Golden Gate Biosphere Reserve facts for kids
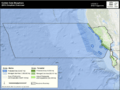
The Golden Gate Biosphere is a special protected area in Northern California. It was created by UNESCO in 1988. This area includes 13 different protected places around the San Francisco Bay Area. It stretches from the Bodega Marine Reserve in the north to Jasper Ridge in the south. It also covers islands like the Farallon Islands, Angel Island, and Alcatraz inside San Francisco Bay.
Contents
What Makes the Golden Gate Biosphere Special?
This biosphere reserve sits on both sides of the famous San Andreas Fault. Each side has a completely different type of rock. The western side of the fault is slowly moving northward.
Amazing Habitats and Animals
The Golden Gate Biosphere has many different kinds of natural places, called habitats. These include areas by the ocean, along the coast, and in the hills. You can find California chaparral and woodlands and Northern California coastal forests here.
- Forests: There are mixed evergreen forests, Coast Redwood forests, Douglas-fir forests, Bishop pine forests, and oak forests.
- Open Areas: You'll also see woodlands, savannas, northern coastal scrub, chaparral, and coastal grasslands.
- Coastal and Ocean: Along the coast, there are coastal dunes, coastal strand (sandy beaches), tidepools, and kelp forests in the ocean.
The animals here are also very diverse. You might spot cougars, Tule elk, California sea lions, and elephant seals. Many different kinds of shorebirds also live in this area.
Exploring the Biosphere
The Golden Gate Biosphere is special because it's right next to a big city, San Francisco. This makes it easy for people to visit and learn about nature. It's also a great place for outdoor fun!
- Activities: You can go fishing, hiking, bicycling, and even whale watching here. It's a perfect spot to enjoy nature close to home.
How the Biosphere is Managed
The Golden Gate Biosphere is run by an association with three main groups. These groups work together on managing the area, doing scientific research, and teaching people.
- Teamwork: For example, they work together to check on tidepools and teach the public about them near Mount Tamalpais State Park.
- Restoration: Another joint project is helping to bring back Coho salmon. This involves mapping and checking the health of important watersheds (areas where water drains into a river or lake).
- Research: Scientists study many things here. They look at how to manage important resources like fish. They also study threats like oil spills, pollution, and invasive species (plants or animals that don't belong and can harm the environment). They also research natural events like wildfires and extreme weather.
![]() This article incorporates text from a free content work. License statement/permission on Wikimedia Commons. Text taken from UNESCO - MAB Biosphere Reserves Directory, UNESCO, UNESCO.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. License statement/permission on Wikimedia Commons. Text taken from UNESCO - MAB Biosphere Reserves Directory, UNESCO, UNESCO.
Images for kids
-
A protected area in Bodega Head State Marine Reserve
-
The endangered Mission blue butterfly found in Marin Headlands
-
Coho salmon are threatened by rising sea temperatures and poor stream conditions
-
The endangered Brown pelican lives on the coasts of the Golden Gate Biosphere
-
Redwood Creek supplies water to the Redwood trees of Muir Woods National Monument
-
Rare Clarkia franciscana plants can be found in Presidio Park, San Francisco
-
The San Francisco Wallflower is a rare perennial plant found in dune habitats
-
Bull kelp beds are an important habitat for marine wildlife in Duxbury Reef
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |