolphins can be from about 1.5 to 4 meters (5 to 13 feet) long. The biggest dolphin is the Killer whale, which can grow to about 8 meters (26 feet) long!
The name 'dolphin' comes from an old Greek word that meant "with a womb." People first thought they were fish with wombs. But now we know they are intelligent mammals. Dolphins breathe air through a hole on top of their heads called a blowhole. This makes it easy for them to breathe when they are at the surface of the water. A dolphin's skin is smooth and soft, but also very firm because of their strong muscles. Dolphins use a special skill called echolocation to find their food.
Contents
Dolphin Families and Types
Dolphins belong to the group of toothed whales. There are many different kinds of dolphins around the world. They are generally split into two main groups: oceanic dolphins and river dolphins.
Some well-known oceanic dolphins include:
- The Common bottlenose dolphin, which you often see in shows.
- The Killer whale (also called Orca), which is the largest dolphin.
- The Common dolphin, known for its sleek body.
- The Spotted dolphin, which has spots on its body.
River dolphins live in freshwater rivers and are often endangered. Some examples are:
- The Amazon river dolphin (or Boto) from South America.
- The Ganges river dolphin from India.
- The Chinese river dolphin (or Baiji), which is sadly thought to be extinct.
How Dolphins Live
Dolphin Bodies
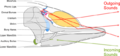
Dolphins have smooth, torpedo-shaped bodies that help them glide through water. Their necks are usually stiff, but river dolphins can turn their heads more. They have two front fins called flippers, a back fin called a dorsal fin, and a powerful tail fin. Their eyes are on the sides of their heads.
Dolphins have cone-shaped teeth, which are perfect for catching fast-moving prey like fish and squid. They also have a thick layer of fat called blubber. This blubber helps them float, protects them from predators, and keeps them warm in cold water. Baby dolphins are born with a thin layer of blubber that grows thicker as they get older.
How Dolphins Move
Dolphins are very fast swimmers! They move their strong tail fin up and down to push themselves through the water. Their flippers help them steer. Some dolphins can swim as fast as 55 kilometers (34 miles) per hour.
When dolphins swim fast, they often leap out of the water. This is called "porpoising" and it helps them save energy because there's less friction in the air than in the water. Dolphins also have a dorsal fin on their back that keeps them stable and stops them from spinning.
Some dolphins can dive very deep. To do this, they can slow down their heart rate and send blood to their most important organs like the heart and brain.
Dolphin Senses
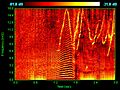
Dolphins have amazing senses, especially their hearing. They use a special skill called echolocation to "see" with sound. They send out high-pitched clicks from an organ in their head called a melon. These clicks travel through the water, hit objects, and bounce back as echoes. Dolphins listen to these echoes to figure out where objects are, how big they are, and what shape they are. It's like having natural sonar!
Dolphins also have good eyesight, even though their eyes are small. They can see well both in dim and bright light underwater. They don't have a sense of smell, and their sense of taste is not very strong.
Dolphin Behavior
Smart Animals
Dolphins are known for being very intelligent animals. They can learn, cooperate, and even grieve for others. Scientists study their brains and have found special cells that are also found in human brains. Killer whales have the second largest brains of any animal on Earth, after sperm whales.
Some research suggests that dolphins might even be self-aware. This means they can recognize themselves, like when they look in a mirror.
Living in Groups
Dolphins are very social animals. They live in groups called "pods," which can have up to a dozen dolphins. Sometimes, if there's a lot of food, many pods might join together to form a "superpod" with over a thousand dolphins!
Dolphins in a pod often help each other. They will stay with injured or sick dolphins and even help them breathe by pushing them to the surface. They have also been seen protecting swimmers from sharks.
Dolphins talk to each other using different sounds, like clicks and whistle-like noises. They also use body language, like touching and different postures.
Some dolphins even have their own "culture." For example, some dolphins in Australia teach their young to use sponges to protect their noses while they look for food on the seafloor. This is a learned behavior passed down from mothers to daughters.
Eating Habits
Dolphins eat mainly fish and squid. Larger dolphins, like the false killer whale and orca, also eat other marine mammals. Orcas can even hunt larger whales!
Dolphins have clever ways to catch food. One way is "herding," where a group of dolphins works together to push a school of fish into a tight ball. Then, individual dolphins take turns swimming through the ball to eat the stunned fish. Some dolphins even chase fish onto beaches to catch them, which is called "strand feeding."
Dolphin Sounds
Dolphins make many different sounds using air sacs near their blowhole. These sounds include whistles, burst-pulsed sounds, and clicks. The clicks are used for echolocation.
Bottlenose dolphins have special "signature whistles" that are unique to each dolphin. It's like their own name! They learn these whistles when they are young and keep them for their whole lives. Dolphins can even copy another dolphin's whistle to "call" to them. They have amazing memories for these whistles, remembering them for over twenty years!
Playing and Jumping
Dolphins love to jump out of the water. They do this for many reasons, like saving energy when traveling (porpoising), looking around, showing off, communicating, or even trying to shake off parasites.
Dolphins are also very playful. They often play with objects, make bubble rings, or play with other dolphins and even other animals. Sometimes, young dolphins have been seen playing with blowfish, which might make them feel a bit strange due to the fish's natural toxins.
Dangers to Dolphins
Natural Dangers
Dolphins don't have many natural enemies. For smaller dolphins, large sharks like the bull shark or great white shark can be a danger, especially to young calves. Sometimes, larger dolphins like orcas might prey on smaller dolphins, but this is rare.
Dolphins can also get sick from diseases and parasites. There's a virus called Cetacean morbillivirus that can cause serious illness and even death in many dolphins. Scientists have also found that dolphins can get a natural form of type 2 diabetes, similar to humans.
Amazingly, dolphins can heal very well from serious injuries, like shark bites. Their wounds heal quickly, and they rarely get infections, even from deep cuts.
Dangers from Humans
Sadly, many dolphin species are in danger, especially river dolphins. The Chinese river dolphin is now thought to be extinct because of human activities.
Dolphins face many threats from humans:
- Pollution: Pesticides, heavy metals, plastics, and other chemicals from farms and factories pollute the oceans and rivers. These harmful substances build up in dolphins' bodies.
- Boat Collisions: Dolphins can get hurt or killed by boats, especially by their propellers.
- Fishing: Many dolphins get caught accidentally in fishing nets, like those used for tuna, or in large drift and gill nets. This is called "by-catch."
- Hunting: In some parts of the world, like Japan and the Faroe Islands, dolphins are hunted for their meat. This is often done by driving whole pods of dolphins into bays or onto beaches. Dolphin meat can be dangerous to eat because it often contains high levels of mercury.
- Noise Pollution: Loud noises underwater from things like naval sonar, military exercises, or building wind farms can harm dolphins. These noises can stress them, damage their hearing, or make them surface too quickly, causing them to get sick.
Dolphins and People
Dolphins in History and Stories
Dolphins have been important to humans for a very long time. In Greek mythology, dolphins were often seen as helpers of people. Many ancient Greek coins show people or gods riding on dolphins. The Greeks believed that seeing dolphins swimming near a ship was a sign of good luck. There are stories of dolphins rescuing people from drowning, like the poet Arion.
Dolphins were also messengers for the sea god Poseidon and were sacred to the gods Aphrodite and Apollo. In some stories, the god Dionysus turned pirates into dolphins because they tried to capture him.
In Hindu mythology, the Ganges river dolphin is linked to the goddess Ganga, who represents the Ganges river. In the Amazon, some people believe that the Amazon river dolphin (Boto) can change into a human shape and even have children with people.
Dolphins in Zoos and Parks
Many people enjoy seeing dolphins in dolphinariums and marine parks around the world. Bottlenose dolphins are the most common type kept in these parks because they are easy to train and have a friendly look. Killer whales are also popular for their amazing shows, even though fewer of them are kept in captivity.
Organizations like the Mote Marine Laboratory help rescue and care for sick, injured, or orphaned dolphins. Other groups, like the Whale and Dolphin Conservation Society, work to protect dolphins and their habitats. India has even made the Ganges river dolphin its national aquatic animal to help protect this endangered species.
Images for kids
-
Killer whales jumping.
-
Biosonar by cetaceans.
-
A group of Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphins in the Red Sea.
-
Dolphins surfing at Snapper Rocks, Queensland, Australia.
-
Dead Atlantic white-sided dolphins in Hvalba on the Faroe Islands, killed in a drive hunt.
-
A vessel shaped like a killer whale from the Nazca culture.
-
A SeaWorld show with bottlenose dolphins and pilot whales.
-
A SeaWorld Pilot Whale with trainers.
-
The face of a common bottlenose dolphin.
-
Silver stater from Tarentum c. 290 BC showing Phalanthos riding a dolphin on one side and a rider with a shield decorated with a dolphin on the other side.
-
Plate of dolphin sashimi.
See also
 In Spanish: Delfines oceánicos para niños
In Spanish: Delfines oceánicos para niños