Budapest facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Budapest
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Skyline with the Chain Bridge, Banks of Danube, Buda Castle and Gellért Hill
Széchenyi Thermal Bath
Opera House on Andrássy Avenue
Fisherman's Bastion with Matthias Church
Great Market Hall on Váci Street
Infopark science and business district
Margaret Island and Margaret Bridge
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Nicknames:
Queen of Danube, Capital of Spas, Heart of Europe, Paris of the East
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Country | |||||||||||||||||||
| Region | Central Hungary | ||||||||||||||||||
| Settled by Romans | AD 41, as Aquincum | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unification of Buda, Pest and Óbuda | 17 November 1873 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Boroughs |
23 districts
I., Várkerület
II. III., Óbuda-Békásmegyer IV., Újpest V., Belváros-Lipótváros VI., Terézváros VII., Erzsébetváros VIII., Józsefváros IX., Ferencváros X., Kőbánya XI., Újbuda XII., Hegyvidék XIII. XIV., Zugló XV., Rákospalota, Pestújhely, Újpalota XVI. XVII., Rákosmente XVIII., Pestszentlőrinc-Pestszentimre XIX., Kispest XX., Pesterzsébet XXI., Csepel XXII., Budafok-Tétény XXIII., Soroksár |
||||||||||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||||||||||
| • Type | Mayor–council government | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Body | General Assembly of Budapest | ||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||
| • Capital city | 525.1 km2 (202.7 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Urban | 2,538 km2 (980 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Metro | 6,917 km2 (2,671 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation | Lowest (Danube) 96 m Highest (János Hill) 529 m (315 to 1,735 ft) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Population
(2025)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| • Capital city | 1,685,209 | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Rank | 1st (10th in EU) | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Density | 3,209/km2 (8,310/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Urban
(2023)
|
2,968,809 | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Metro | 3,303,786 | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Metro density | 477.63/km2 (1,237.06/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Demonyms | Budapester, budapesti (HU) | ||||||||||||||||||
| GDP | |||||||||||||||||||
| • Metro | €98.64 billion (US$FXConvert/Wordify error: cannot parse value "Lua error in Module:Math at line 586: attempt to call field '?' (a nil value).") (2023) | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Per capita | 168% of EU average (2023) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Postal code(s) |
1011–1239
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Area code | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | HU-BU | ||||||||||||||||||
| NUTS code | HU101 | ||||||||||||||||||
| HDI (2022) | 0.934 – very high · 1st | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Budapest is the exciting capital city of Hungary. It's the biggest city in the country, with about 1.7 million people living there. If you count the areas around it, the population grows to about 3.3 million! Budapest is super important for Hungary's government, economy, and culture. It's also one of the top ten largest cities in the European Union.
This amazing city sits right on the River Danube. It's in a special spot called the Pannonian Basin, which has been a crossroads for trade routes for a very long time. Budapest is known as a "global city." This means it's one of the most important cities in the world. It's also considered a top cultural city and one of the most comfortable places to live.
Budapest is a hub for learning, with over 30 universities and more than 150,000 students. Many of these universities are famous worldwide for subjects like science, engineering, and medicine. The city also hosts offices for big international groups, including some from the United Nations.
Did you know Budapest had the first underground train line in mainland Europe? It opened way back in 1896 and is still used today! The city's public transport system, with its metro and tram lines, helps 2.2 million people get around every day.
Contents
- What's in a Name?
- A Look Back in Time
- Budapest's Location and Weather
- Amazing Architecture
- City Districts
- People of Budapest
- Budapest's Economy
- How Budapest is Governed
- Top Sights and Fun Things to Do
- Parks, Islands, and Spas
- Getting Around Budapest
- Culture and Fun
- Sports in Budapest
- Learning in Budapest
- Sister Cities
- See also
What's in a Name?
The name Budapest came about in 1873 when three separate towns joined together: Buda, Óbuda, and Pest. Before that, people sometimes called the area "Pest-Buda."
Today, when Hungarians talk about "Pest," they often mean the whole city. But technically, Pest is the part of the city east of the Danube River. "Buda" refers to the hilly areas on the west side, including old Óbuda. The islands in the Danube, like Csepel, are not part of either Buda or Pest.
