Futurism facts for kids
Futurism was an exciting modern art and cultural movement that started in Italy in the early 1900s. It was mostly popular in Italy, but similar ideas popped up in Russia and England too.
Futurists used many types of art to express their ideas. They created paintings, sculptures, and even designed buildings (architecture). They also explored theatre, movies, fashion, literature, and music.
Contents
The Start of Futurism in Italy
The person who started Futurism and was its main leader was an Italian writer named Filippo Tommaso Marinetti. He officially launched the movement in a special article called the Futurist Manifesto. This article was first published in an Italian newspaper in February 1909. Soon after, it was printed in a big French newspaper called Le Figaro.
Marinetti strongly disliked anything old or traditional. He wrote, "We want no part of it, the past!" The Futurists loved speed, technology, and everything new. They admired cars, airplanes, and busy industrial cities. They believed these things showed how humans were conquering nature with technology. They were also very proud of Italy and loved their country.
They wanted to be original and daring. They didn't care what art critics thought and rebelled against old ideas of harmony and good taste. They were excited about science and new inventions.
Publishing these special articles, called manifestos, was a big part of Futurism. Marinetti and other Futurists wrote manifestos about many topics. These included painting, architecture, clothing, and even cooking!
Futurist Art and Ideas
The first manifesto didn't explain exactly how Futurist art should look. So, the artists wrote another one called the Technical Manifesto of Futurist Painting. This new manifesto talked about showing "universal dynamism" in their art. This means they wanted to show movement and energy in their paintings.
Many Futurist artworks were influenced by Cubism, an art style that used geometric shapes. However, Futurist paintings often felt more active and full of motion than Cubist art. People sometimes called their early work 'plastic dynamism' because it showed movement and changing forms.
A rich businessman in Milan named Antonio Bernocchi was a big supporter of Futurism. He even created one of the first examples of Italian industrial design, a lamp called "Luminator Bernocchi", inspired by Futurist ideas.
Later Years and Influence
Many Italian Futurists supported Fascism, a political movement, because they hoped it would help modernize Italy. Italy at the time was divided between the industrial north and the older, rural south. Like the Fascists, Futurists were strong Italian nationalists. They were also against parliamentary democracy. Marinetti himself was one of the first members of the National Fascist Party. He continued to support Italian Fascism until he died in 1944.
Because of their connection with Fascism, Futurists gained official acceptance in Italy after 1922. This allowed them to work on important projects, especially in architecture. However, after World War II, many Futurist artists found it hard to continue their careers. This was because Fascism had been defeated and was no longer popular.
The Futurist movement kept changing and renewing itself until Marinetti's death.
The Legacy of Futurism
Futurism had a huge impact on many other art movements in the 20th century. These include Art Deco, Vorticism, Constructivism, Surrealism, and Dadaism. In some ways, Futurism was so focused on the future that the future itself caught up to it!
Even today, the ideas of Futurism are still part of modern Western culture. The focus on youth, speed, power, and technology can be seen in many modern movies and cultural trends. For example, the director Ridley Scott used design ideas from the Futurist architect Antonio Sant'Elia in his famous movie Blade Runner.
Marinetti's idea of the "dreamt-of metallization of the human body" (meaning humans becoming more like machines) is still strong in Japanese culture. You can see this in manga and anime, and in the works of artists like Shinya Tsukamoto, who directed the "Tetsuo" (meaning "Ironman") films.
Futurism also influenced the literary genre of cyberpunk. Artists who became famous when the internet first started, like Stelarc and Mariko Mori, created art inspired by Futurist ideas. A new version of the Futurist movement, called Neo-Futurism, began in 1988 in Chicago. This theatre style uses Futurism's focus on speed and quickness to create a new type of immediate performance. There are active Neo-Futurist groups in Chicago, New York, and Montreal.
Images for kids
-
Gino Severini, 1912, Dynamic Hieroglyphic of the Bal Tabarin. This painting shows movement and light.
-
Italian Futurists Luigi Russolo, Carlo Carrà, Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, Umberto Boccioni, and Gino Severini in front of the Le Figaro newspaper office in Paris, 1912.
-
Umberto Boccioni, a sketch for The City Rises (1910).
-
Giacomo Balla, 1912, Dinamismo di un Cane al Guinzaglio (Dynamism of a Dog on a Leash). Notice how it shows motion!
-
Umberto Boccioni, 1913, Dynamism of a Cyclist (Dinamismo di un ciclista).
-
From left to right: Aldo Palazzeschi, Carlo Carrà, Giovanni Papini, Umberto Boccioni, and Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, 1914.
-
Natalia Goncharova, Cyclist, 1913. An example of a similar style from Russia.
-
A group photo of some Russian Futurists. From left to right: Aleksei Kruchyonykh, Vladimir Burliuk, Vladimir Mayakovsky, David Burliuk, and Benedikt Livshits.
-
An example of Futurist architecture designed by Antonio Sant'Elia.
-
Joseph Stella, 1919–20, Brooklyn Bridge. This American artist was influenced by Futurism.
-
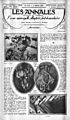
Paintings by Jean Metzinger, Gino Severini, and Albert Gleizes, published in a French magazine in 1912.
-
Paintings by Gino Severini, La Danse du Pan-Pan and L'autobus, published in a French magazine in 1920.
-
More paintings by Gino Severini, Albert Gleizes, and Luigi Russolo, published in a French magazine in 1920.
See also
 In Spanish: Futurismo para niños
In Spanish: Futurismo para niños