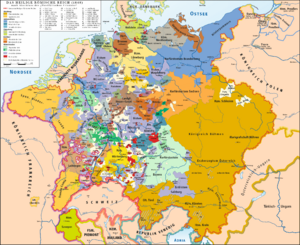
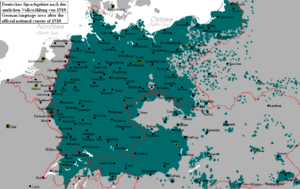
History of German facts for kids
The German language started to appear in the Early Middle Ages. This was when a big change happened in how German sounds, called the High German consonant shift. Over many centuries, German changed from Old High German to Middle High German, and then to Early New High German. These changes happened during the time of the Holy Roman Empire. In the 19th and 20th centuries, Standard German became very popular, and people started using fewer different local ways of speaking (dialects).
Contents
High German Language History
Old High German Beginnings
The very first examples of Old High German writing are from the 6th century. These are short messages carved into things. The first longer texts, like the Hildebrandslied, appeared in the 9th century.
Middle High German Period
Middle High German was the form of the German language used between the years 1050 and 1350. It came after Old High German and before Early New High German. This period saw many important stories and poems written in German.
Early New High German and Luther's Bible

The Protestant reformer Martin Luther translated the Christian Bible into High German. The New Testament was published in 1522, and the whole Bible was finished in 1534. He used a type of German that many people already understood. This language was based on dialects from eastern parts of Germany.
Luther wanted his translation to sound natural. He listened to how mothers, children, and common people spoke. He believed the Bible should be easy for everyone to understand. His translation helped a lot to make a common, standard German language. It also helped more people learn to read in Germany.
At first, Roman Catholics did not use Luther's translation. They tried to make their own standard German. But it was very similar to Luther's German. By the mid-1700s, a widely accepted standard German was finally created. This marked the end of the Early New High German period.
Low German Language History
Low German is a group of dialects or a language spoken in northern Germany. It is different from High German. It has a less clear history because it is connected to many other languages.
Low German was the main language in most of northern Germany for a long time. Older forms, like Old Saxon and Middle Low German, are seen as separate languages.
Low German was greatly influenced by High German during the Holy Roman Empire. After the Hanseatic League ended in the 17th century, Low German became mostly local dialects.
Old Saxon Language
Old Saxon, also called Old Low German, is a West Germanic language. We have writings from it between the 9th and 12th centuries. After that, it changed into Middle Low German. People in the northwest of Germany and in Denmark spoke Old Saxon. It is similar to Old English and Old Frisian.
Middle Low German Importance
Middle Low German is an older form of modern Low German. It was spoken from about 1100 to 1500. This language was very important for trade. It was the common language of the Hanseatic League. This was a powerful group of trading cities around the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Because of this, Middle Low German was spoken in many different places. A standard written form of the language started to develop, especially based on the language of Lübeck.
German in the 19th Century
In the Habsburg Empire, German was the language used for business and government. This empire covered a large part of Central and Eastern Europe. Until the mid-1800s, German was mainly spoken by people in towns and cities. If you spoke German, it often meant you were a merchant or lived in a city.
Many cities, like Budapest and Bratislava, became more German-speaking over time. Even cities like Prague and Zagreb, surrounded by other languages, were mostly German-speaking early in the century.
Until about 1800, standard German was mostly a written language. People in northern Germany, who spoke very different dialects, learned it almost like a foreign language. They tried to pronounce it exactly as it was spelled. However, the actual pronunciation of standard German varied from place to place.
German was also used in parts of the Russian Empire, like in Riga and Tallinn. It was their official language for administration until the late 1800s.
Today, almost all media and books are in standard German. This means people in all German-speaking areas can understand it. The first dictionary by the Brothers Grimm was published between 1852 and 1860. It is still a very important guide to the German language.
German in the 20th Century
In 1880, the first rules for German grammar and spelling appeared in the Duden Handbook. In 1901, these rules were officially declared the standard for the German language. German spelling stayed mostly the same until 1998. That's when a new spelling reform was officially started by Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, and Switzerland.
Before World War II, German was a very important language for science. Many major scientific papers, like those by Albert Einstein, were first published in German.
However, after World War II ended in 1945, things changed. Many German scientists were no longer able to work. This meant that German science and the German language lost their leading position in the scientific world.
See also
- German Language Literature
- German dialects
- Standard German
- German as a minority language
- Ethnic Germans