In English, the "s" in Budapest sounds like the "s" in "pest." But in Hungarian, it sounds more like "sh" as in "wash."
The names "Buda" and "Pest" have interesting, but unclear, origins. "Buda" might have come from the name of an old fortress leader or a Turkish or Slavic name meaning "twig." Some old stories even say it came from Bleda, the brother of the famous Hunnic ruler Attila.
"Pest" also has a few possible origins. It could come from an old Roman name, "Pession." Another idea is that it comes from a Slavic word for "cave" or a place where fires burned.
A Look Back in Time
The story of Budapest began with a Celtic settlement before the year 1 AD. Later, the Romans took over and built a town called Aquincum. This became an important Roman city in the 1st century AD. The Romans built roads, theaters, and baths there. You can still see the ruins of Aquincum in the Óbuda district today!
Around the end of the 9th century, the Magyar tribes arrived and settled in the area. They officially founded the Kingdom of Hungary about a century later. In the 13th century, the Mongols attacked, showing that the flat land was hard to defend. So, King Béla IV of Hungary ordered strong stone walls to be built around the towns. He also put his royal palace on the hills of Buda for better protection. In 1361, Buda became the capital of Hungary.
Buda became a center for art and learning in the 15th century, especially under King Matthias Corvinus. He had a huge library, the Bibliotheca Corviniana, which was one of the biggest in Europe! The first Hungarian book was printed in Buda in 1473.
The Ottomans took control of Buda in 1541, and their rule lasted for over 150 years. During this time, they built many famous bathhouses, some of which are still used today, like the Rudas Baths and Király Baths. In 1686, a large army from different European countries took Buda back from the Ottomans. This marked the end of Turkish rule in the region.
Modern Budapest's Journey
The 19th century was a time of big changes for Hungary. There was a fight for independence from the Habsburg monarchy in 1848. In 1867, Hungary and Austria formed the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and Budapest became one of its two capitals. This led to a huge growth spurt for the city.
In 1849, the Chain Bridge was built, connecting Buda and Pest for the first time. Then, in 1873, Buda, Pest, and Óbuda officially merged to create the city of Budapest. Pest quickly became the busy center for government, business, and culture.
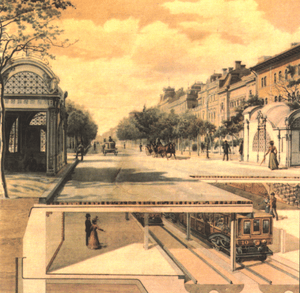
The city faced tough times during World War I and World War II. In 1944-1945, Budapest was heavily damaged by air raids and a long battle. All the bridges over the Danube were destroyed, but thankfully, the stone lions on the Chain Bridge survived!
After World War II, Hungary came under Soviet influence. In 1956, people in Budapest held a peaceful protest asking for democratic changes. This led to the Hungarian Revolution of 1956, an uprising against Soviet control. Sadly, it was put down by Soviet tanks, and many lives were lost. A monument was built in 2006 to remember this important event.
From the 1960s to the 1980s, the city slowly recovered. The last bridge, Erzsébet Bridge, was rebuilt in 1964. The metro system also expanded. In 1987, the Buda Castle and the banks of the Danube became a World Heritage Site. Later, Andrássy Avenue and the Millennium Underground were also added to this special list.
In 1989-1990, the communist system ended, and Hungary became a democracy. Budapest continued to grow and change, with new buildings and renovated public spaces.
Budapest's Location and Weather
Budapest is in the middle of Hungary, surrounded by smaller towns. The city stretches about 25 kilometers (15 miles) north to south and 29 kilometers (18 miles) east to west. The River Danube flows through the city, creating islands like Margaret Island.
The city has two main parts: Buda and Pest. Buda is hilly, built on higher ground. Pest is much flatter and larger, spreading out on a sandy plain. The Danube is about 230 meters (750 feet) wide at its narrowest point in Budapest.
The Buda hills are mostly made of limestone, and they have cool caves like the Pálvölgyi cave. The highest point in Budapest is János Hill, which is 527 meters (1,730 feet) above sea level. Budapest is also a green city, with lots of parks and forests.
One unique thing about Budapest is its thermal springs. It's one of only three capital cities in the world with so many! About 125 springs produce millions of liters of warm water every day, some reaching 58°C (136°F). These waters are believed to have healing properties.
Budapest has a mix of warm summers and chilly winters. Summers are long and can be very warm, with occasional heavy rain. Winters are cold, with snow often falling. Spring and autumn offer pleasant weather with moderate temperatures.
Amazing Architecture
Budapest is like an open-air museum of buildings! You can see many different styles from ancient times to today. The Roman city of Aquincum shows us ancient architecture.
In the Castle District, you can find some old Gothic architecture buildings from the 14th and 15th centuries. But some of the most famous Gothic-style buildings, like the Hungarian Parliament Building and the Matthias Church, are actually "Neo-Gothic," meaning they were built later to look Gothic.
The Renaissance architecture style came to Budapest in the 15th century. Many beautiful buildings were inspired by this style, like the Hungarian State Opera House and St. Stephen's Basilica.
During the time of Ottoman rule, Islamic culture brought Ottoman architecture to Budapest. They built mosques and baths. Some of these Turkish baths, like Rudas and Király Baths, are still used today! The Tomb of Gül Baba, a famous Turkish holy man, is also in Budapest.
After the Ottomans left, Baroque architecture became popular. You can see many Baroque buildings, like the Church of St. Anna. Later, Classical architecture and Neoclassical architecture brought us buildings like the Hungarian National Museum and the famous Széchenyi Chain Bridge.

At the end of the 19th century, Art Nouveau became fashionable. This style in Hungary has a unique blend of local designs and influences from other cultures. The Museum of Applied Arts and the Gresham Palace are great examples.
Today, Budapest continues to build new and modern structures while also protecting its historic look. The city has many new public spaces, theaters, and bridges, like the National Theatre and the Megyeri Bridge.
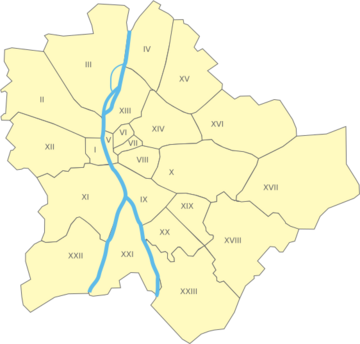
City Districts
Budapest is divided into 23 districts, each with its own local government and mayor. These districts have special names, some of which are old village names that became part of the city.
The districts are numbered in a way that forms circles. District I is in central Buda, including the Castle Quarter. Districts II and III stretch north in Buda. District IV is in northern Pest, but then District V is in the very center of Pest. The numbers then loop around through Pest and back to Buda.
People of Budapest
Budapest is Hungary's most populated city. In 2019, about 1.76 million people lived here. The city is growing, with more people moving in than out. It's one of the most densely populated cities in Hungary.
Most people in Budapest are Hungarian. But you'll also find many people from other countries living and working here. Hungarian is the main language, but many people also speak English and German.
Budapest has a large Christian community, with many Roman Catholics and Calvinists. It's also home to one of the biggest Jewish communities in Europe.
Budapest's Economy

Budapest is a very important economic center. It's one of the fastest-growing city economies in Europe. The city produces a large part of Hungary's total economic output.
It's a major hub for banking, finance, real estate, shopping, and tourism. Many Hungarian and international companies have their main offices here. Budapest is also known for its new technology and start-up companies, like Prezi and LogMeIn.
The city is a leader in science and research, especially in biotechnology and medicine. Many big tech companies like Nokia and Ericsson have research centers here.
Tourism is a huge part of Budapest's economy. Millions of visitors come each year to see the sights, enjoy the spas, and try the delicious food. The city has many hotels, restaurants, and famous "ruin bars."
Money and Business
The Budapest Stock Exchange is where important Hungarian companies trade their shares. Big companies like MOL Group (an oil and gas company) and OTP Bank (a bank) are based in Budapest.
Many international banks and financial companies also have offices in Budapest. The city is also strong in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry. Companies like Pfizer and Teva have research and production facilities here.
How Budapest is Governed

As the capital, Budapest is where Hungary's national government is located. The President of Hungary lives and works in the Sándor Palace in the Buda Castle District. The Prime Minister's office is also in the Castle District.
The National Assembly, which makes the country's laws, meets in the beautiful Hungarian Parliament Building. Hungary's highest courts are also in Budapest.
Budapest is also home to many international organizations, like some United Nations agencies. This shows its importance on the world stage.
The city government works hard to make Budapest a great place to live. They focus on things like public transport, housing, and keeping the city clean. They also try to reduce car use and pollution by improving public transportation. Budapest has one of the best public transport systems in Europe!
City Leadership
Budapest has a mayor-council government. The Mayor of Budapest is Gergely Karácsony, who was elected in 2019. The mayor and the members of the General Assembly are elected for five-year terms.
The General Assembly has 33 members, including the 23 district mayors and the Mayor of Budapest. They make decisions about the city's budget and other important matters.
Top Sights and Fun Things to Do
Budapest is famous for its beautiful old buildings and landmarks. It's a city full of history and charm!
The most famous sight is the Parliament, a huge Neo-Gothic building. It's the biggest building in Hungary and holds the Hungarian Crown Jewels.
St. Stephen's Basilica is the city's most important church. You can see the Holy Right Hand of Hungary's first king, Saint Stephen, there.
You can enjoy delicious Hungarian cuisine and café culture at many places, like the famous Gerbeaud Café.
Budapest has 223 museums and galleries! You can explore Roman ruins at the Aquincum Museum or learn about history at the House of Terror. The Buda Castle area, the Danube riverbanks, and Andrássy Avenue are all UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Exploring Castle Hill
The Castle District is a must-see! It has three churches, six museums, and many interesting streets. The old Royal Palace, now home to two museums and a library, has been important since the 13th century. Nearby, the Sándor Palace is where the President of Hungary works.
The seven-hundred-year-old Matthias Church is stunning with its colorful roof and tall spires. Next to it is the Fisherman's Bastion, built in 1905. It offers amazing views of the whole city!
Pest's Grand Avenue
In Pest, Andrássy Avenue is a beautiful, tree-lined street about 2.5 kilometers (1.5 miles) long. It leads to Heroes' Square and is also a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Underneath it runs Europe's oldest underground railway!
Heroes' Square has the huge Millenary Monument and the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier. On either side are the Museum of Fine Arts and the Kunsthalle Budapest. Behind the square is City Park with the Vajdahunyad Castle. The Hungarian State Opera House is another jewel on Andrássy Avenue.
The Dohány Street Synagogue is the largest synagogue in Europe. It's in the Jewish district and can seat 3,000 people. Next to it is a sculpture of a weeping willow tree, remembering those lost in the Holocaust.
Budapest also has the largest medicinal bath in Europe, the Széchenyi Medicinal Bath, and the third-largest Parliament building in the world.
Bridges Over the Danube
The seven bridges over the Danube are also famous sights. From north to south, they are:
- The Árpád Bridge
- The Margaret Bridge
- The Chain Bridge (a city icon!)
- The Elisabeth Bridge
- The Liberty Bridge (Art Nouveau style)
- The Petőfi Bridge
- The Rákóczi Bridge
The Margaret Bridge, Chain Bridge, and Liberty Bridge are especially beautiful.
Parks, Islands, and Spas
Budapest has many wonderful parks with playgrounds and activities. The City Park and Margaret Island are very popular. The Buda Hills offer great outdoor fun and views, like at Normafa, which is even used for skiing in winter!
Danube Islands
Several islands dot the Danube in Budapest:
- Margaret Island is a long park, perfect for sports and relaxing. It has dance clubs, pools, and running tracks.
- Csepel Island is the largest island in the Hungarian Danube, but only its northern tip is within the city.
- Hajógyári Island (also called Óbuda Island) is a man-made island known for water sports and dance clubs. It also hosts the huge Sziget Festival every year, with hundreds of thousands of visitors!
Relaxing in Spas
Budapest is known as the "City of Spas" because of its many thermal springs. The Romans loved these springs, and you can still see ruins of their ancient baths. The Turkish baths built centuries ago are still in use today!
The Gellért Baths and Hotel, built in 1918, are famous for their beautiful Art Nouveau style. The Széchenyi Baths are one of the largest bath complexes in Europe, with indoor and outdoor pools open all year. They are built in a grand Renaissance style.
Getting Around Budapest

Budapest has a busy international airport, Budapest Ferenc Liszt International Airport, named after the famous composer Franz Liszt. It connects Budapest to cities all over the world.
The city's public transport system is excellent. It includes 4 metro lines (one of which is the oldest underground railway in mainland Europe!), 5 suburban railway lines, 33 tram lines, 15 trolleybus lines, and 264 bus lines. Over 3.9 million people use public transport every day! Kids under 14 and adults over 65 can travel for free.

Budapest also has a smart bicycle sharing network called BuBi. There are about 180 kilometers (112 miles) of bike paths in the city.
The city's roads are set up like Paris, with ring roads and avenues spreading out from the center. All major highways and railway lines in Hungary lead to Budapest. The city has three main railway stations: Keleti (Eastern), Nyugati (Western), and Déli (Southern).
The Danube River is also important for transport. There are commercial ports and passenger ships. You can even take a hydrofoil to Vienna in the summer!
Special vehicles in Budapest include the Budapest Castle Hill Funicular (a cable car up to Buda Castle), a chairlift, a cog-wheel railway, and even a children's railway in the Buda hills.
Culture and Fun
Budapest is a lively center for music, film, theater, dance, and art. It was even named a "City of Design" by UNESCO!
Museums and Art
The city has 223 museums and galleries! You can see Hungarian art, European art, and learn about science and history. Some top museums include the Hungarian National Museum, the Hungarian National Gallery, and the Museum of Fine Arts.
Books and Libraries
Budapest has many libraries with special collections. The National Széchényi Library keeps old historical documents. The Metropolitan Szabó Ervin Library is important for public education.
Shows and Music
There are 40 theaters, seven concert halls, and an opera house in Budapest. You can enjoy outdoor festivals, concerts, and plays, especially in the summer. The Hungarian State Opera House is a beautiful place to see a show.
Festivals and Events
Budapest hosts many exciting festivals! The Sziget Festival is one of Europe's biggest outdoor music festivals. The Budapest Spring Festival has concerts all over the city. There are also food festivals like the Budapest Wine Festival and Budapest Pálinka Festival. The Budapest Jewish Summer Festival is one of the largest in Europe.
Fashion and Style
Budapest has its own fashion week twice a year, where designers show off their latest collections. You'll find many popular fashion brands in the city's shopping malls and on streets like Váci Street and Andrássy Avenue. Luxury brands also have stores in the upscale Leopoldtown district.
Delicious Food
Budapest has its own special cuisine, blending ancient Hungarian traditions with influences from French, German, Italian, and Slavic cooking. You'll find delicious sweets, meat dishes, and vegetable dishes. Hungarian cuisine was also influenced by Austrian food during the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
Budapest has many restaurants, from traditional places to fancy ones with Michelin stars.
Sports in Budapest
Budapest has hosted many big sports events, like the 2023 World Athletics Championships and matches for the UEFA Euro 2020 football tournament at the huge Puskás Aréna.
Hungary has a strong history in sports, especially in fencing, swimming, water polo, and wrestling. Many Olympic medalists live in Budapest. The city also hosts the Budapest Marathon and Budapest Half Marathon every year.
Football is very popular, and Budapest has many famous football clubs. The city's largest football stadium is named after Ferenc Puskás, a legendary player.
The Hungarian Grand Prix Formula One race is held just outside the city at the Hungaroring track.
Learning in Budapest
Budapest is a great place for education, with over 35 universities and colleges. Many students from other countries come here to study medicine, engineering, and other subjects. Most universities offer courses in English.
Some of the well-known universities include:
- Budapest University of Technology and Economics (one of the oldest technology institutes in the world!)
- Eötvös Loránd University (a large and respected university)
- Semmelweis University (famous for medicine)
- Liszt Ferenc Academy of Music (for music studies)
Sister Cities
Budapest has many "sister cities" and partner cities around the world. These are often other important capital cities. This helps Budapest share ideas and work together with cities like New York City, Berlin, Vienna, and Prague on things like city management, culture, and tourism.
See also
 In Spanish: Budapest para niños
In Spanish: Budapest para niños
- Bridges of Budapest
- List of cities and towns on the river Danube
- Spas in Budapest